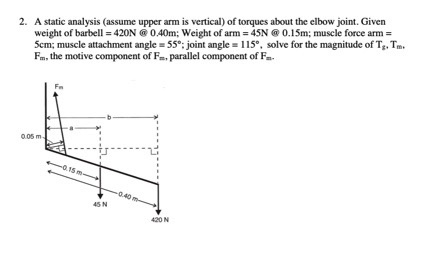
Solved 2 A Static Analysis Assume Upper Arm Is Vertical Chegg A static analysis (assume upper arm is vertical) of torques about the elbow joint. given weight of barbell =420 [email protected] m; weight of arm=45 [email protected] m; muscle force arm= 5 cm; muscle attachment angle =55∘; joint angle =115∘, solve for the magnitude of tz,tm. Your analysis should be static and 2d (in the sagittal plane), looking at the left side of the worker. use g=9.8 m s2 for all calculations. 1) using the information provided above, determine the segment mass and the center of mass locations of the following: upper arm, lower arm and torso. illustrate the com locations on the stick figure.
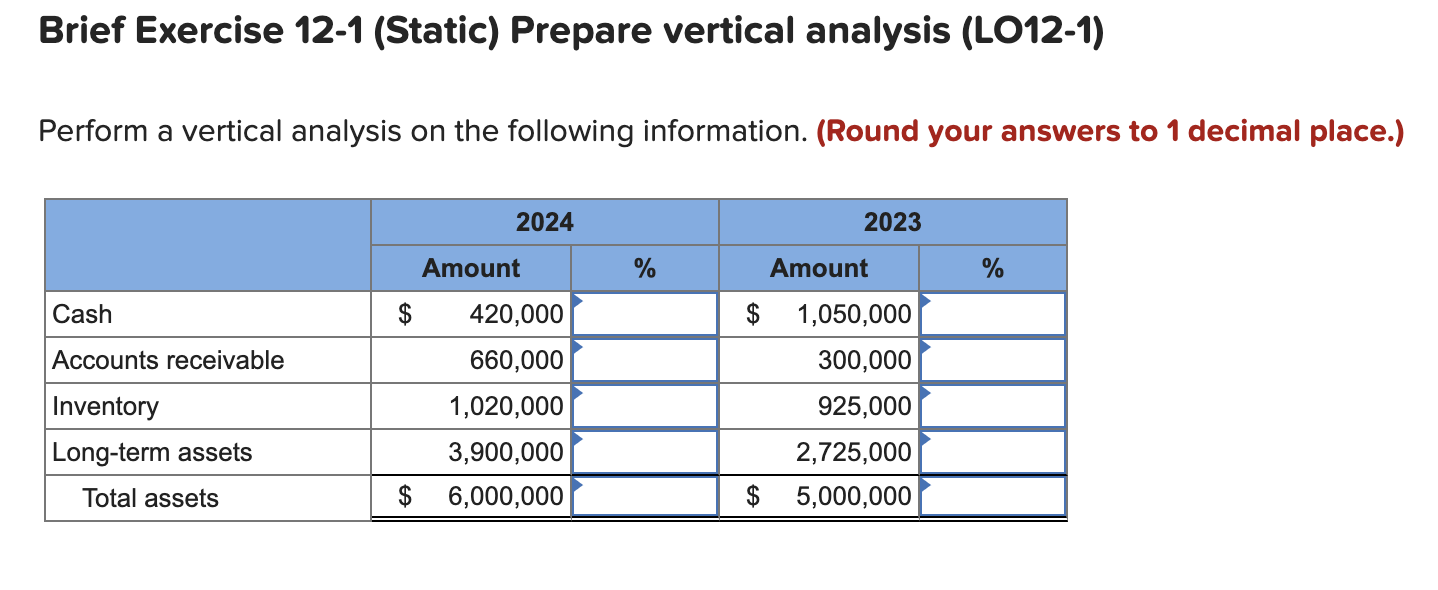
Solved Brief Exercise 12 1 Static ï Prepare Vertical Chegg Homework assignment use the two segment 2d static model on slide 14 to calculate the reactive force and moment at the shoulder joint when the person is holding a 20 kg weight in hand do this in a segment by segment manner (i.e., find out what happens at the elbow first, then the shoulder). be sure to have a free body diagram (fbd) for each. For the upper arm, the moment arm can be calculated as the length of the upper arm (29.80 cm) multiplied by the sine of the angle between the upper arm and the vertical axis (assuming the upper arm is vertical). since the upper arm is vertical, the angle is 90 degrees, so the moment arm of the upper arm is 29.80 cm. Assume the upper arm is in the vertical position and the elbow is flexed 90 degrees, so that the hand and forearm are horizontal. consider the hand and forearm to be a single rigid body. find the elbow joint reaction force and elbow flexor muscle force when a $5 \mathrm{~kg}$ mass is held in the hand. Assume the upper arm is in the vertical position and the elbow is flexed 90. degrees, so that the hand and forearm are horizontal. consider the hand and forearm. to be a single rigid body. find the elbow joint reaction i biceps muscle mo anchoring force fr frx . force exerted. by the fluid on the elbow b.
