Solved 1 Point Let A 3 6 6 And B 10 5 1 Be Chegg
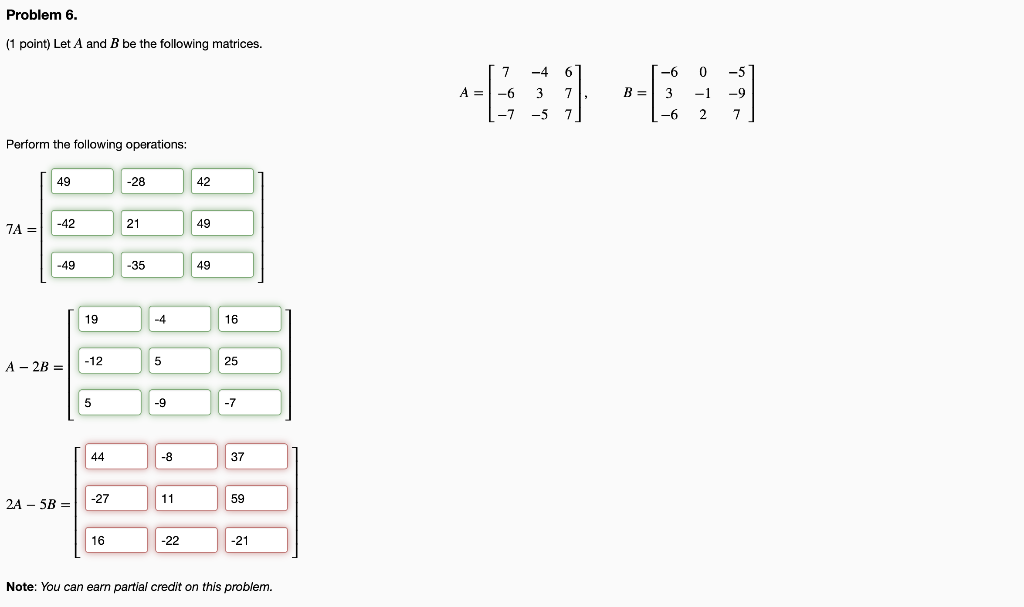
Solved Problem 6 1 Point Let A And B Be The Following Chegg Question: (1 point) let a = ( 3, 6, 6) and b = (10, 5, 1) be vectors. find the scalar, vector, and orthogonal projections of b onto a. note: if v is the vector projection of b onto a, then b v is the orthogonal projection. scalar projection: vector projection: orthogonal projection: show transcribed image text. Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ a (3, 6), b (5, 10) are two points on a line a) find the slope of the line? 110 to if (x, y) is a point on….
