Solved Consider The Following Game With 2 Players And Chegg
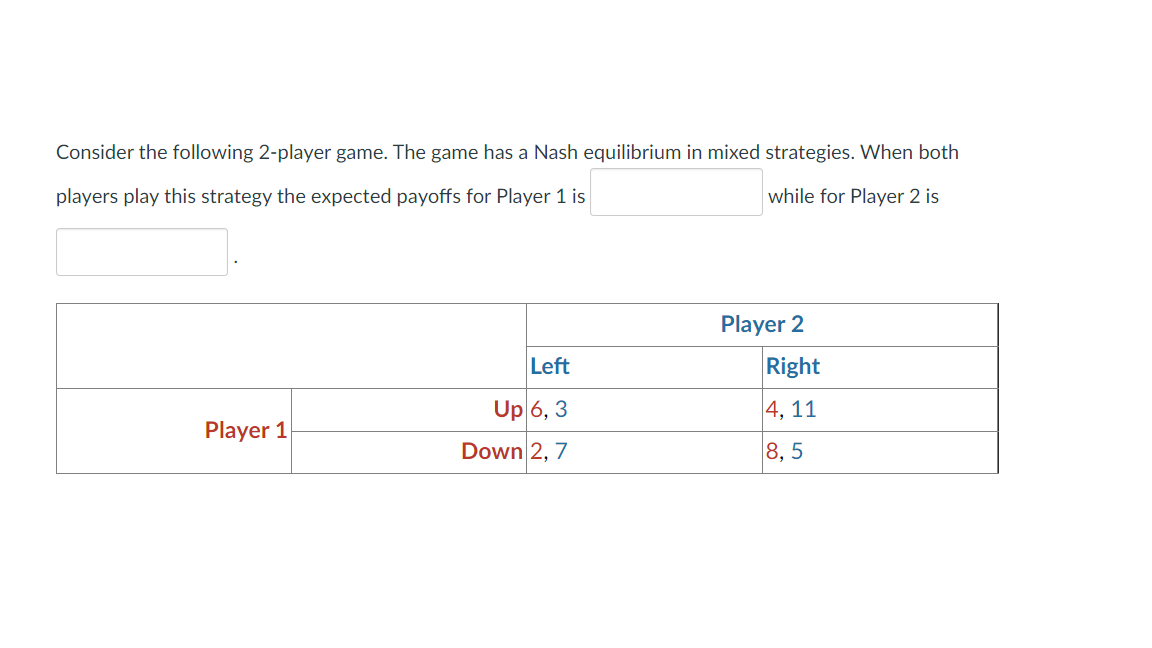
Solved Consider The Following 2 Player Game The Game Has A Chegg Consider the following 2 player game. the game has a nash equilibrium in mixed strategies. when both players play this strategy the expected payoffs for player 1 is while for player 2 is player 2 left right up 6,3 4, 11 player 1 down 2,7 8,5. your solution’s ready to go!. Consider the following game in matrix form with two players. payoffs for the row player shelia are indicated first in each cell, and payoffs for the column player thomas are second.
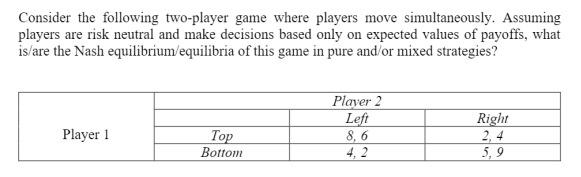
Solved Consider The Following Two Player Game Where Players Chegg To find the best response for player 1, we need to determine the strategy that maximizes player 1's payoff for any given strategy of player 2. let's consider the three cases: case 1: s1 < s2 in this case, player 1's payoff is (s1 s2) 2. Consider a two player game with five strategies for each player: we will start by finding the best responses for player 1. that is, for every possible strategy of player 2, we will identify player 1's best response. This university level economics assignment 2 covers game theory concepts like nash equilibrium, dominated strategies, and best responses through problems on penalty shots, dollar splitting, and vaccination externalities. ideal for econ2141 students. 14 chapter 4. stable play: nash equilibrium in discrete games with two or three players 4 4.1 defining nash equilibrium the game of chicken can you find a solution to this game using last chapter’s approach? there are no dominant strategies for either player, so we need to use another approach: the nash equilibrium. 4 4.1 defining nash equilibrium there are two components of a nash.

Solved Consider The Following Game With 2 Players Player A Chegg This university level economics assignment 2 covers game theory concepts like nash equilibrium, dominated strategies, and best responses through problems on penalty shots, dollar splitting, and vaccination externalities. ideal for econ2141 students. 14 chapter 4. stable play: nash equilibrium in discrete games with two or three players 4 4.1 defining nash equilibrium the game of chicken can you find a solution to this game using last chapter’s approach? there are no dominant strategies for either player, so we need to use another approach: the nash equilibrium. 4 4.1 defining nash equilibrium there are two components of a nash. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: consider the following game, where a two player game in which player 1 and player 2 must simultaneously choose one of two strategies: "cooperate" or "defect." the payoff matrix is shown below. For a simple example, first consider the following simultaneous game. the nash equilibrium of the simultaneous game is (b,z). suppose instead that the game is played sequentially, with player 1 selecting his strategy first. player 2 then observes player 1’s choice and selects his own strategy. Zermelo's theorem (game theory) in game theory, zermelo's theorem is a theorem about finite two person games of perfect information in which the players move alternately and in which chance does not affect the decision making process. Consider the following 2 player game. the game has one nash equilibrium in mixed strategies where player 1 plays up (populate your answer as a simplified fraction, e.g., 1 9) of the time and down of the time while player 2 plays left of the time and right of the time. your solution’s ready to go!.

Solved Consider The Following Game With 2 Players 2 Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: consider the following game, where a two player game in which player 1 and player 2 must simultaneously choose one of two strategies: "cooperate" or "defect." the payoff matrix is shown below. For a simple example, first consider the following simultaneous game. the nash equilibrium of the simultaneous game is (b,z). suppose instead that the game is played sequentially, with player 1 selecting his strategy first. player 2 then observes player 1’s choice and selects his own strategy. Zermelo's theorem (game theory) in game theory, zermelo's theorem is a theorem about finite two person games of perfect information in which the players move alternately and in which chance does not affect the decision making process. Consider the following 2 player game. the game has one nash equilibrium in mixed strategies where player 1 plays up (populate your answer as a simplified fraction, e.g., 1 9) of the time and down of the time while player 2 plays left of the time and right of the time. your solution’s ready to go!.

Solved Exercise 2 Consider The Following Game With Two Chegg Zermelo's theorem (game theory) in game theory, zermelo's theorem is a theorem about finite two person games of perfect information in which the players move alternately and in which chance does not affect the decision making process. Consider the following 2 player game. the game has one nash equilibrium in mixed strategies where player 1 plays up (populate your answer as a simplified fraction, e.g., 1 9) of the time and down of the time while player 2 plays left of the time and right of the time. your solution’s ready to go!.
Comments are closed.