
Solved Consider The Following Chegg There’s just one step to solve this. the given reaction is : i. Δg =Δh tΔs = 177.8 kj mol 2. consider the following reaction: 2pts caco3( s)

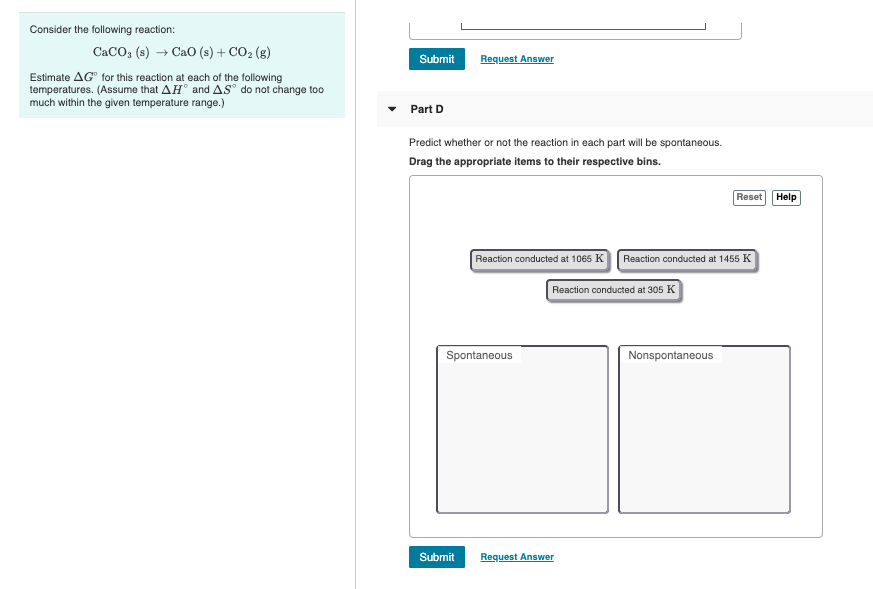
Solved Consider The Following Reaction Caco3 S Cao S Chegg Adding more co 2 increases the concentration of co 2 and causes the reaction to shift to the left. adding more caco 3 does not increase the concentration of caco 3 because caco 3 is a solid and thus has a constant concentration. it is therefore not included in the equilibrium expression and has no effect on the position of the equilibrium. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like at 1173 k, keq = 0.0108 for the following reaction: caco3 (s) ⇄ cao (s) co2 (g) the reaction takes place in a 10.0 l vessel at 1173 k. if a mixture of 15.0 g caco3, 15.0 g cao, and 4.25 g co2 is allowed to approach equilibrium, what will happen to the amount of caco3?. Question: consider the following reaction: caco3(s)→cao(s) co2(g). estimate Δg∘ for this reaction at each of the following temperatures. (assume that Δh∘ and Δs∘ do not change too much within the given temperature range.). To estimate the gibbs free energy change (Δg°) for the reaction at different temperatures, we can use the gibbs helmholtz equation: Δg° = Δh° tΔs°. where: Δg° is the standard. chem lab 4 chem lab 4 thermokinetics, includes abstract, discussion, results and introduction. estimate Δg∘ for this reaction at each of the following temperatures.

Solved Consider The Following Reaction Caco3 S Cao S Chegg Question: consider the following reaction: caco3(s)→cao(s) co2(g). estimate Δg∘ for this reaction at each of the following temperatures. (assume that Δh∘ and Δs∘ do not change too much within the given temperature range.). To estimate the gibbs free energy change (Δg°) for the reaction at different temperatures, we can use the gibbs helmholtz equation: Δg° = Δh° tΔs°. where: Δg° is the standard. chem lab 4 chem lab 4 thermokinetics, includes abstract, discussion, results and introduction. estimate Δg∘ for this reaction at each of the following temperatures. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2nh3 (g) <==> n2 (g) 3h2 (g) Δh° = 92.4 kj le châtelier's principle predicts that removing n2 (g) to the system at equilibrium will result in ., for the endothermic reaction caco3 (s) <==> cao (s) co2 (g) le châtelier's. Video answer: the reaction of calcium carbonate can produce calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. we have to calculate the equilibrium constant in this question. the data is given the question are partial pressure off c. it is equal to 0.0135 eight pm. Video answer: we were asked to think about the reaction. calcium oxide and co2 are created when calcium carbonate is broken down. we are asked to find the free energy of reaction at a number of locations. we are told that our delta h and delta s. Consider the following reaction: 2pts caco3 (s) < > cao (s) co2 (g) using the data from the text (appendix thermodynamic tables) calculate the equilibrium pressure of co, at: (hint: find ag°) a. 298k pco b. 800k Рcore umorita strong acids bases table 15.1, ii. your solution’s ready to go!.
Solved Consider The Following Reaction Caco3 S Cao S Chegg Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2nh3 (g) <==> n2 (g) 3h2 (g) Δh° = 92.4 kj le châtelier's principle predicts that removing n2 (g) to the system at equilibrium will result in ., for the endothermic reaction caco3 (s) <==> cao (s) co2 (g) le châtelier's. Video answer: the reaction of calcium carbonate can produce calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. we have to calculate the equilibrium constant in this question. the data is given the question are partial pressure off c. it is equal to 0.0135 eight pm. Video answer: we were asked to think about the reaction. calcium oxide and co2 are created when calcium carbonate is broken down. we are asked to find the free energy of reaction at a number of locations. we are told that our delta h and delta s. Consider the following reaction: 2pts caco3 (s) < > cao (s) co2 (g) using the data from the text (appendix thermodynamic tables) calculate the equilibrium pressure of co, at: (hint: find ag°) a. 298k pco b. 800k Рcore umorita strong acids bases table 15.1, ii. your solution’s ready to go!.

Solved Consider The Following Reaction Caco3 S Co2 G Chegg Video answer: we were asked to think about the reaction. calcium oxide and co2 are created when calcium carbonate is broken down. we are asked to find the free energy of reaction at a number of locations. we are told that our delta h and delta s. Consider the following reaction: 2pts caco3 (s) < > cao (s) co2 (g) using the data from the text (appendix thermodynamic tables) calculate the equilibrium pressure of co, at: (hint: find ag°) a. 298k pco b. 800k Рcore umorita strong acids bases table 15.1, ii. your solution’s ready to go!.
