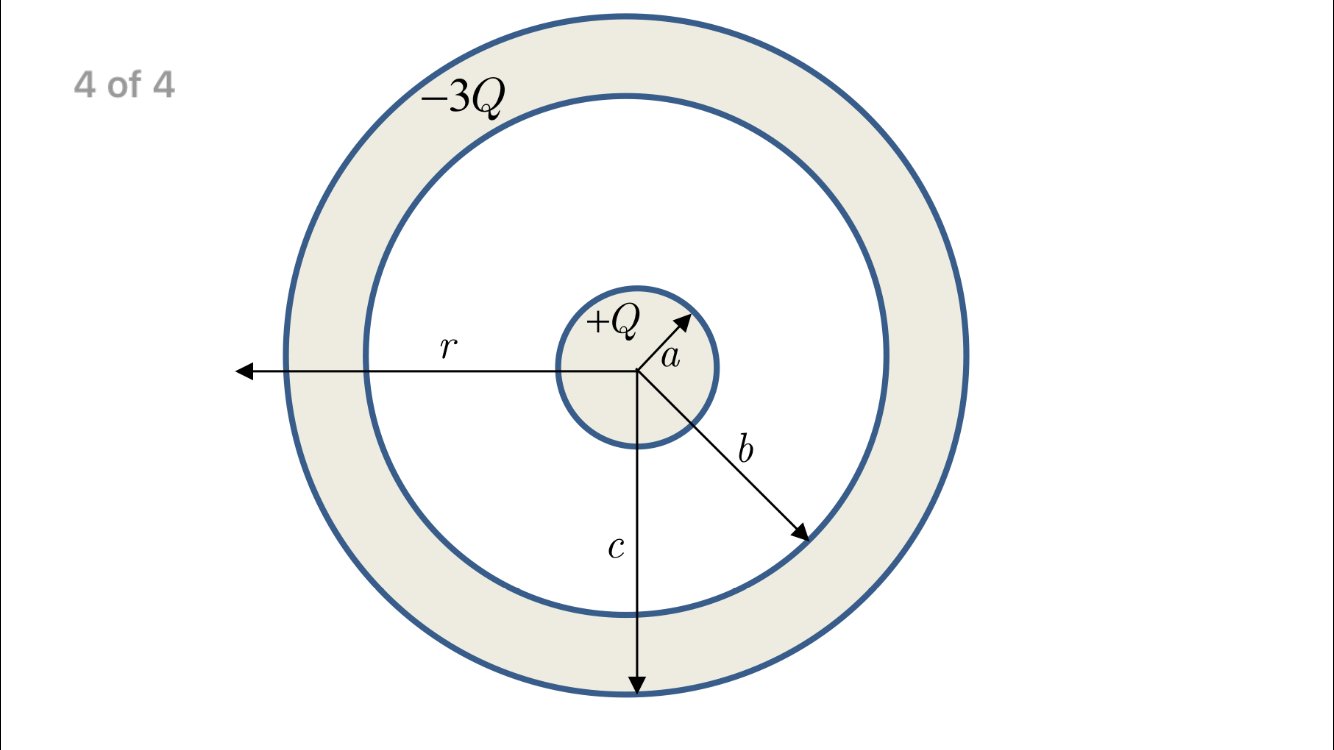
Solved A Solid Conducting Sphere Lies At The Center Of A Chegg Question: 2. a solid spherical conducting shell has an inner radius a and outer radius 2a. at the centre of the shell is located a point charge q. what must the excess charge of the shell be in order for the charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell to be exactly equal? (0 = А $ e da 04 a) b) 3q 30 4q c) d) 40 50 leave. Physics ninja looks at a classic gauss's law problem involving a sphere and a conducting shell. the inner sphere can be a conductor or an insulator and the outer shell is assumed to.

Solved A Solid Conducting Sphere Lies At The Center Of A Chegg A point charge with magnitude q is located inside the cavity of a spherical conducting shell. the shell has an inner radius equal to a, an outer radius equal to b, and holds a net charge of 3q, as shown in the figure. The correct option is: (a) –5q explanation: the charge density is q area which is q 4πr2 so for the inner surface it is q 4πa2 and for the outer surface it is q 16πa2. for these to be equal q must be 4q. because of the q charge inside, there is a charge of –q induced on the inner surface, which means the outer surface must have charge. A solid conducting sphere of radius r a is placed concentrically inside a conducting spherical shell of inner radius r b1 and outer radius r b2. the inner sphere carries a charge q while the outer sphere does not carry any net charge. What must the excess charge of the shell be in order for the charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell to be exactly equal? (o = $£ dos a) b) c) d) *30 50 40 30 e) 2 what is the amount of energy per charge?.

