Solved A Saturated Solution Of Ca Oh 2 Has A Ph Of 12 40 Chegg

Solved A Saturated Solution Of Ca Oh 2 Has A Ph Of 12 40 Chegg Science chemistry chemistry questions and answers a saturated solution of ca (oh) 2 has a ph of 12.40. what is the ksp of ca (oh) 2? calculate the maximum ph that could be achieved in a solution of manganese (ii) hydroxide, mn (oh) 2 (ksp = 2.1 times 10^ 13). To find the ksp (solubility product constant) for ca (oh)2 from its ph, we must first calculate the concentration of hydroxide ions, [oh ], in the solution. the ph of 12.40 indicates a poh of 1.60 (since ph poh = 14).

Solved What Is The Ph Of A Saturated Solution Of Ca Oh 2 Chegg Given the ph of the saturated solution of is 12.35, we can calculate the poh and hydroxide ion concentration as follows:. Chapter 17: problem 67 a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide, ca (oh) 2, has a ph of 12.35. find the hydroxide ion concentration and calculate the equilibrium constant. short answer expert verified. A saturated aqueous solution of ca (oh)2 has ph = 12.40. what is the concentration of hydroxide ion in this solution? you may assume the temperature is 25 °c. Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. see answer.
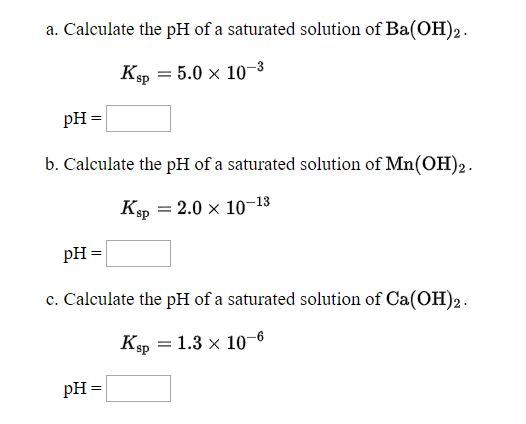
Solved A Calculate The Ph Of A Saturated Solution Of Chegg A saturated aqueous solution of ca (oh)2 has ph = 12.40. what is the concentration of hydroxide ion in this solution? you may assume the temperature is 25 °c. Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. see answer. To find the solubility product constant, ksp, for calcium hydroxide, ca (oh)₂, when you have the ph of a saturated solution, you can follow these steps: determine the concentration of hydroxide ions, [oh⁻]:. Science chemistry chemistry questions and answers answers from question 1 4: using your ph measurement (12.5), calculate the [oh ] ion in the saturated solution of calcium hydroxide at room temperature 25 °c. we have , ph = 14 poh thus, poh = 1.5 poh = log [oh ] [oh ] = 10^ 1.5 = 0.0316 m 2. using stoichiometry of the reaction and [oh ], calculate the concentration of ca2 at room. To determine the equilibrium constant for calcium hydroxide from a saturated solution for which we know a ph we first need to write the equilibrium reaction. it'll be calcium hydroxide dissociate. To determine the ksp (solubility product constant) of ca (oh)₂, we can use the ph of the saturated solution. the ph of 12.40 indicates the concentration of hydroxide ions (oh⁻) in the solution.

Solved A Saturated Solution Of Ca Oh 2 Has A Ph Of 12 35 Chegg To find the solubility product constant, ksp, for calcium hydroxide, ca (oh)₂, when you have the ph of a saturated solution, you can follow these steps: determine the concentration of hydroxide ions, [oh⁻]:. Science chemistry chemistry questions and answers answers from question 1 4: using your ph measurement (12.5), calculate the [oh ] ion in the saturated solution of calcium hydroxide at room temperature 25 °c. we have , ph = 14 poh thus, poh = 1.5 poh = log [oh ] [oh ] = 10^ 1.5 = 0.0316 m 2. using stoichiometry of the reaction and [oh ], calculate the concentration of ca2 at room. To determine the equilibrium constant for calcium hydroxide from a saturated solution for which we know a ph we first need to write the equilibrium reaction. it'll be calcium hydroxide dissociate. To determine the ksp (solubility product constant) of ca (oh)₂, we can use the ph of the saturated solution. the ph of 12.40 indicates the concentration of hydroxide ions (oh⁻) in the solution.

Solved At 25 C Consider A Solution Saturated With Ca Oh 2 Chegg To determine the equilibrium constant for calcium hydroxide from a saturated solution for which we know a ph we first need to write the equilibrium reaction. it'll be calcium hydroxide dissociate. To determine the ksp (solubility product constant) of ca (oh)₂, we can use the ph of the saturated solution. the ph of 12.40 indicates the concentration of hydroxide ions (oh⁻) in the solution.
Comments are closed.