Solved 13 Find F 2 F 3 And F 4 Using F 1 5 And For Chegg
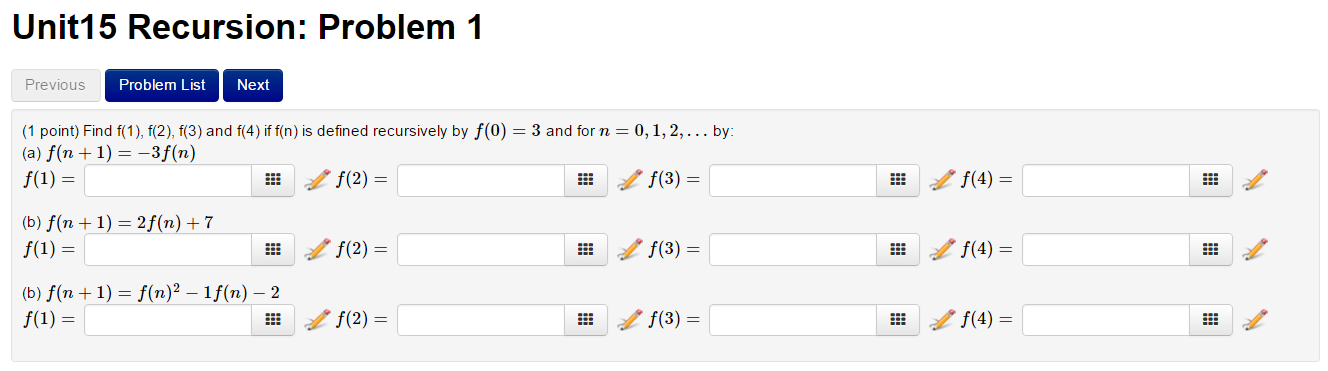
Solved Find F 1 F 2 F 3 And F 4 If F N Is Defined Chegg Question: find f (2), f (3), and f (4), using f (1) = 5, and for n = 1, 2, 3, n = a) f (n 1) 5f (n) 2 b) f (n 1) = f (n) 1 show transcribed image text. For each part, we use the given recursion formula starting with the initial conditions f (0) = f (1) = 1. let's calculate the values for parts (a), (b), (c), and (d).
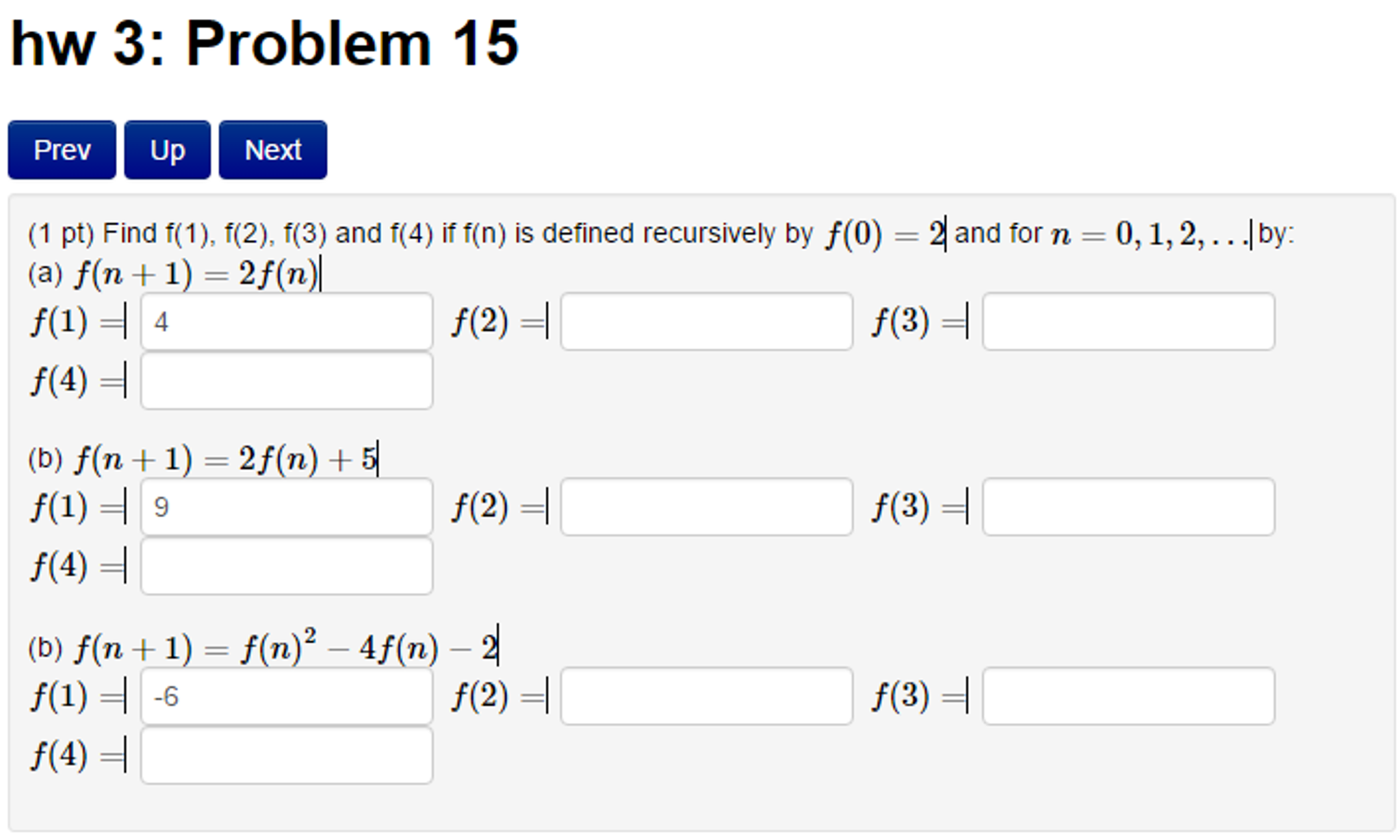
Solved Find F 1 F 2 F 3 And F 4 If F N Is Defined Chegg We calculated the values of f (1),f (2),f (3),f (4), and f (5) based on different recursive definitions, starting from f (0) = 3, using straightforward algebraic transformations for each case. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. there are 2 steps to solve this one. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step by step explanations, just like a math tutor. In this question, the inductive step is f12 f22 fk2 = fk fk 1 for some arbitrary integer k > 0. assume f12 f22 fk2 = fk fk 1 for any arbitrary integer k > 0.