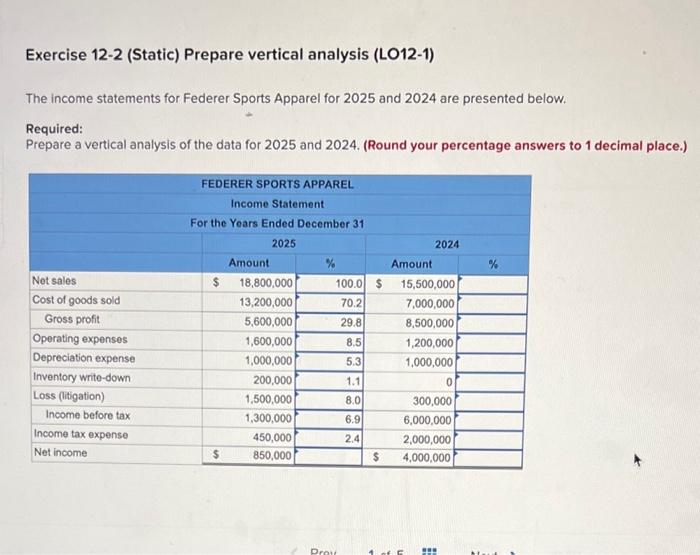
Solved Exercise 12 2 Static Prepare Vertical Analysis Chegg Assume the upper arm is in the vertical position and the elbow is flexed 90 degrees, so that the hand and forearm are horizontal. consider the hand and forearm to be a single rigid body. find the elbow joint reaction force and elbow flexor muscle force when a $5 \mathrm{~kg}$ mass is held in the hand. Assume the upper arm is in the vertical position and the elbow is flexed 90. degrees, so that the hand and forearm are horizontal. consider the hand and forearm. to be a single rigid body. find the elbow joint reaction i biceps muscle mo anchoring force fr frx . force exerted. by the fluid on the elbow b. How does the deltoid muscle maintain arm's static equilibrium? what is the required muscle force to hold an outstretched arm? can you solve these challenging static equilibrium physics problems? homework statement (a) calculate the magnitude of the force, fm, required of the "deltoid" muscle to hold up the outstretched arm shown in the figure. Static force analysis makes direct use of static force equilibrium equations. for an analytical solution formulation one must draw the free body diagram of each rigid body and must identify the unknown forces. next, one must write the static force equilibrium equations for each link. There are 3 steps to solve this one. using the principles of static equilibrium, which state the sum of the forces and moments acting on a rigid body is zero, identify the forces developed by the biceps, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles. to solve for the muscle forces and joint reaction force for the given conditions, we can use the pri. The vertical direction is the direction of the weight, which is the same as the direction of the upper arm. the x axis makes an angle [latex]\beta =60\text{°}[ latex] with the vertical. the y axis is perpendicular to the x axis. now we set up the free body diagram for the forearm.
