Solved 6 Problem 4 The Figure Below Shows Two Current Chegg
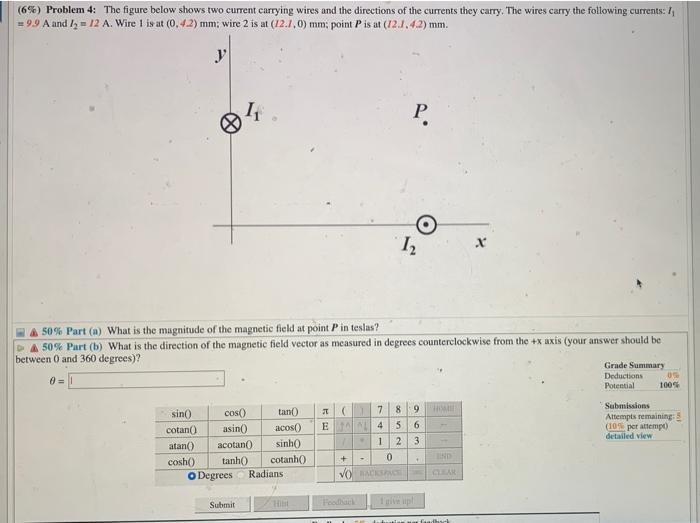
Solved 6 Problem 4 The Figure Below Shows Two Current Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. The figure below shows two current carrying wires and the directions of the currents they carry. the wires carry the following currents: i1 = 9.2 a and i2 = 8.9 a. wire 1 is at (0, 9.9) mm; wire 2 is at (12, 0) mm; point p is at (12, 9.9) mm.
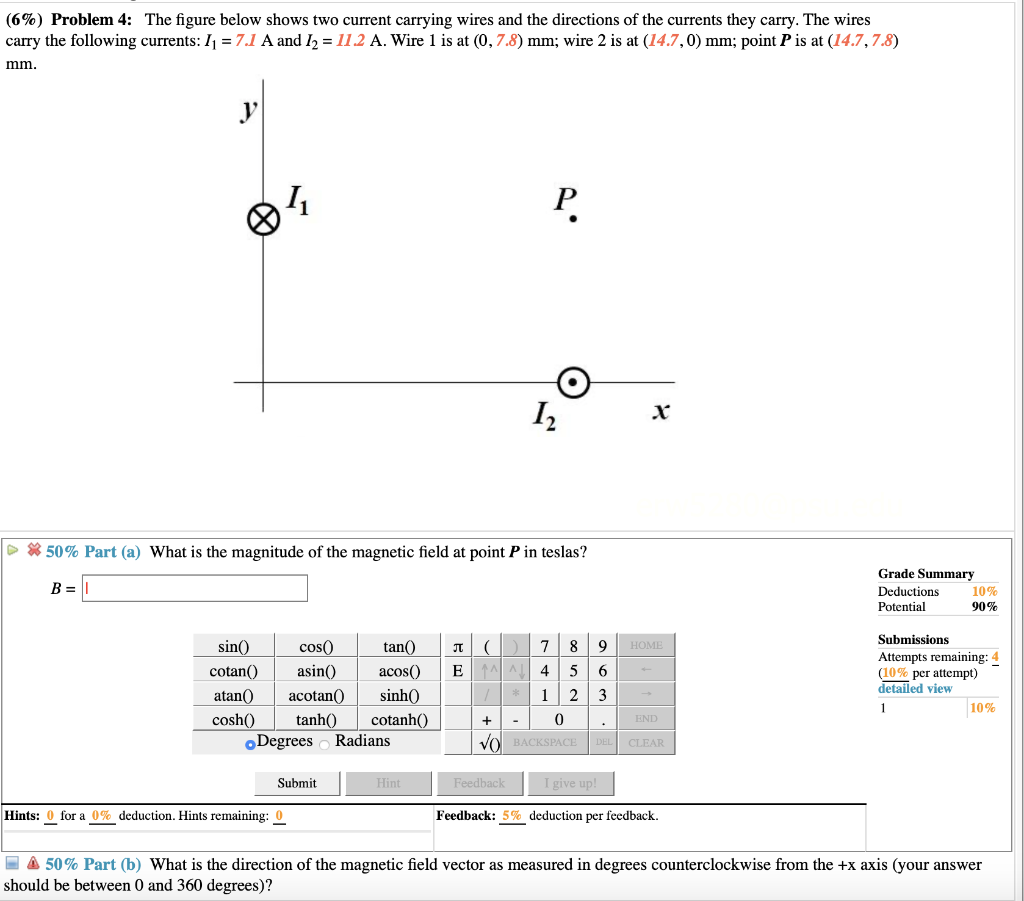
Solved 6 Problem 4 The Figure Below Shows Two Current Chegg The figure below shows two current segments. the lower segment carries a current of i1 = 0.61a and includes a circular arc with a radius of 8.2 cm and an angle of 180∘. To solve this problem, we will use the biot savart law to find the magnetic field produced by each current segment and then determine the net magnetic field by adding the contributions from each segment. The figure below shows how a bleeder resistor (r = 236 kΩ) is used to discharge a capacitor (c = 58.7 µf) after an electronic device is shut off, allowing a person to work on the electronics with less risk of shock. First, we need to find the magnetic field due to each current segment at point p.
