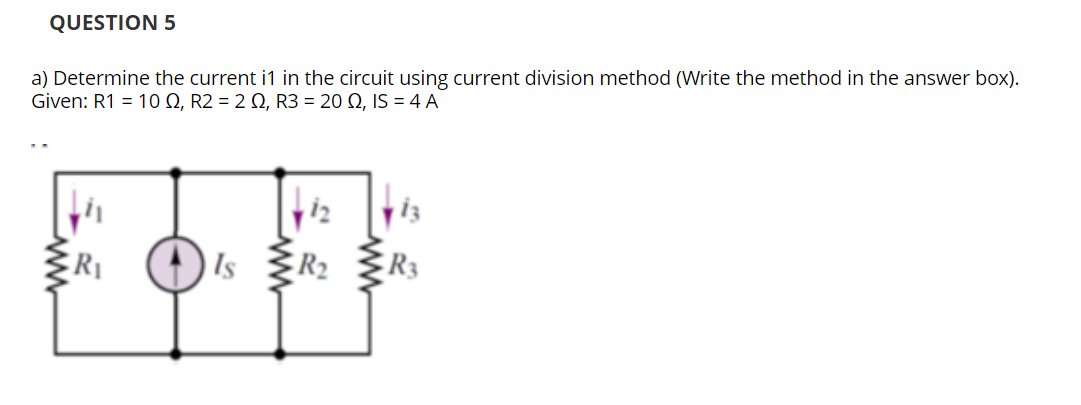
Solved A Determine The Current I1 In The Circuit Using Chegg A) determine the current i1 in the circuit using current division method (write the method in the answer box). given: r1=10Ω,r2=2Ω,r3=20Ω,is=4 a. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Determine the current i1 in the following circuit, along with the power supplied by the current source and power absorbed by the 8Ω resistor. here’s the best way to solve it. solution.
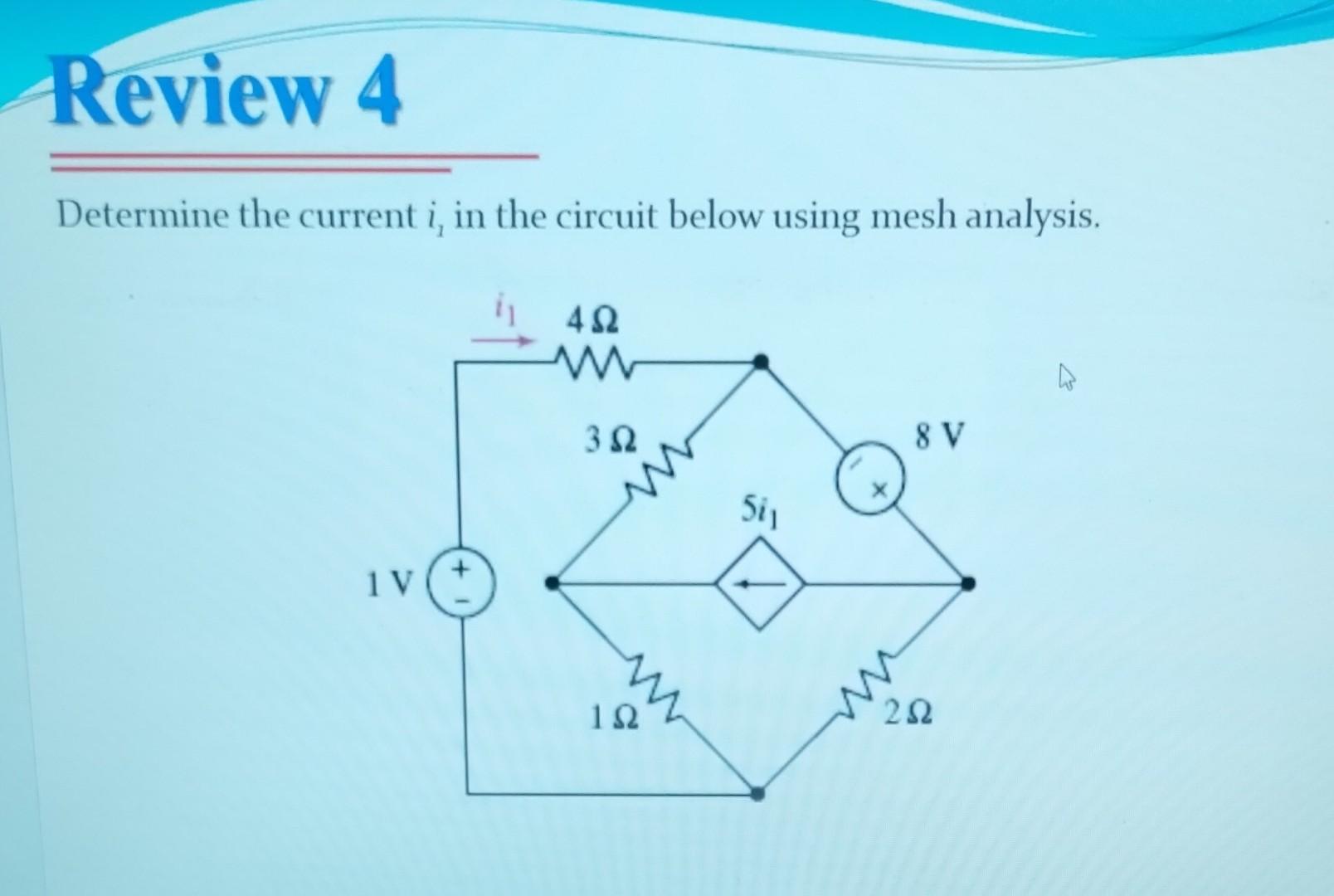
Solved Determine The Current I1 In The Circuit Below Using Chegg The instantaneous value of current flowing in a circuit is expressed as i = 8 sin ωt 6 sin 2ωt. if this current flows through a resistance of 10 Ω, what will be the power dissipated?. Determine the value of current i 1 in the following circuit. concept: kirchhoff’s current law (kcl): it states that the algebraic sum of currents entering a node or closed boundary is zero. mathematically, kcl implies that. where n is the number of branches connected to the node. and i n is the n th current entering or leaving the node. Following the current flow direction assumptions: i1 = 0.946 a. i2 = 1.75676 a. i3 = 2.7027 a. The current in the circuit is 2.87 a. here's how we can find it: apply kirchhoff's current law (kcl) a.
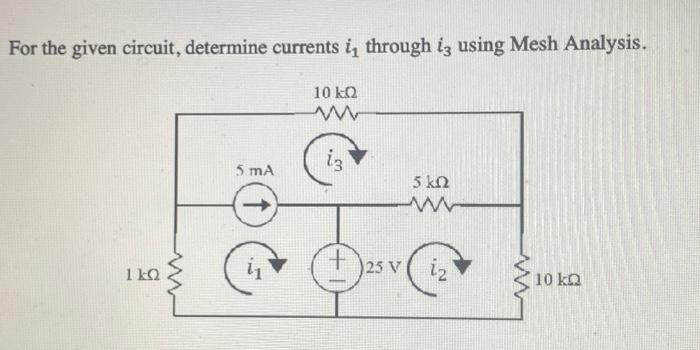
