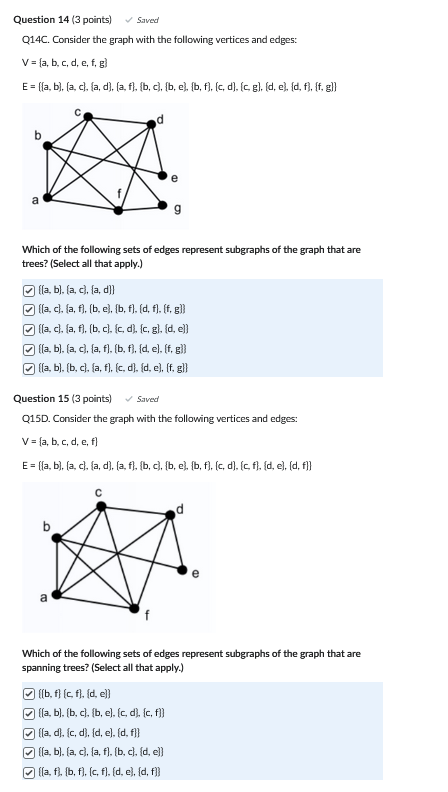
Solved Consider The Following Network Where A B C D E F Chegg
Solved Chegg Consider the following network where a, b, c, d, e, f are hosts, r is a router and s is a switch. hosts a, b, c are connected to router r. hosts d, e, f and router r are all star connected into switch s. suppose the router r and switch s have the forwarding tables for all the hosts of the network. 4) consider the following bayesian network. a, b, c, and d are boolean random variables. if we know that a is true, what is the probability of d being true? we know that x and z are not guaranteed to be independent if the value of y is unknown.
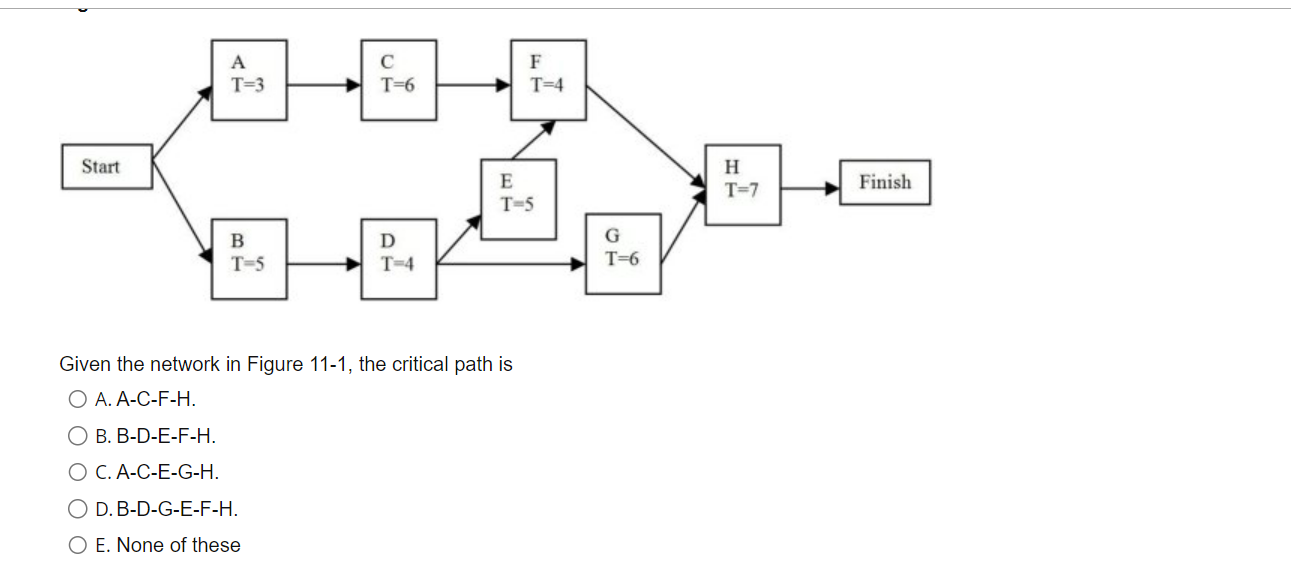
Solved Given The Network In Figure 11 1 The Critical Path Chegg F solution: with s2 = true, observing s4 = true still gives us information only about d3. if we had observed s3 = true instead of s2, then observing s4 = true would have given us information about d1 and d3 due to explaining away. Bayesian net example consider the following bayesian network: thus, the independence expressed in this bayesian net are that. Answer: false. there is an unblocked (or not d separated) path from a to b to e, and then thru f to g to c. note that without information about f, the path from e to g is blocked. Answer the distance vector algorithm, also known as the bellman ford algorithm, is used to find the shortest path between nodes in a network. each node maintains a distance table. note: the link between as4 and as2 is currently dotted, meaning there is no physical link.