Solved A Solid Conducting Sphere Lies At The Center Of A Chegg A solid conducting sphere of radius r a is placed concentrically inside a conducting spherical shell of inner radius r b1 and outer radius r b2. the inner sphere carries a charge q while the outer sphere does not carry any net charge. What must the excess charge of the shell be in order for the charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell to be exactly equal? (o = $£ dos a) b) c) d) *30 50 40 30 e) 2 what is the amount of energy per charge?. A solid spherical conducting shell has an inner radius and outer radius r. at the center of the shell is located a point charge q. what must the excess charge of the shell be in order for the charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell to be exactly equal? (ε0 = 9 x 10^9 nm^2 c^2). Consider a spherical conducting shell with inner radius r2 and outer radius r3, that has other spherical conductor inside it with radius r1 (this one is solid). A thick conducting spherical shell has inner radius r and outer radius r, as shown in the diagram. a point charge of –qis located at the center of the sphere and a charge of qis placed on the conducting shell. Since the charges are free to flow, the point charge in the center will be able to pull in a total of negative charge with the same magnitude to the inner surface of the spherical shell.

Solved Spherical Conducting Shell A Spherical Conducting Chegg A solid spherical conducting shell has an inner radius and outer radius r. at the center of the shell is located a point charge q. what must the excess charge of the shell be in order for the charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell to be exactly equal? (ε0 = 9 x 10^9 nm^2 c^2). Consider a spherical conducting shell with inner radius r2 and outer radius r3, that has other spherical conductor inside it with radius r1 (this one is solid). A thick conducting spherical shell has inner radius r and outer radius r, as shown in the diagram. a point charge of –qis located at the center of the sphere and a charge of qis placed on the conducting shell. Since the charges are free to flow, the point charge in the center will be able to pull in a total of negative charge with the same magnitude to the inner surface of the spherical shell.
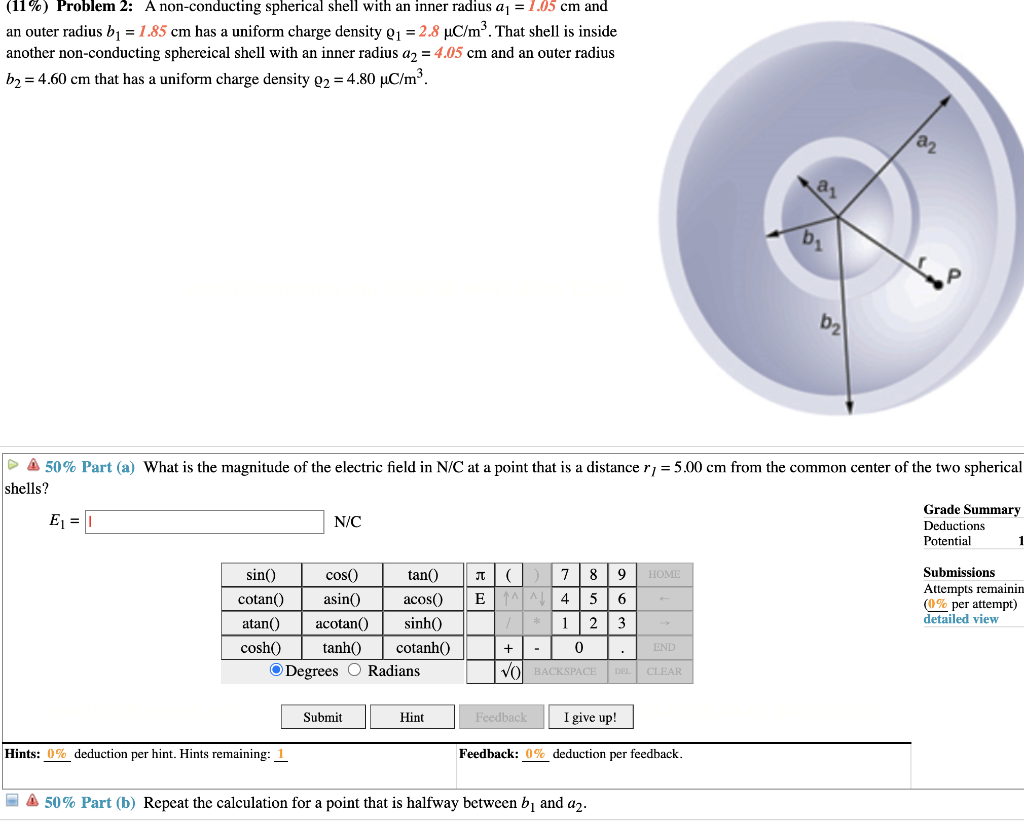
Solved 11 Problem 2 A Non Conducting Spherical Shell Chegg A thick conducting spherical shell has inner radius r and outer radius r, as shown in the diagram. a point charge of –qis located at the center of the sphere and a charge of qis placed on the conducting shell. Since the charges are free to flow, the point charge in the center will be able to pull in a total of negative charge with the same magnitude to the inner surface of the spherical shell.
