Solved Consider The Truss Shown In Figure 1 Suppose That Chegg
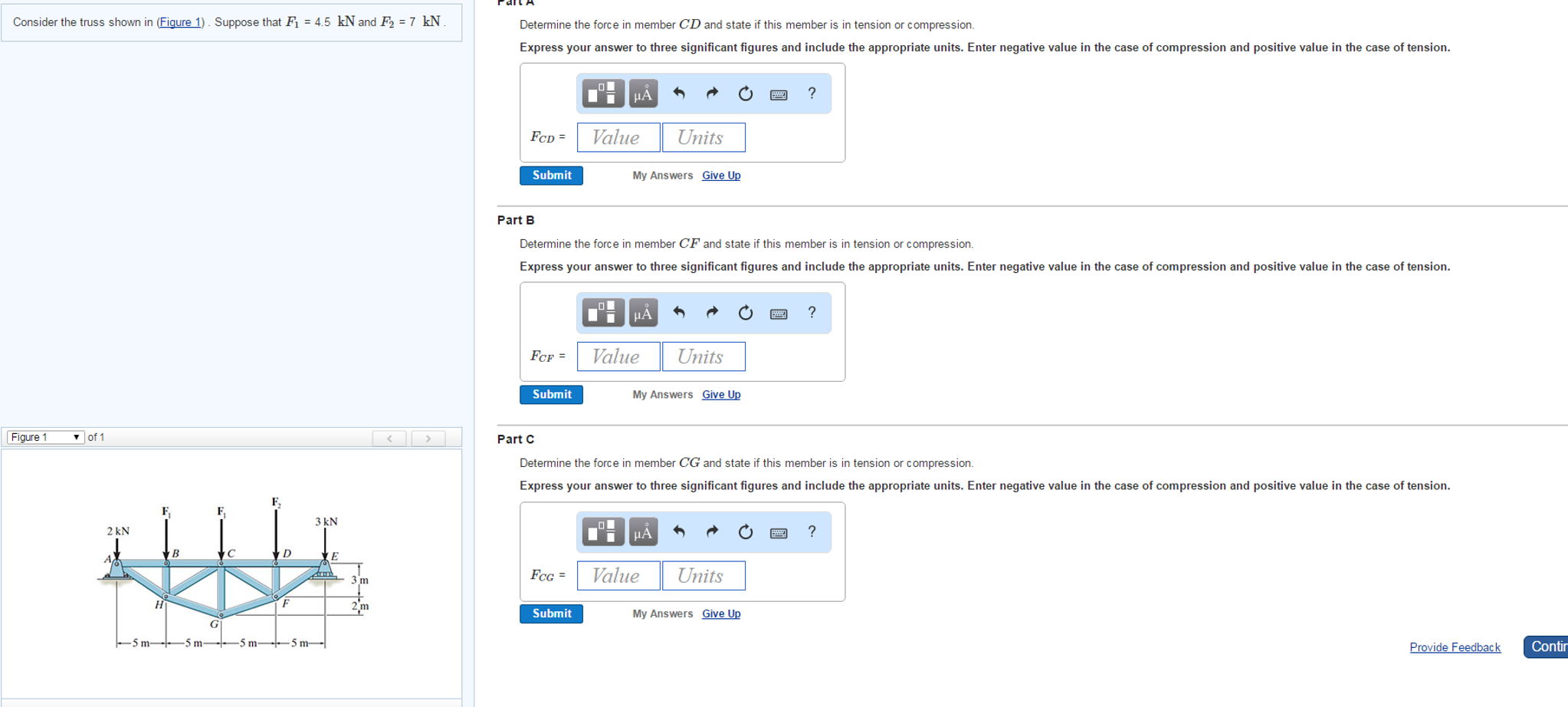
Solved Consider The Truss Shown In Figure 1 Suppose That Chegg Figure 1 of 1 part a determine the force in member ed of the truss, and state if the member is in tension or compression. express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. To determine the force in member cd, we can use the method of joints. first, we need to find the external reactions at a and e. then, we can solve for the internal forces in the truss members. the external reactions at a and e can be calculated using the equations of equilibrium.
