Solved Exercise 2 Let V Be A Vector Space And Let S Be A Chegg
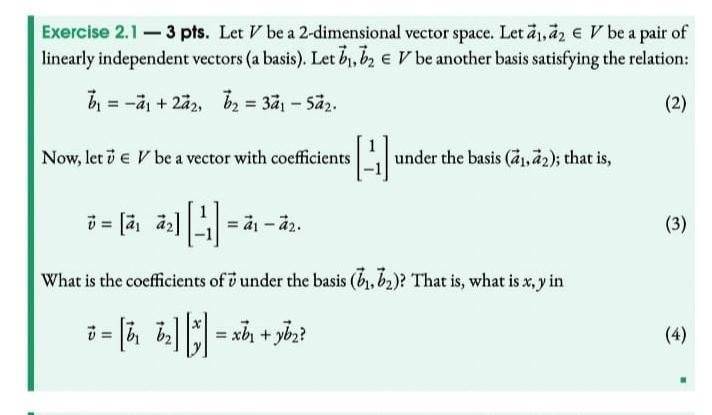
Solved Exercise 2 1 3 Pts Let V Be A 2 Dimensional Vector Chegg Question: exercise 2 let v be a vector space and let s be a subset of v. determine for the following choices, whether s is a subspace or not. explain your answer. If one is given a vector space and a basis, any problem that is posed about the space can be quickly solved using the basis. a basis for a vector space is so important that the reader has certainly already encountered and used them in their math.
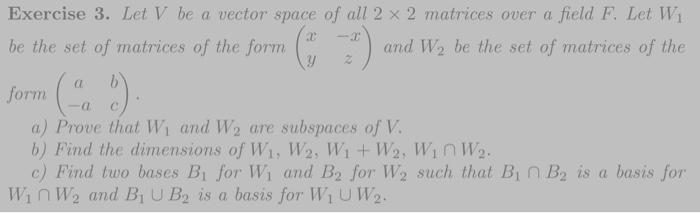
Solved Exercise 3 Let V Be A Vector Space Of All 2 2 Chegg The definition of vector spaces in linear algebra is presented along with examples and their detailed solutions. (5.3) v1 v2 () v1 v2 2 s is an equivalence relation and that the set of equivalence classes, denoted usually v=s; is a vector space in a natural way. problem 5.4. in case you do not know it, go through the basic theory of nite dimensional vector spaces. Determine whether the given set is a vector space. if not, give at least one axiom that is not satisfied. unless otherwise stated, assume that vector addition and scalar multiplication are the ordinary operations defined on the set. answer: this is not a vector space. 1.11. show that the set 4 −2 2 −2 1 −1 , 2 1 0 2 , −1 1 = t is linearly independent and use the method in the proof of corollary 1.25 to extend it to a basis of r4. date: september 30, 2009.

Solved Exercise 4 2 12 Let V Be A Vector Space Over Field F Chegg Determine whether the given set is a vector space. if not, give at least one axiom that is not satisfied. unless otherwise stated, assume that vector addition and scalar multiplication are the ordinary operations defined on the set. answer: this is not a vector space. 1.11. show that the set 4 −2 2 −2 1 −1 , 2 1 0 2 , −1 1 = t is linearly independent and use the method in the proof of corollary 1.25 to extend it to a basis of r4. date: september 30, 2009. Remark. the theorem 4.5.8 means that, if dimension of v matches with the number of (i.e. ’cardinality’ of) s, then to check if s is a basis of v or not, you have check only one of the two required prperties (1) indpendece or (2) spannning. You'll need to complete a few actions and gain 15 reputation points before being able to upvote. upvoting indicates when questions and answers are useful. what's reputation and how do i get it? instead, you can save this post to reference later. The solution set s of the differential equation y00 = −y, that is the set of all real functions f(x) such that f00(x) = −f(x), is a like a vector space. if f and g are both in s and r ∈ r then the reader should be able to check that f(x) g(x) and rf(x) are also in s. Question: exercise 2 (20 points). let v be a vector space and si and s2 be subspaces of vector space v. show the following 1. intersection of sı and s2 is a subspace. 2. union of si and s2 is in general not a subspace. 3. bonus 10 points: space formed by sum of vectors from si and s2 is a subspace.

Solved Let V Be A Vector Space And Let W1 And W2 Be Two Chegg Remark. the theorem 4.5.8 means that, if dimension of v matches with the number of (i.e. ’cardinality’ of) s, then to check if s is a basis of v or not, you have check only one of the two required prperties (1) indpendece or (2) spannning. You'll need to complete a few actions and gain 15 reputation points before being able to upvote. upvoting indicates when questions and answers are useful. what's reputation and how do i get it? instead, you can save this post to reference later. The solution set s of the differential equation y00 = −y, that is the set of all real functions f(x) such that f00(x) = −f(x), is a like a vector space. if f and g are both in s and r ∈ r then the reader should be able to check that f(x) g(x) and rf(x) are also in s. Question: exercise 2 (20 points). let v be a vector space and si and s2 be subspaces of vector space v. show the following 1. intersection of sı and s2 is a subspace. 2. union of si and s2 is in general not a subspace. 3. bonus 10 points: space formed by sum of vectors from si and s2 is a subspace.
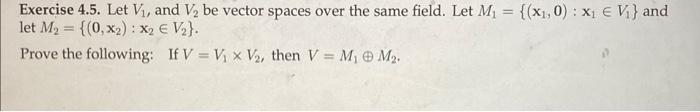
Solved Exercise 4 5 Let V1 And V2 Be Vector Spaces Over Chegg The solution set s of the differential equation y00 = −y, that is the set of all real functions f(x) such that f00(x) = −f(x), is a like a vector space. if f and g are both in s and r ∈ r then the reader should be able to check that f(x) g(x) and rf(x) are also in s. Question: exercise 2 (20 points). let v be a vector space and si and s2 be subspaces of vector space v. show the following 1. intersection of sı and s2 is a subspace. 2. union of si and s2 is in general not a subspace. 3. bonus 10 points: space formed by sum of vectors from si and s2 is a subspace.
Comments are closed.