
Solved If Det A B C D E F G H I 7 Then Find A D E F Chegg Answer to 2. given that, for some a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i e. Assume that we have added a pointer type to decaf that can point to integers and booleans. we want to extend our type system (our attributed grammar) to handle these types. we have added a pointer(t) type to the type system to denote a pointer of type t.
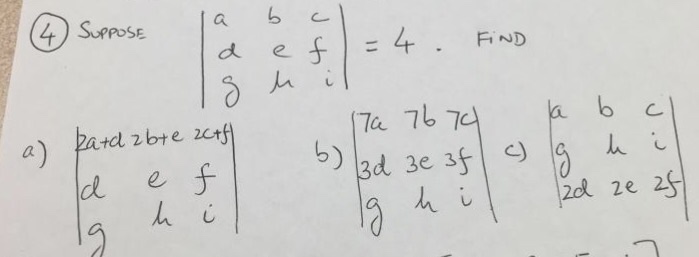
Solved Suppose A B C D E F G H I 4 Find 2a D 2b Chegg 故,我们设置一个大小为2*n的结构体数组并使用其中1到2*n 1(共计n n 1个位子)来建立哈夫曼树。 每次我们通过线性查找得到2个最小值,并做标记。 这时,我们仅仅需要从n 1这个位置开始 记录 最小两值所处位置 直至2*n 1这个位置,而2*n 1这. Given a relation r( a, b, c, d, e) and functional dependency set fd = { a → b, b → e, c → d}, determine whether the given r is in 2nf? if not convert it into 2 nf. solution: let us construct an arrow diagram on r using fd to calculate the candidate key. If $a*b*c=e$, then $a^{ 1} = b*c$. because inverses are commutative, this means that $e = a * (b*c) = a * a^{ 1} = a^{ 1} * a = (b*c)*a = b*c*a$, as desired. the strange thing is, my professor has told me this proof is wrong, and that $b*c$ is "just a right inverse of $a$", so i cannot say it is the inverse of $a$. Consider a relation r (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h), where each attribute is atomic, and following functional dependencies exist. the relation r is . the correct answer is option 1. explanation: since attribute d is not a part of any fd, it must be a part of the candidate key. ad = {abcdefgh} bd = {abcdefgh} ed = {abcdefgh} fd = {abcdefgh}.
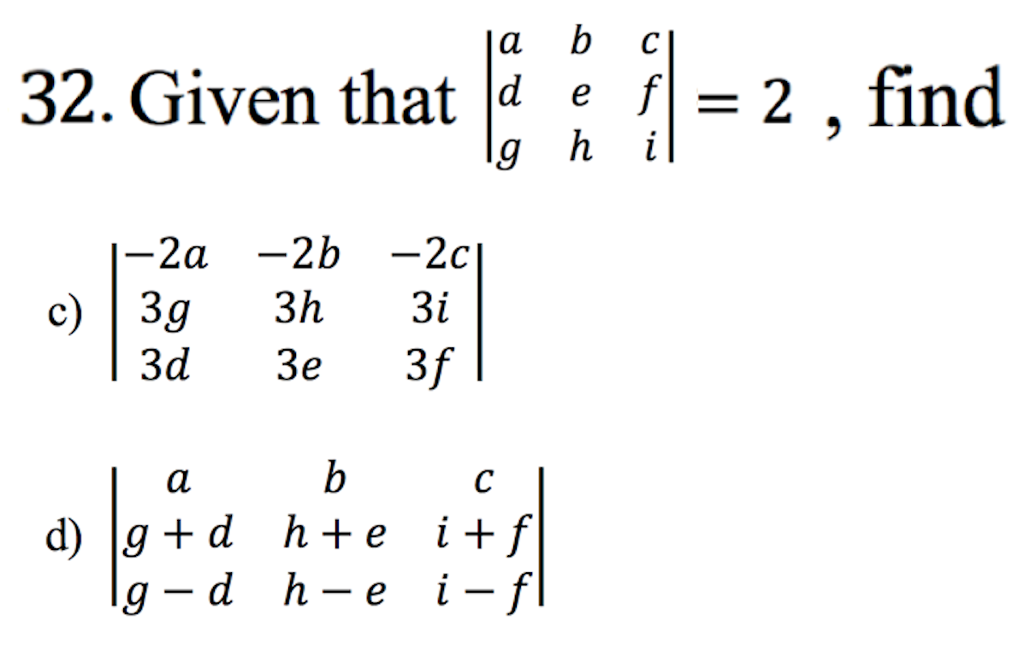
Solved Given That A B C D E F G H I 2 Find 2a 2b Chegg If $a*b*c=e$, then $a^{ 1} = b*c$. because inverses are commutative, this means that $e = a * (b*c) = a * a^{ 1} = a^{ 1} * a = (b*c)*a = b*c*a$, as desired. the strange thing is, my professor has told me this proof is wrong, and that $b*c$ is "just a right inverse of $a$", so i cannot say it is the inverse of $a$. Consider a relation r (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h), where each attribute is atomic, and following functional dependencies exist. the relation r is . the correct answer is option 1. explanation: since attribute d is not a part of any fd, it must be a part of the candidate key. ad = {abcdefgh} bd = {abcdefgh} ed = {abcdefgh} fd = {abcdefgh}. Given that $$\begin {vmatrix} a & b & c \\ d & f & g\\ q & w & e \end {vmatrix} =5$$ it is a whole matrix above. $$\begin {vmatrix} a & b & c \\ d & f &. What happens if (a, b) is counterclockwise of (c, d)? what do you know about the transformation? what happens to a transformation matrix when we flip a dimension? what does that do to the determinant? what does it mean (geometrically) when a 3x3 matrix has a zero determinant? what kind of a transformation is it?. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 4. given that, for some a, b, c, d, e, f,g,h,i e r de7, g h2 evaluate the following determinants: b h he (a) 3 points] a b c (b) 3 points] 3a 4g 3b 4h 3e 4i (4 points] a 9 9 d c i i f g h i d e f. here’s the best way to solve it. 4. Given a relation r with attributes (a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j) with functional dependencies shown diagrammatically, determine what is the normal form of the relation and if it is not in 3nf convert into 3nf. (attributes are named a,b,…just for ease of writing, practically the attributes will be something like in q1 above. fd1: ab >c fd2: b >f.