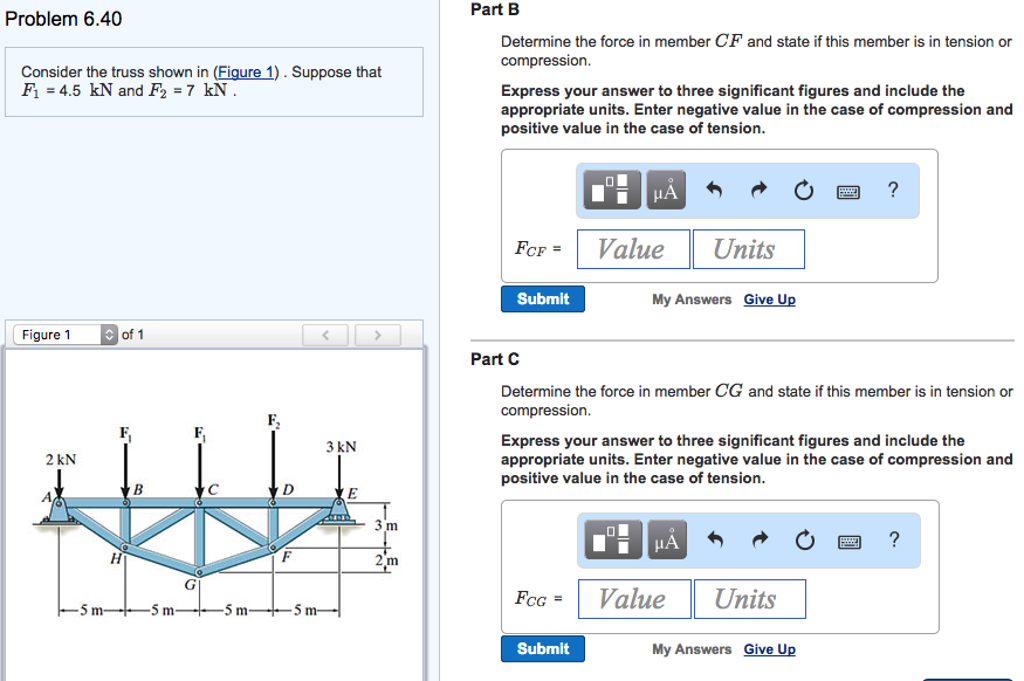
Solved Consider The Truss Shown In Figure 1 Suppose That Chegg To solve this problem, we need to analyze the truss under the given distributed loads w1 and w2. the truss has two segments, ab and bc, and we need to determine the reactions at a and c. Notice that there is only one horizontal force acting on the truss, thus, the support reaction at the pin a will counteract this force in the opposite direction. Method of sections: cut the truss into sections, and analyze the equilibrium of forces and moments acting on each section. this method is useful when you need to find the forces in specific members without analyzing the entire truss. Truss analysis is a structural analysis method used to determine the forces in the members of a truss structure. it involves applying equilibrium equations to solve for unknown forces.
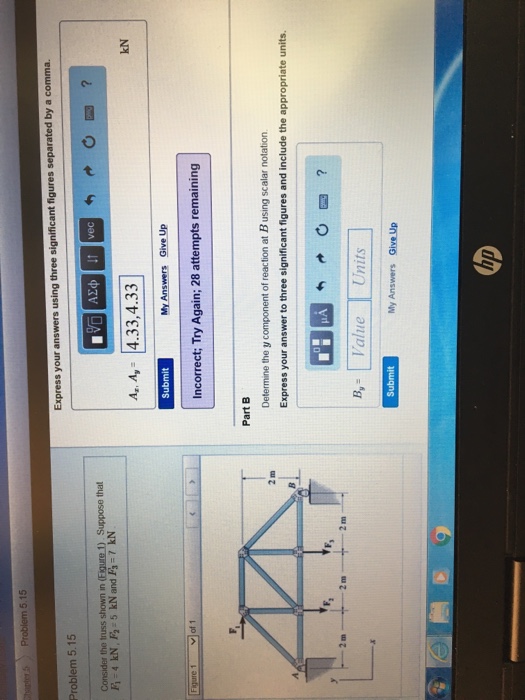
Solved Consider The Truss Shown In Figure 1 Suppose That Chegg Method of sections: cut the truss into sections, and analyze the equilibrium of forces and moments acting on each section. this method is useful when you need to find the forces in specific members without analyzing the entire truss. Truss analysis is a structural analysis method used to determine the forces in the members of a truss structure. it involves applying equilibrium equations to solve for unknown forces. For the truss shown in figure 1, calculate the normal stresses in member ac and member bd. the cross sectional area of each member is 900mm². figure 2 shows a two member truss supporting a block of weight w. the cross sections of the members are 800mm² and 400mm² for ac. Consider the truss shown in (figure 1). suppose that f =12kn .determine the force in member ch of the truss and state if the member is in tension or compression. determine the force in member gh of the truss and state if the member is in tension or compression. determine the force in member cg. Determine the force in the member \ ( b d \) of the truss. express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. enter a negative value in the case of compression and a positive value in the case of tension. If a force of f = 80 n acts at its end as shown, determine the moment of this force about point b. 3 m 1 m 2 m x c a y z 3 m o f ⫽ 80 n b 45⬚ probs. 4–36 37 4–38. force f acts perpendicular to the inclined plane. determine the moment produced by f about point a. express the result as a cartesian vector. 4–39.