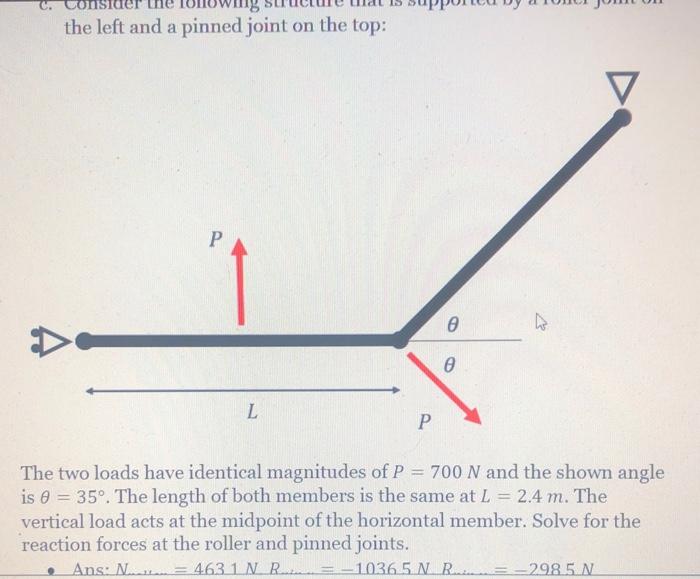
Solved Problem 2 Static Analysis 10 Points For The Chegg How does the deltoid muscle maintain arm's static equilibrium? what is the required muscle force to hold an outstretched arm? can you solve these challenging static equilibrium physics problems? homework statement (a) calculate the magnitude of the force, fm, required of the "deltoid" muscle to hold up the outstretched arm shown in the figure. Static force analysis makes direct use of static force equilibrium equations. for an analytical solution formulation one must draw the free body diagram of each rigid body and must identify the unknown forces. next, one must write the static force equilibrium equations for each link. There are 3 steps to solve this one. using the principles of static equilibrium, which state the sum of the forces and moments acting on a rigid body is zero, identify the forces developed by the biceps, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles. to solve for the muscle forces and joint reaction force for the given conditions, we can use the pri. The vertical direction is the direction of the weight, which is the same as the direction of the upper arm. the x axis makes an angle [latex]\beta =60\text{°}[ latex] with the vertical. the y axis is perpendicular to the x axis. now we set up the free body diagram for the forearm.
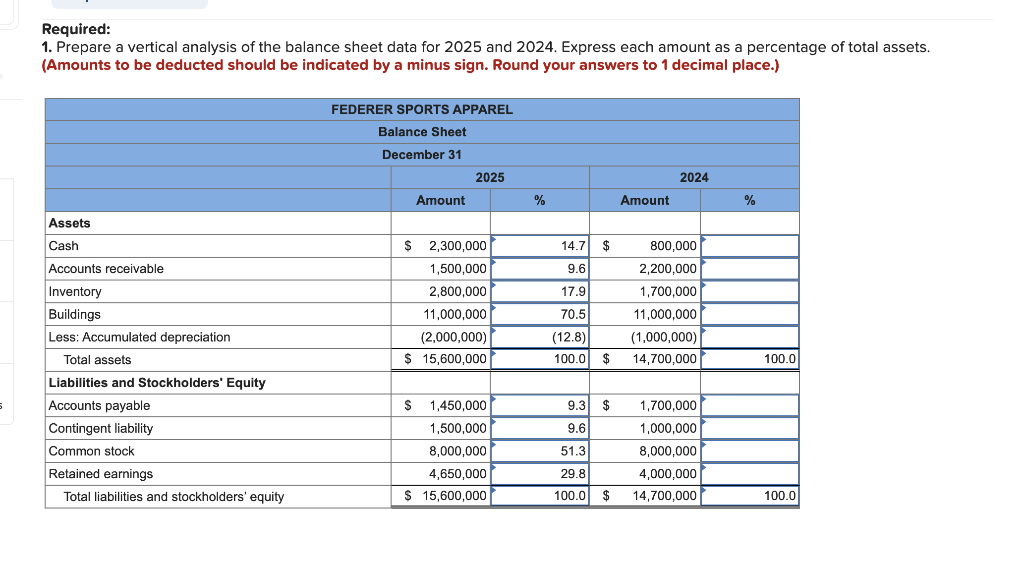
Solved Exercise 12 4 Static Prepare Vertical And Chegg There are 3 steps to solve this one. using the principles of static equilibrium, which state the sum of the forces and moments acting on a rigid body is zero, identify the forces developed by the biceps, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles. to solve for the muscle forces and joint reaction force for the given conditions, we can use the pri. The vertical direction is the direction of the weight, which is the same as the direction of the upper arm. the x axis makes an angle [latex]\beta =60\text{°}[ latex] with the vertical. the y axis is perpendicular to the x axis. now we set up the free body diagram for the forearm.