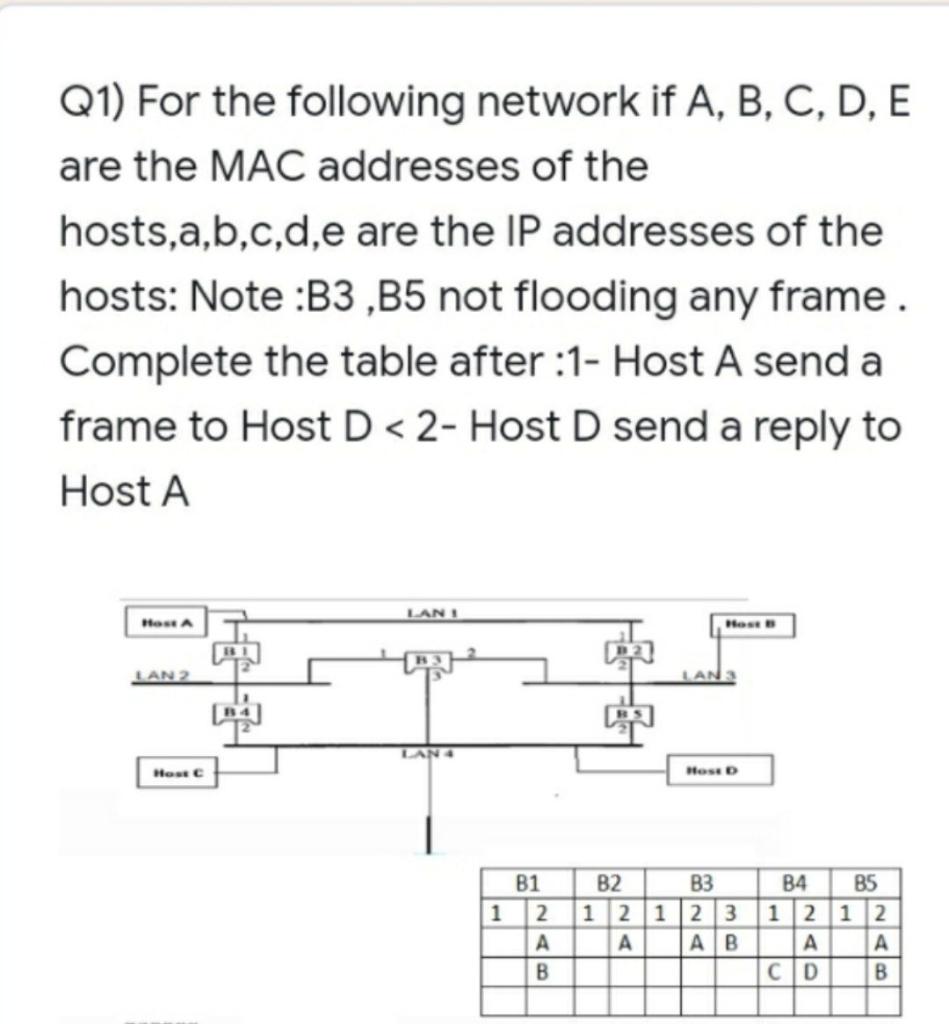
Q1 For The Following Network If A B C D E Are Chegg Answer: false. there is an unblocked (or not d separated) path from a to b to e, and then thru f to g to c. note that without information about f, the path from e to g is blocked. Answer the distance vector algorithm, also known as the bellman ford algorithm, is used to find the shortest path between nodes in a network. each node maintains a distance table. note: the link between as4 and as2 is currently dotted, meaning there is no physical link. Important: in addition to these problems, please solve the problems at the end of chapters 17 and 18. problem 1. consider the following networks: network i (containing nodes a, b, c) and network ii (containing nodes d, e, f). the distance vector protocol described in class is used in both networks. What is project completion time?, the network below represents a project being analyzed by critical path methods. activity durations are a=5, b=2, c=12, d=3, e=5, f=1, g=7, h=2, i=10, and j=6. The given **bayesian network **represents the relationships between five boolean variables: a, b, c, d, and e. to answer the questions, we need to calculate the probabilities based on the provided conditional probabilities. Consider the following bayesian network: a) compute p (f | a). show your work. b) compute p (f | ∼c). show your work. c) compute p (f | a,b). show your work. d) compute p (f | a,b,c). your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.
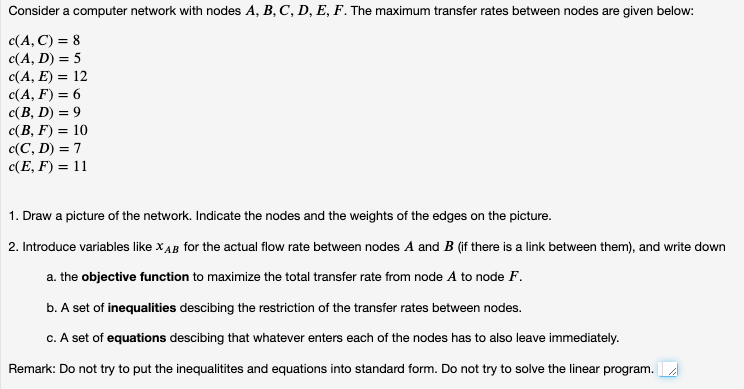
Consider A Computer Network With Nodes A B C D E Chegg Important: in addition to these problems, please solve the problems at the end of chapters 17 and 18. problem 1. consider the following networks: network i (containing nodes a, b, c) and network ii (containing nodes d, e, f). the distance vector protocol described in class is used in both networks. What is project completion time?, the network below represents a project being analyzed by critical path methods. activity durations are a=5, b=2, c=12, d=3, e=5, f=1, g=7, h=2, i=10, and j=6. The given **bayesian network **represents the relationships between five boolean variables: a, b, c, d, and e. to answer the questions, we need to calculate the probabilities based on the provided conditional probabilities. Consider the following bayesian network: a) compute p (f | a). show your work. b) compute p (f | ∼c). show your work. c) compute p (f | a,b). show your work. d) compute p (f | a,b,c). your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.
