Solved 3 Consider The Reaction 2 No G O2 G 2 Chegg

Solved Consider The Reaction 2no G O G 2no G Chegg The overall order of a reaction is the sum of the orders of all the reactants in the rate law. in this case, the reaction is second order with respect to no and zero order with respect to o2. For example, a negative Δg means that the reaction can occur without any external input of energy. this relates to common reactions, like combustion, where products are favored and released energy makes the process spontaneous.

Solved 13 7 Consider The Reaction 2no G O G 2no G Chegg Consider the reaction n2 (g) o2 (g) ⇌ 2 no (g), for which kc=0.10 at 2,000°c. starting with initial concentrations of 0.040 m of n2 and 0.040 m of o2, determine the equilibrium concentration of no. Temperature plays a crucial role in determining the spontaneity of a reaction as it affects the balance between enthalpy and entropy. in the gibbs free energy equation, increasing temperature (t) can enhance the impact of entropy (Δs) on Δg. $$estimate $\delta g^ {\circ}$ for this reaction at each temperature and predict whether or not the reaction is spontaneous. (assume that $\delta h^ {\circ}$ and $\delta s^ {\circ}$ do not change too much within the given temperature range.). In most cases, kc ≠ kp so the following equation is used to convert between them: consider the equilibrium and answer the questions below. round each answer to two places past the decimal in scientific notation.
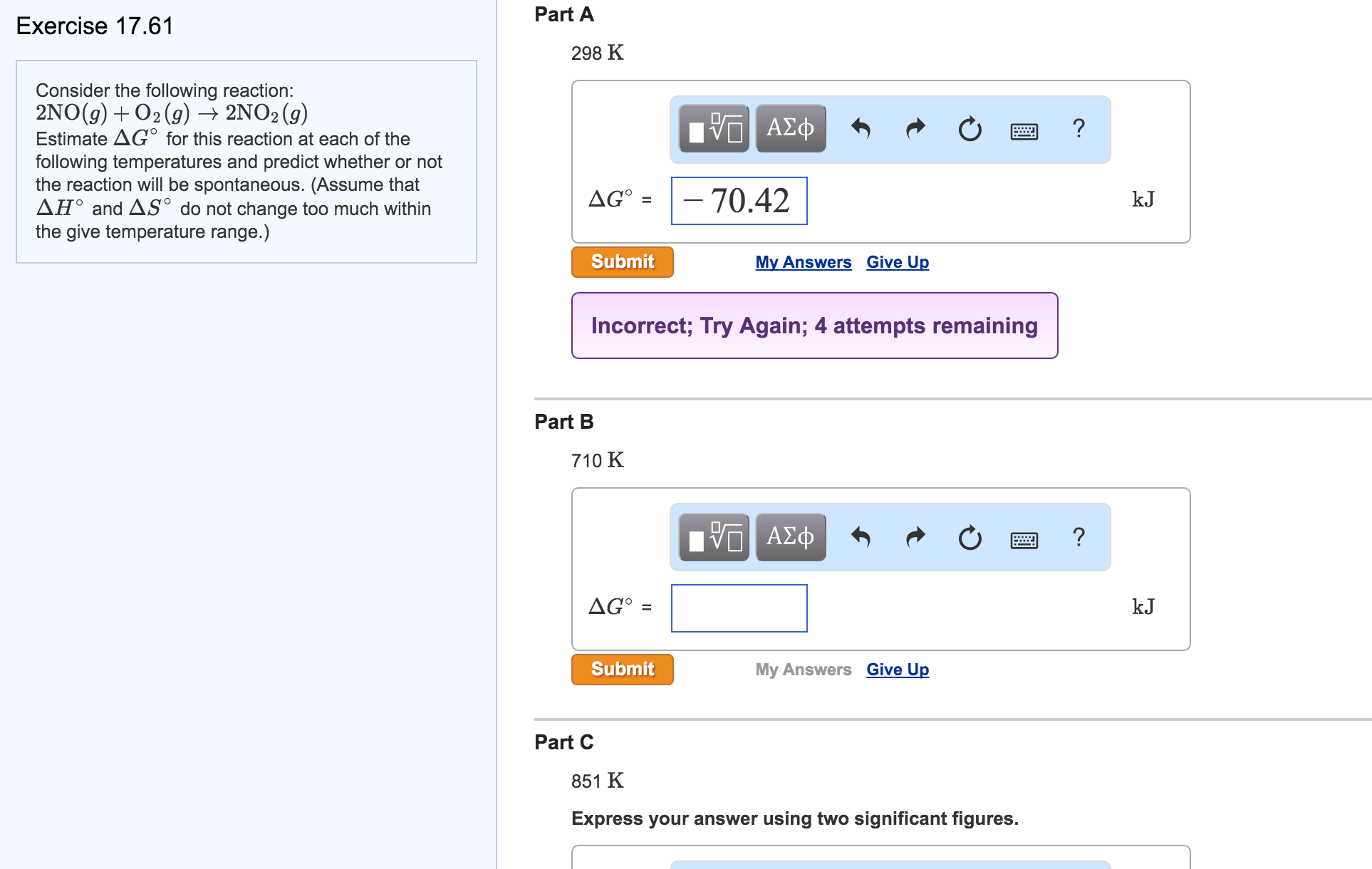
Solved Consider The Following Reaction 2no G O 2 G Chegg $$estimate $\delta g^ {\circ}$ for this reaction at each temperature and predict whether or not the reaction is spontaneous. (assume that $\delta h^ {\circ}$ and $\delta s^ {\circ}$ do not change too much within the given temperature range.). In most cases, kc ≠ kp so the following equation is used to convert between them: consider the equilibrium and answer the questions below. round each answer to two places past the decimal in scientific notation. The rate law consistent with the reaction mechanism is rate = k[no]2[o2], where the reaction is second order in no and first order in o2. this is derived from considering the rate determining step and substituting the intermediate concentration into the rate equation.

