
Solved 1 Draw The Total Stresses Distribution And Compute Chegg Draw the total stresses distribution and compute the total force and its location, acting on a 12 m high gravity (rigid) retaining system with a vertical smooth face which is allowed to yield and therefore mobilize the full strength of the soil in an active stress condition. This video shows how to find total stress, effective stress and pore water pressure in a soil. one numerical problem is solved in this lecture and the problem states that find out the total.

Solved Given Required Compute And Plot The Distribution Of Chegg • discussion on stresses in soils will be divided into three parts: 1) usage of mohr’s circle to compute stresses at a point; 2) usage of elasticity to compute spatial distributions of stresses. Chaoyang university of technology stress distribution 121 value, are presented and papers in which the more complete solutions are published are referenced. the theoretical solutions give total stresses in a weightless elastic medium. total stresses are given because the soil is assumed to be a continuum. their resolution into effective stresses. Estimate the stress at a point 3 m below and 4 m away from the point of action of the load by boussinesq’s formula. compare the value with the result from westergaard’s theory. solution: example 10.3: a line load of 100 kn metre run extends to a long distance. Calculate the total stress, effective stress and pwp on a horizontal plane 9m below the ground surface and draw pressure distribution diagrams down to this level. assume the specific gravity of soil grains equal to 2.65 for both the sand and clay layer.

Solved Given The Following Principal Stresses Compute The Chegg Estimate the stress at a point 3 m below and 4 m away from the point of action of the load by boussinesq’s formula. compare the value with the result from westergaard’s theory. solution: example 10.3: a line load of 100 kn metre run extends to a long distance. Calculate the total stress, effective stress and pwp on a horizontal plane 9m below the ground surface and draw pressure distribution diagrams down to this level. assume the specific gravity of soil grains equal to 2.65 for both the sand and clay layer. To sketch the stress distribution, we need to determine the maximum and minimum normal stress developed in the section a−a. now to determine the stresses developed in this section, we can start by determining the internal loadings acting on this section. Draw the total stresses distribution and compute the total force and its location, acting on a 1 2 m high gravity (rigid) retaining system with a vertical smooth face which is allowed to yield and therefore mobilize the full strength of the soil in an active stress condition. (a) what is the distribution of the traction vector in the six faces of the cube. draw the distribution of tractions. (b) compute the total resultant force acting on face at y = 0. (c) what is the total resultant force acting in the cube. problem 3 given the following stress distribution where is a function of and . find. Draw the normal stress distribution in the section. what is the shear stress and normal stress at point 1 and 2. draw shear stress. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: draw the normal stress distribution in the section.
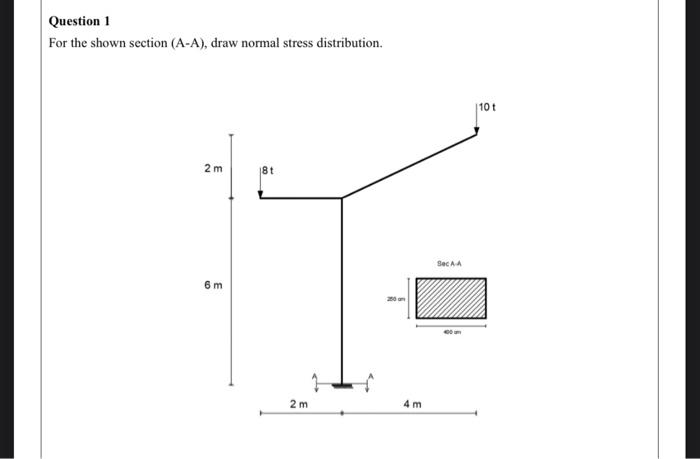
Solved Question 1 For The Shown Section A A Draw Normal Chegg To sketch the stress distribution, we need to determine the maximum and minimum normal stress developed in the section a−a. now to determine the stresses developed in this section, we can start by determining the internal loadings acting on this section. Draw the total stresses distribution and compute the total force and its location, acting on a 1 2 m high gravity (rigid) retaining system with a vertical smooth face which is allowed to yield and therefore mobilize the full strength of the soil in an active stress condition. (a) what is the distribution of the traction vector in the six faces of the cube. draw the distribution of tractions. (b) compute the total resultant force acting on face at y = 0. (c) what is the total resultant force acting in the cube. problem 3 given the following stress distribution where is a function of and . find. Draw the normal stress distribution in the section. what is the shear stress and normal stress at point 1 and 2. draw shear stress. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: draw the normal stress distribution in the section.

Solved Question 1 For The Given Sets Of Stresses Draw The Chegg (a) what is the distribution of the traction vector in the six faces of the cube. draw the distribution of tractions. (b) compute the total resultant force acting on face at y = 0. (c) what is the total resultant force acting in the cube. problem 3 given the following stress distribution where is a function of and . find. Draw the normal stress distribution in the section. what is the shear stress and normal stress at point 1 and 2. draw shear stress. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: draw the normal stress distribution in the section.