Solved For The Given Circuit Determine Currents I1 Through Chegg Following the current flow direction assumptions: i1 = 0.946 a. i2 = 1.75676 a. i3 = 2.7027 a. The current in the circuit is 2.87 a. here's how we can find it: apply kirchhoff's current law (kcl) a. Let i o = i1 i 2 i 3 , where i1 , i 2 , and i 3 are respectively due to the 24 v dc source, the ac voltage source, and the ac current source. for i1 , consider the circuit in fig. (a). 1Ω 24 v 1 6 f 2h − i1 2Ω 4Ω since the capacitor is an open circuit to dc, 24 i1 = =4a 4 2 for i 2 , consider the circuit in fig. (b). ω=1 2h. Here’s the best way to solve it. using nodal analus … not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. For i3 loop 12.00v 10 (i3) 8 (i1) 1 (i2)=0 by plugging in i1 and i2 i get i3 to be 5a. ah. don't forget to apply kcl at the nodes where currents join split. for the "i1 loop", for example, i3 joins the party at the rightmost node, so the current through the 8.00 ohm resistor is actually i1 i3. label the net currents on wires around the nodes. The document contains solutions to 3 assignments for a circuit theory course. in the first assignment, the document solves for total resistance, current values, and voltages in various circuit diagrams using steps like applying ohm's law and kirchhoff's laws. it also explains the differences between voltage division and current division rules.