Solved Consider The Following Reaction 2no G O 2 G Chegg The rate law consistent with the reaction mechanism is rate = k[no]2[o2], where the reaction is second order in no and first order in o2. this is derived from considering the rate determining step and substituting the intermediate concentration into the rate equation.
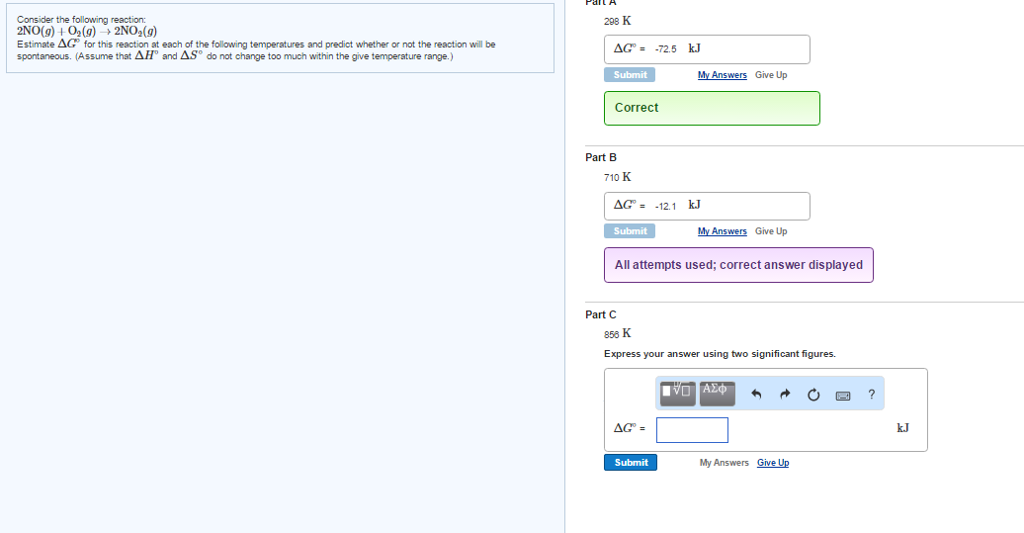
Solved Consider The Following Reaction 2no G O 2 G Chegg

Solved 11 Consider The Following Reaction 2 No G O2 G Chegg
Comments are closed.