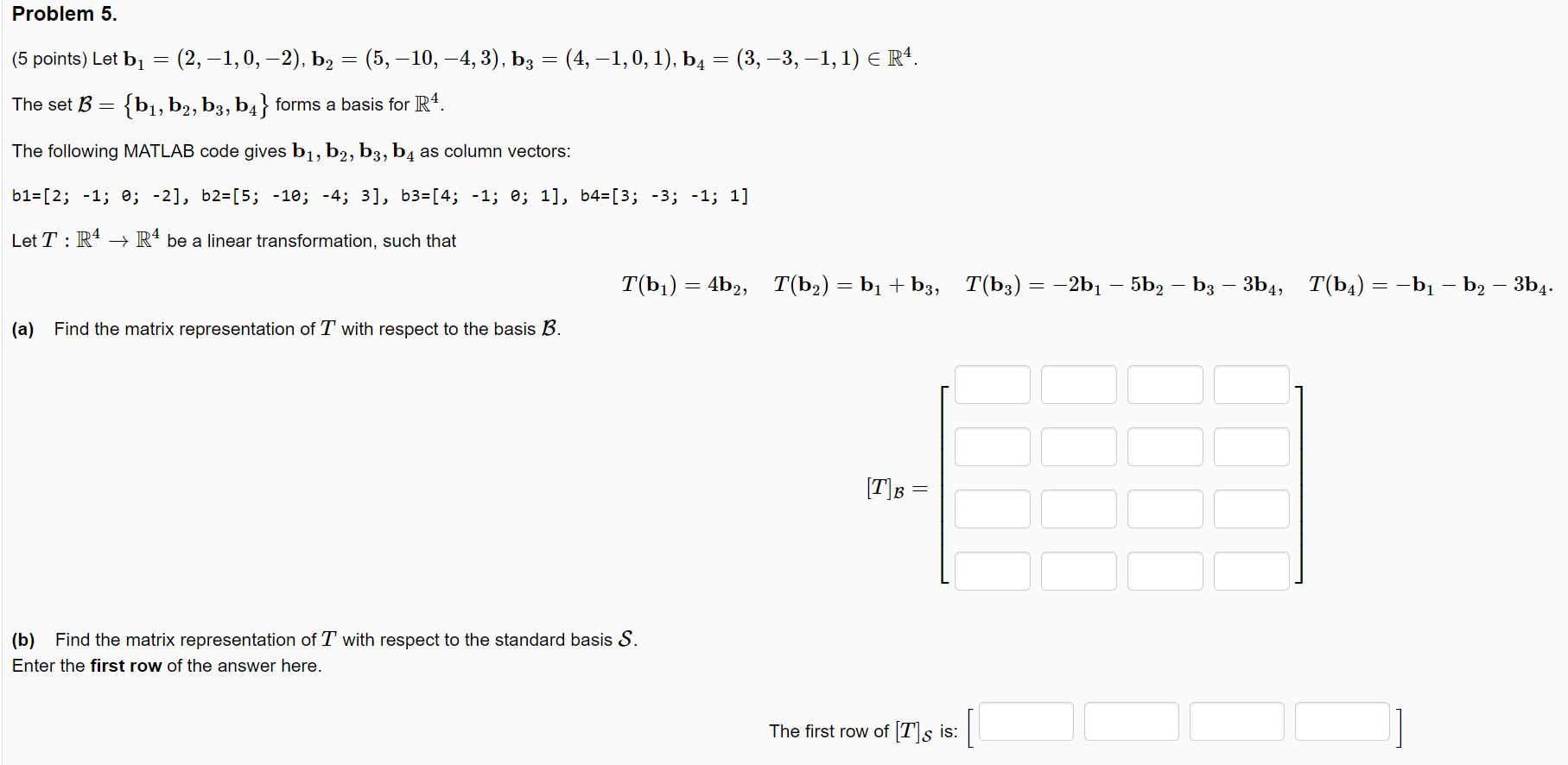
Solved Problem 5 5 Points Let B 2 1 0 2 B Chegg Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like let a = {1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} and b = {1, 5, 6}. indicate if each statement is true or false. 7∈a b⊂a, let u=u= {1,2,3, ,10}, a=a= {1,3,5,7}, b=b= {1,2,3,4}, and c=c= {3,4,6,7,9}. Answer & explanation solved by verified expert answered by anupambrn123 b can not be written as linear combination of columns of a. answer: no. Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Here’s the best way to solve it. (1 point) let a = ( 6,3, 1) and b = (10.5. 3) be vectors.