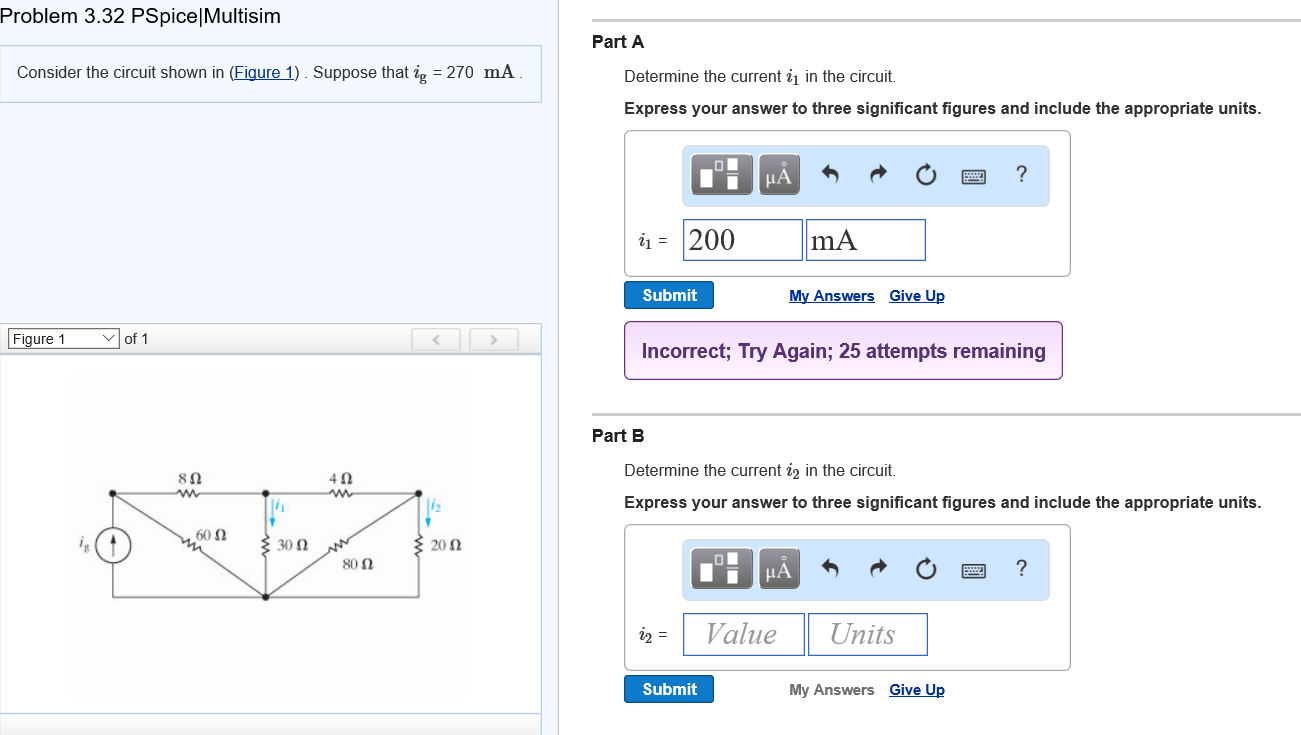
Solved Consider The Circuit Shown In Figure 1 Suppose Chegg Let i o = i1 i 2 i 3 , where i1 , i 2 , and i 3 are respectively due to the 24 v dc source, the ac voltage source, and the ac current source. for i1 , consider the circuit in fig. (a). 1Ω 24 v 1 6 f 2h − i1 2Ω 4Ω since the capacitor is an open circuit to dc, 24 i1 = =4a 4 2 for i 2 , consider the circuit in fig. (b). ω=1 2h. Here’s the best way to solve it. using nodal analus … not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. For i3 loop 12.00v 10 (i3) 8 (i1) 1 (i2)=0 by plugging in i1 and i2 i get i3 to be 5a. ah. don't forget to apply kcl at the nodes where currents join split. for the "i1 loop", for example, i3 joins the party at the rightmost node, so the current through the 8.00 ohm resistor is actually i1 i3. label the net currents on wires around the nodes. The document contains solutions to 3 assignments for a circuit theory course. in the first assignment, the document solves for total resistance, current values, and voltages in various circuit diagrams using steps like applying ohm's law and kirchhoff's laws. it also explains the differences between voltage division and current division rules.