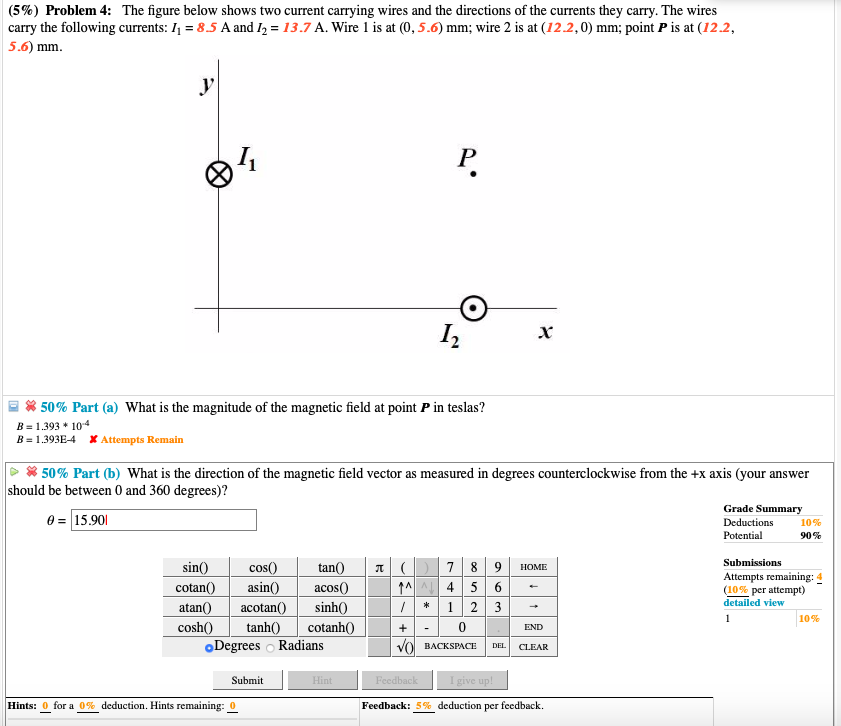
Solved 5 Problem 4 The Figure Below Shows Two Current Chegg The figure below shows how a bleeder resistor (r = 236 kΩ) is used to discharge a capacitor (c = 58.7 µf) after an electronic device is shut off, allowing a person to work on the electronics with less risk of shock. First, we need to find the magnetic field due to each current segment at point p. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: (6%) problem 4: the figure below shows two current carrying wires and the directions of the currents they carry. (6\%) problem 4: the figure below shows two current carrying wires and the directions of the currents they carry. It is common in electronics to convert a current signal into a voltage signal. one case where this is necessary, is when converting the photocurrent generated by a photodiode into a voltage. Now, to find the net magnetic field at point p, we need to add the two magnetic fields vectorially. since the two magnetic fields are in the same direction (into the page), we can simply add their magnitudes: b = b1 b2 = 3.28 × 10^ 6 t so the magnitude of the net magnetic field is 3.28 × 10^ 6 t, and its direction is into the page.