Solved Find F 1 F 2 F 3 And F 4 If F N Is Defined Chegg Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step by step explanations, just like a math tutor. In this question, the inductive step is f12 f22 fk2 = fk fk 1 for some arbitrary integer k > 0. assume f12 f22 fk2 = fk fk 1 for any arbitrary integer k > 0. We know that f (0) = 1 and f (1) = 1. we need to find f (2), f (3), f (4), and f (5) for different recurrence relations. Video answer: if f (x) = f (xf (xf (x))), where f (1) = 2, f' (2) = 3, f' (1) = 4, f' (2) = 5, and f' (3) = 6, find f' (1). Sequence calculation involves finding the terms of a sequence based on a given rule. in our exercise, we calculate terms using recursive formulas. we start from an initial value and apply the formula repeatedly to generate the next terms. for example, let's take the sequence in part a):. [bonus] write an algorithm and the corresponding iterative program that computes the recursive function in problem 14 c using the programming language learned in cs1, and run it.

Solved Find F 2 F 3 F 4 And F 5 If F N Is Defined Chegg We know that f (0) = 1 and f (1) = 1. we need to find f (2), f (3), f (4), and f (5) for different recurrence relations. Video answer: if f (x) = f (xf (xf (x))), where f (1) = 2, f' (2) = 3, f' (1) = 4, f' (2) = 5, and f' (3) = 6, find f' (1). Sequence calculation involves finding the terms of a sequence based on a given rule. in our exercise, we calculate terms using recursive formulas. we start from an initial value and apply the formula repeatedly to generate the next terms. for example, let's take the sequence in part a):. [bonus] write an algorithm and the corresponding iterative program that computes the recursive function in problem 14 c using the programming language learned in cs1, and run it.

Solved 9 Find F 2 F 3 F 4 And F 5 If F Is Chegg Sequence calculation involves finding the terms of a sequence based on a given rule. in our exercise, we calculate terms using recursive formulas. we start from an initial value and apply the formula repeatedly to generate the next terms. for example, let's take the sequence in part a):. [bonus] write an algorithm and the corresponding iterative program that computes the recursive function in problem 14 c using the programming language learned in cs1, and run it.
Comments are closed.