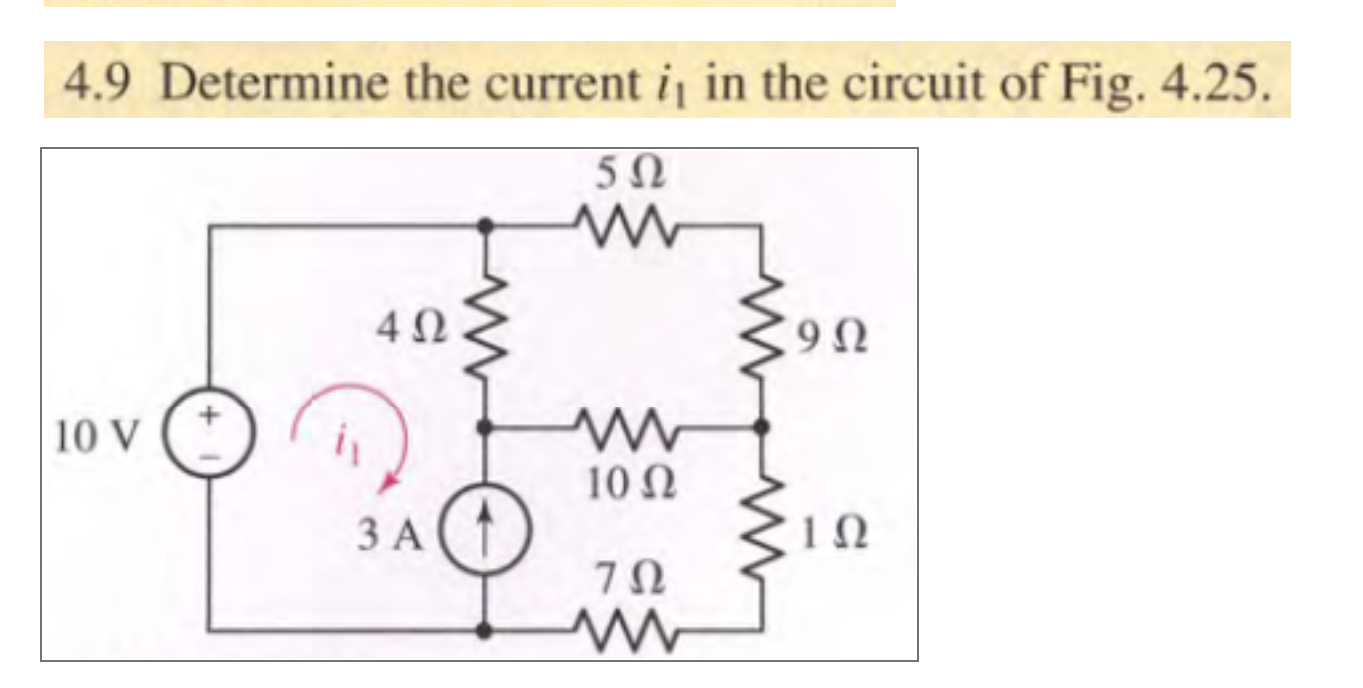
Solved 4 9 Determine The Current I1 In The Circuit Of Fig Chegg For i3 loop 12.00v 10 (i3) 8 (i1) 1 (i2)=0 by plugging in i1 and i2 i get i3 to be 5a. ah. don't forget to apply kcl at the nodes where currents join split. for the "i1 loop", for example, i3 joins the party at the rightmost node, so the current through the 8.00 ohm resistor is actually i1 i3. label the net currents on wires around the nodes. The document contains solutions to 3 assignments for a circuit theory course. in the first assignment, the document solves for total resistance, current values, and voltages in various circuit diagrams using steps like applying ohm's law and kirchhoff's laws. it also explains the differences between voltage division and current division rules.