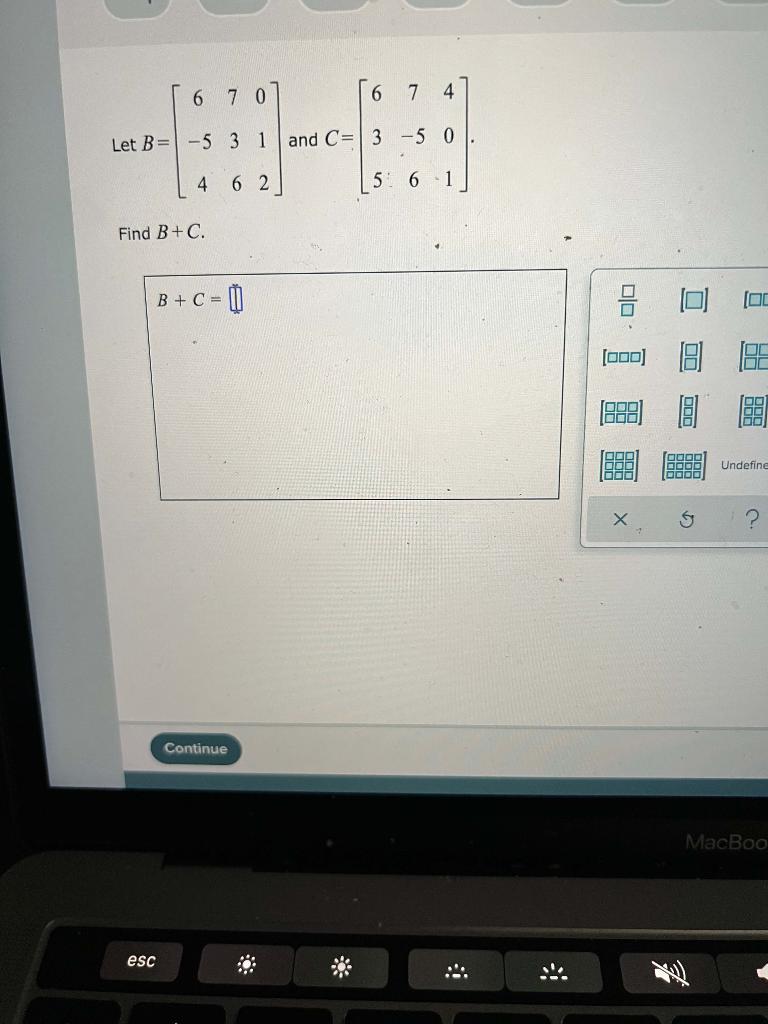
Solved 6 7 0 6 7 4 Let B 5 3 1 And C 3 5 0 4 62 5 6 1 Chegg Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Here’s the best way to solve it. (1 point) let a = ( 6,3, 1) and b = (10.5. 3) be vectors. To find the intersection of two sets, we need to determine which elements are common to both sets. given: the intersection of sets a and b, denoted as a ∩ b, consists of all elements that are present in both sets. let's find the common elements: the first element in set a is 3. check if 3 is in set b. yes, 3 is in both sets. Let r be a relation defined on a × b such that r = { ( (a1, b1), (a2, b2)) : a1 ≤ b2 and b1 ≤ a2}. then the number of elements in the set r is. let a = {1, 3, 4, 6, 9} and b = {2, 4, 5, 8, 10}. let r be a relation defined on a b such that r = r is (1) 26 (2) 160 (3) 180 (4) 52. To solve the operations with the sets a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {0, 3, 6}, we use the definitions of set union, intersection, and difference. union: finding the union of two sets (a ∪ b) involves combining all unique elements from both sets. so, a ∪ b = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. Concept: intersection of sets: let a and b be two sets. the intersection of a and b is the set of all those elements which are present in both sets a and b.

Solved 1 Let A 1 3 5 7 9 B 3 6 9 C 2 4 6 8 Chegg To find the intersection of two sets, we need to determine which elements are common to both sets. given: the intersection of sets a and b, denoted as a ∩ b, consists of all elements that are present in both sets. let's find the common elements: the first element in set a is 3. check if 3 is in set b. yes, 3 is in both sets. Let r be a relation defined on a × b such that r = { ( (a1, b1), (a2, b2)) : a1 ≤ b2 and b1 ≤ a2}. then the number of elements in the set r is. let a = {1, 3, 4, 6, 9} and b = {2, 4, 5, 8, 10}. let r be a relation defined on a b such that r = r is (1) 26 (2) 160 (3) 180 (4) 52. To solve the operations with the sets a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {0, 3, 6}, we use the definitions of set union, intersection, and difference. union: finding the union of two sets (a ∪ b) involves combining all unique elements from both sets. so, a ∪ b = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. Concept: intersection of sets: let a and b be two sets. the intersection of a and b is the set of all those elements which are present in both sets a and b.
Comments are closed.