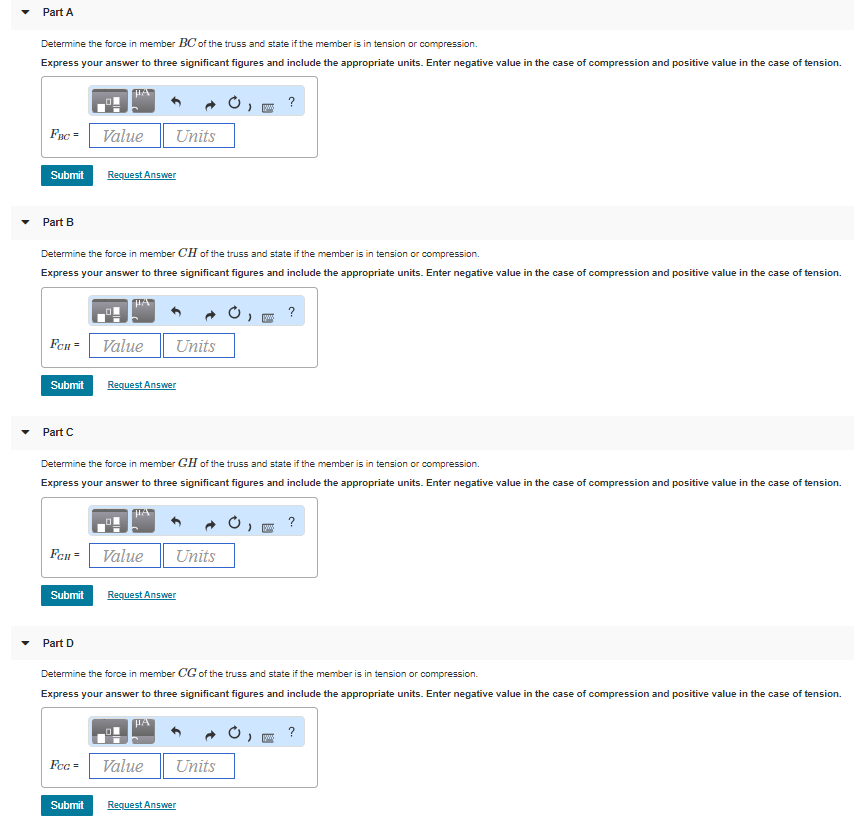
Solved Consider The Truss Shown In Figure 1 Suppose That Chegg For the truss shown in figure 1, calculate the normal stresses in member ac and member bd. the cross sectional area of each member is 900mm². figure 2 shows a two member truss supporting a block of weight w. the cross sections of the members are 800mm² and 400mm² for ac. Consider the truss shown in (figure 1). suppose that f =12kn .determine the force in member ch of the truss and state if the member is in tension or compression. determine the force in member gh of the truss and state if the member is in tension or compression. determine the force in member cg. Determine the force in the member \ ( b d \) of the truss. express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. enter a negative value in the case of compression and a positive value in the case of tension. If a force of f = 80 n acts at its end as shown, determine the moment of this force about point b. 3 m 1 m 2 m x c a y z 3 m o f ⫽ 80 n b 45⬚ probs. 4–36 37 4–38. force f acts perpendicular to the inclined plane. determine the moment produced by f about point a. express the result as a cartesian vector. 4–39.
Comments are closed.