Solved Determine If The Pairs Of Vectors Below Are Chegg

Solved 1 Determine Which Of The Following Vectors Is Chegg Determine if the pairs of vectors below are "parallel", "orthogonal", or "neither". a = ( 5, 2, 1) and b : (10, 4,58) are = a = ( 5,2, 1) and b = (10, 4, 2) are a = ( 5, 2, 1) and b = ( 25, 10, 6) are. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. To determine if the pairs of vectors are "parallel," "orthogonal," or "neither," we need to look at the relationships between them based on their components. let's analyze each pair step by step: check for parallelism: two vectors are parallel if their corresponding components are proportional.

Solved For Each Of The Following Pairs Of Vectors Determine Chegg In the context of the provided exercise, the dot product is used to determine if pairs of vectors are orthogonal. for example, when the dot product of vectors a and b was calculated and found to be zero, it was concluded that the vectors are orthogonal—as seen with the first pair in the exercise. For two vectors to be parallel, their direction must be the same or opposite, which means one is a scalar multiple of the other. two vectors are orthogonal if their dot product is zero. The dot product of two vectors is the sum of the products of the their components. Examples for section 4.5 whether the vectors (5, −2, 4), (2, − , 5), and ( 7) are linearly independent or dependent. −1, 9), ~v = (−2, −2, 1, 3) are linearly independent. if possible, expre s ~w = (4, 1, −2, 0), ~w = (0, −1, 1, 1) are linearly independent. if possible, express ~z = (2, −3, 2.
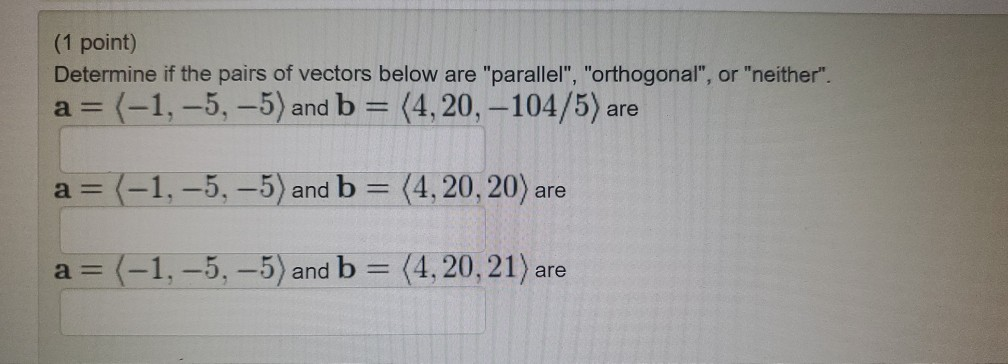
Solved Determine If The Pairs Of Vectors Below Are Chegg The dot product of two vectors is the sum of the products of the their components. Examples for section 4.5 whether the vectors (5, −2, 4), (2, − , 5), and ( 7) are linearly independent or dependent. −1, 9), ~v = (−2, −2, 1, 3) are linearly independent. if possible, expre s ~w = (4, 1, −2, 0), ~w = (0, −1, 1, 1) are linearly independent. if possible, express ~z = (2, −3, 2. Use the pythagorean theorem to determine the value of the resultant vr for the two vectors shown. round your final answer to the nearest whole number. 2x1 −4x2 5x3 = 8 −7x1 14x2 4x3 = −28 3x1 −6x3 x3 = 12 determine, if this system is consistent.if yes, write the solution in the form x = xh xp where xh is a solution of the corresponding homoge neous system ax = 0 and xp is a particular solution. To show how to add forces and resolve them into components using the parallelogram law. to express force and position in cartesian vector form and explain how to determine the vector’s magnitude and direction. to introduce the dot product in order to determine the angle between two vectors or the projection of one vector onto another. Sketch the pair of vectors and determine whether they are equivalent. use the following ordered pairs for the initial and terminal points. $$\begin {a… transcript.

Solved Consider The Vectors Which Pairs If Any Of These Chegg Use the pythagorean theorem to determine the value of the resultant vr for the two vectors shown. round your final answer to the nearest whole number. 2x1 −4x2 5x3 = 8 −7x1 14x2 4x3 = −28 3x1 −6x3 x3 = 12 determine, if this system is consistent.if yes, write the solution in the form x = xh xp where xh is a solution of the corresponding homoge neous system ax = 0 and xp is a particular solution. To show how to add forces and resolve them into components using the parallelogram law. to express force and position in cartesian vector form and explain how to determine the vector’s magnitude and direction. to introduce the dot product in order to determine the angle between two vectors or the projection of one vector onto another. Sketch the pair of vectors and determine whether they are equivalent. use the following ordered pairs for the initial and terminal points. $$\begin {a… transcript.

C 4 For Each Of The Following Pairs Of Vectors Chegg To show how to add forces and resolve them into components using the parallelogram law. to express force and position in cartesian vector form and explain how to determine the vector’s magnitude and direction. to introduce the dot product in order to determine the angle between two vectors or the projection of one vector onto another. Sketch the pair of vectors and determine whether they are equivalent. use the following ordered pairs for the initial and terminal points. $$\begin {a… transcript.

Solved 4 Determine Whether The Following Pairs Of Vectors Chegg
Comments are closed.