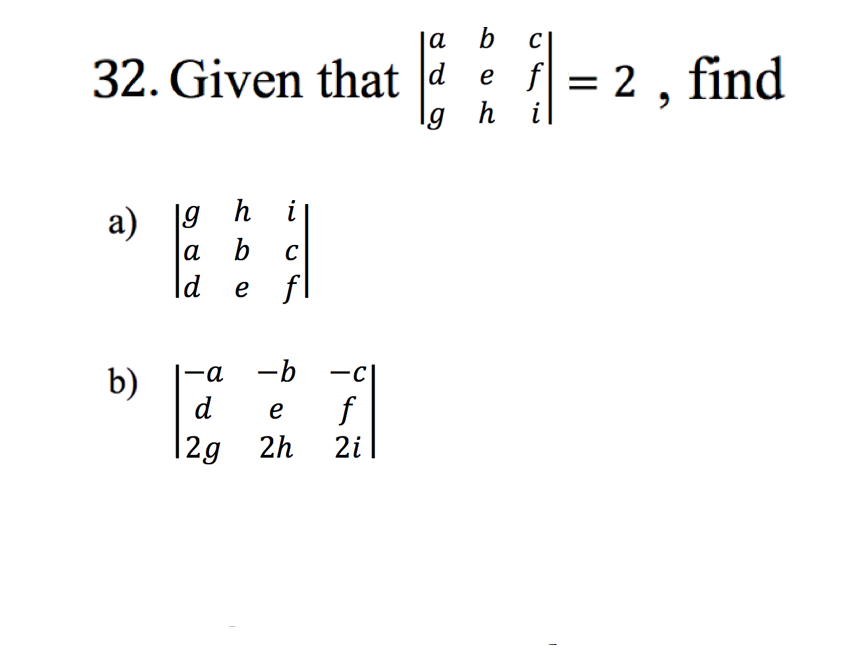
Solved Given That A B C D E F G H I 2 Find G H I A Chegg Given that $$\begin {vmatrix} a & b & c \\ d & f & g\\ q & w & e \end {vmatrix} =5$$ it is a whole matrix above. $$\begin {vmatrix} a & b & c \\ d & f &. What happens if (a, b) is counterclockwise of (c, d)? what do you know about the transformation? what happens to a transformation matrix when we flip a dimension? what does that do to the determinant? what does it mean (geometrically) when a 3x3 matrix has a zero determinant? what kind of a transformation is it?. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 4. given that, for some a, b, c, d, e, f,g,h,i e r de7, g h2 evaluate the following determinants: b h he (a) 3 points] a b c (b) 3 points] 3a 4g 3b 4h 3e 4i (4 points] a 9 9 d c i i f g h i d e f. here’s the best way to solve it. 4. Given a relation r with attributes (a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j) with functional dependencies shown diagrammatically, determine what is the normal form of the relation and if it is not in 3nf convert into 3nf. (attributes are named a,b,…just for ease of writing, practically the attributes will be something like in q1 above. fd1: ab >c fd2: b >f.

Solved 3 Given A A B C D E B A B D F 8 C Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 4. given that, for some a, b, c, d, e, f,g,h,i e r de7, g h2 evaluate the following determinants: b h he (a) 3 points] a b c (b) 3 points] 3a 4g 3b 4h 3e 4i (4 points] a 9 9 d c i i f g h i d e f. here’s the best way to solve it. 4. Given a relation r with attributes (a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j) with functional dependencies shown diagrammatically, determine what is the normal form of the relation and if it is not in 3nf convert into 3nf. (attributes are named a,b,…just for ease of writing, practically the attributes will be something like in q1 above. fd1: ab >c fd2: b >f.

Solved Given That A B C D E F G H I 5 Find The Value Chegg
