Solved Consider The Following Reaction 2 No2 G N204 G Chegg

Solved Consider The Following Reaction 2 No2 G N204 G Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: consider the following reaction. 2 no2 (g) = n204 (g) kp = 27.4 at 300 k the initial pressures are as follows. p (no2) = 0.8 atm p (n204)0 = 0.2 atm what is the equilibrium pressure of no2? o 0.27 atm o 0.68 atm o 0.14 atm o 0.71 atm o 0.44 atm. 3) consider the reaction: n204 (g) 2 no2 (g), ah = 58 kj use le chatelier's principle to predict the effect of the answered step by step solved by verified expert portland community college.

Solved Consider The Following Reaction 2 No2 G N204 G Chegg Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2 no (g) o2 (g) ⇌ 2 no2 (g) in most cases, kc ≠ kp so the following equation is used to convert between them: consider the equilibrium and answer the questions below. round each answer to two places past the decimal in scientific notation. The calculations of Δg° and q are based on standard thermodynamic principles and provided gibbs free energy of formation values, which are commonly used to evaluate reaction spontaneity. Consider the reaction: 2 no (g) o2(g) ⇌ 2 no2(g) the following data show the equilibrium constant for this reaction measured at several different temperatures. use the data to find Δh°rxn and Δs°rxn for the reaction. Video answer: we know that the equilibrium partial pressures of n, 2, o 2 and n o 2 point have already been balanced. we need to know what the k p is so we can write it.
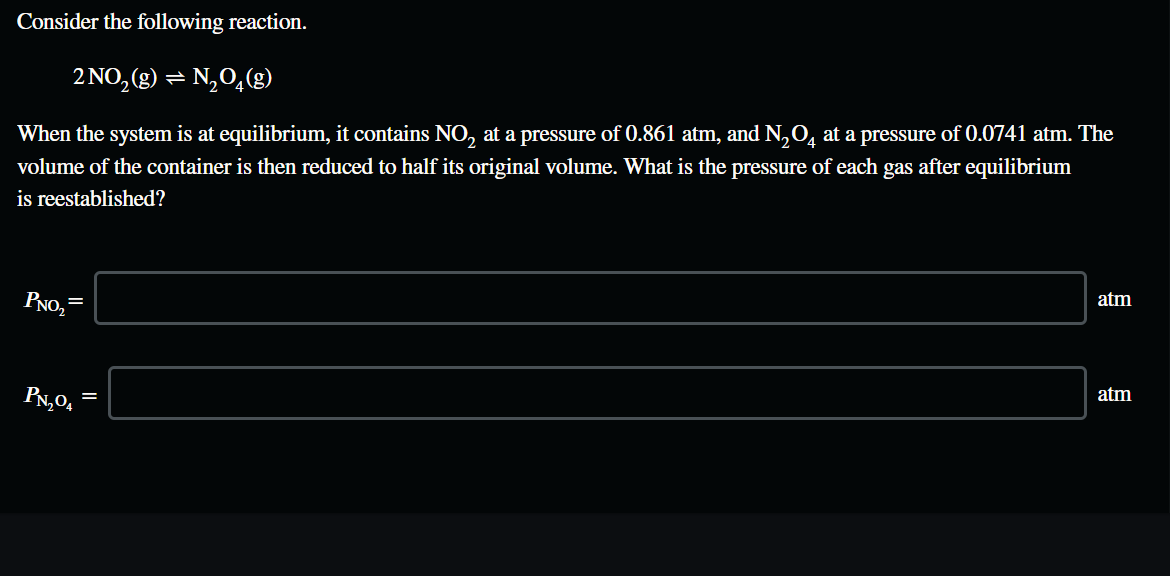
Solved Consider The Following Reaction 2 No2 G N204 G Chegg Consider the reaction: 2 no (g) o2(g) ⇌ 2 no2(g) the following data show the equilibrium constant for this reaction measured at several different temperatures. use the data to find Δh°rxn and Δs°rxn for the reaction. Video answer: we know that the equilibrium partial pressures of n, 2, o 2 and n o 2 point have already been balanced. we need to know what the k p is so we can write it. Consider the following reaction. 2 no2 (g) = n204 (g) when the system is at equilibrium, it contains no2 at a pressure of 0.707 atm, and n204 at a pressure of 0.0500 atm. As for the reactants (no2), we're given a molar entropy of 240 j (mol⋅k). however, since there are two moles of no2 involved in the reaction, the overall entropy for the reactants is 240 j (mol⋅k) x 2. To increase the molar concentration at equilibrium of the product n2o4 in the reaction 2no2 = n2o4, you can use le chatelier's principle. a change that would increase the concentration of n2o4 would be to decrease the temperature or to increase the pressure. Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2 no (g) o2 (g) ⇌ 2 no2 (g) consider the equilibrium and answer the questions below. round each answer to two places past the decimal in scientific notation.

Solved Consider The Following Reaction 2 No2 G N204 G Chegg Consider the following reaction. 2 no2 (g) = n204 (g) when the system is at equilibrium, it contains no2 at a pressure of 0.707 atm, and n204 at a pressure of 0.0500 atm. As for the reactants (no2), we're given a molar entropy of 240 j (mol⋅k). however, since there are two moles of no2 involved in the reaction, the overall entropy for the reactants is 240 j (mol⋅k) x 2. To increase the molar concentration at equilibrium of the product n2o4 in the reaction 2no2 = n2o4, you can use le chatelier's principle. a change that would increase the concentration of n2o4 would be to decrease the temperature or to increase the pressure. Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2 no (g) o2 (g) ⇌ 2 no2 (g) consider the equilibrium and answer the questions below. round each answer to two places past the decimal in scientific notation.

Solved 8 Consider The Following Reaction N204 2 No2 G A Chegg To increase the molar concentration at equilibrium of the product n2o4 in the reaction 2no2 = n2o4, you can use le chatelier's principle. a change that would increase the concentration of n2o4 would be to decrease the temperature or to increase the pressure. Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2 no (g) o2 (g) ⇌ 2 no2 (g) consider the equilibrium and answer the questions below. round each answer to two places past the decimal in scientific notation.
Comments are closed.