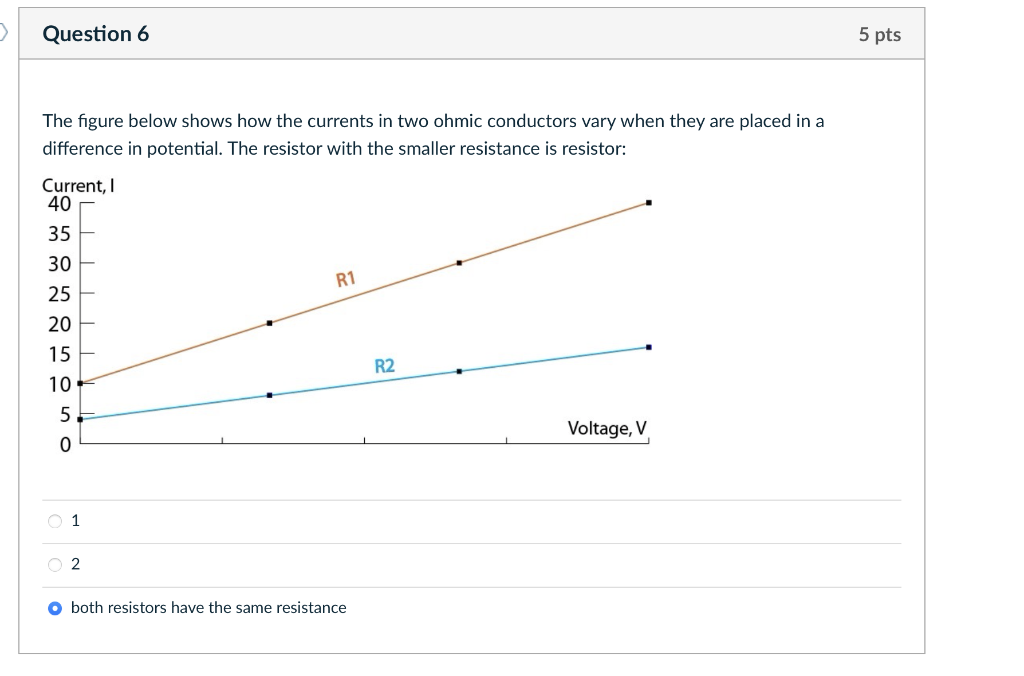
Solved Question 6 The Figure Below Shows How The Currents In Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: (6%) problem 4: the figure below shows two current carrying wires and the directions of the currents they carry. (6\%) problem 4: the figure below shows two current carrying wires and the directions of the currents they carry. It is common in electronics to convert a current signal into a voltage signal. one case where this is necessary, is when converting the photocurrent generated by a photodiode into a voltage. Now, to find the net magnetic field at point p, we need to add the two magnetic fields vectorially. since the two magnetic fields are in the same direction (into the page), we can simply add their magnitudes: b = b1 b2 = 3.28 × 10^ 6 t so the magnitude of the net magnetic field is 3.28 × 10^ 6 t, and its direction is into the page.
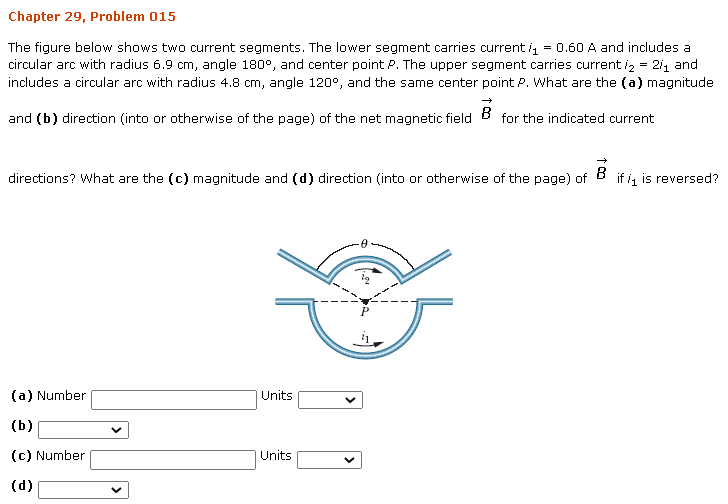
Solved Chapter 29 Problem 015 The Figure Below Shows Two Chegg It is common in electronics to convert a current signal into a voltage signal. one case where this is necessary, is when converting the photocurrent generated by a photodiode into a voltage. Now, to find the net magnetic field at point p, we need to add the two magnetic fields vectorially. since the two magnetic fields are in the same direction (into the page), we can simply add their magnitudes: b = b1 b2 = 3.28 × 10^ 6 t so the magnitude of the net magnetic field is 3.28 × 10^ 6 t, and its direction is into the page.

Solved The Figure Below Shows Two Wires Carrying Currents Of Chegg
Comments are closed.