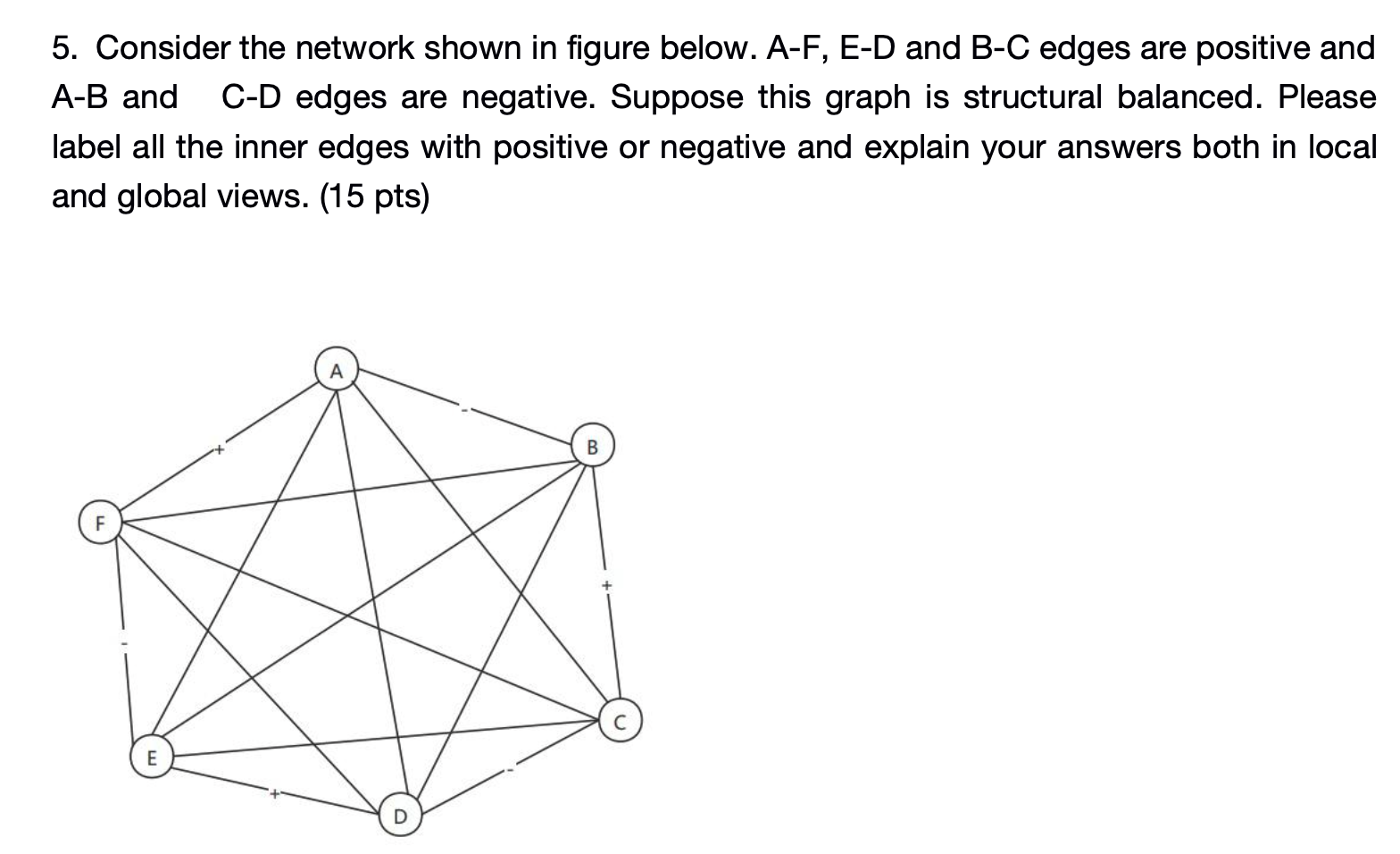
Solved 5 Consider The Network Shown In Figure Below A F Chegg The given **bayesian network **represents the relationships between five boolean variables: a, b, c, d, and e. to answer the questions, we need to calculate the probabilities based on the provided conditional probabilities. Consider the following bayesian network: a) compute p (f | a). show your work. b) compute p (f | ∼c). show your work. c) compute p (f | a,b). show your work. d) compute p (f | a,b,c). your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.
Comments are closed.