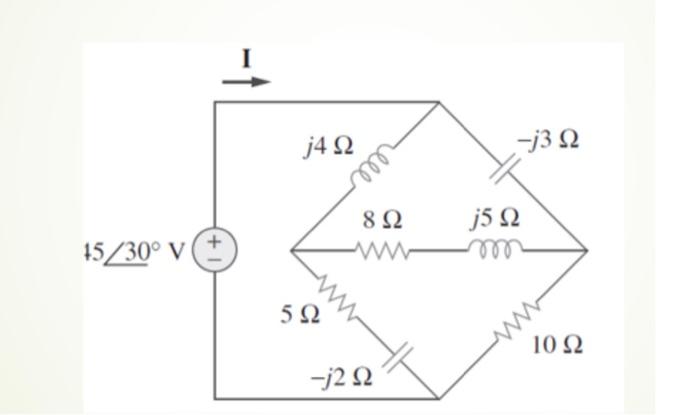
Solved Find Current I In The Following Circuit Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. here’s the best way to solve it. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. there are 3 steps to solve this one. to find thevenin resistance, the current source is open circuited and the voltage source is short ci not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly.
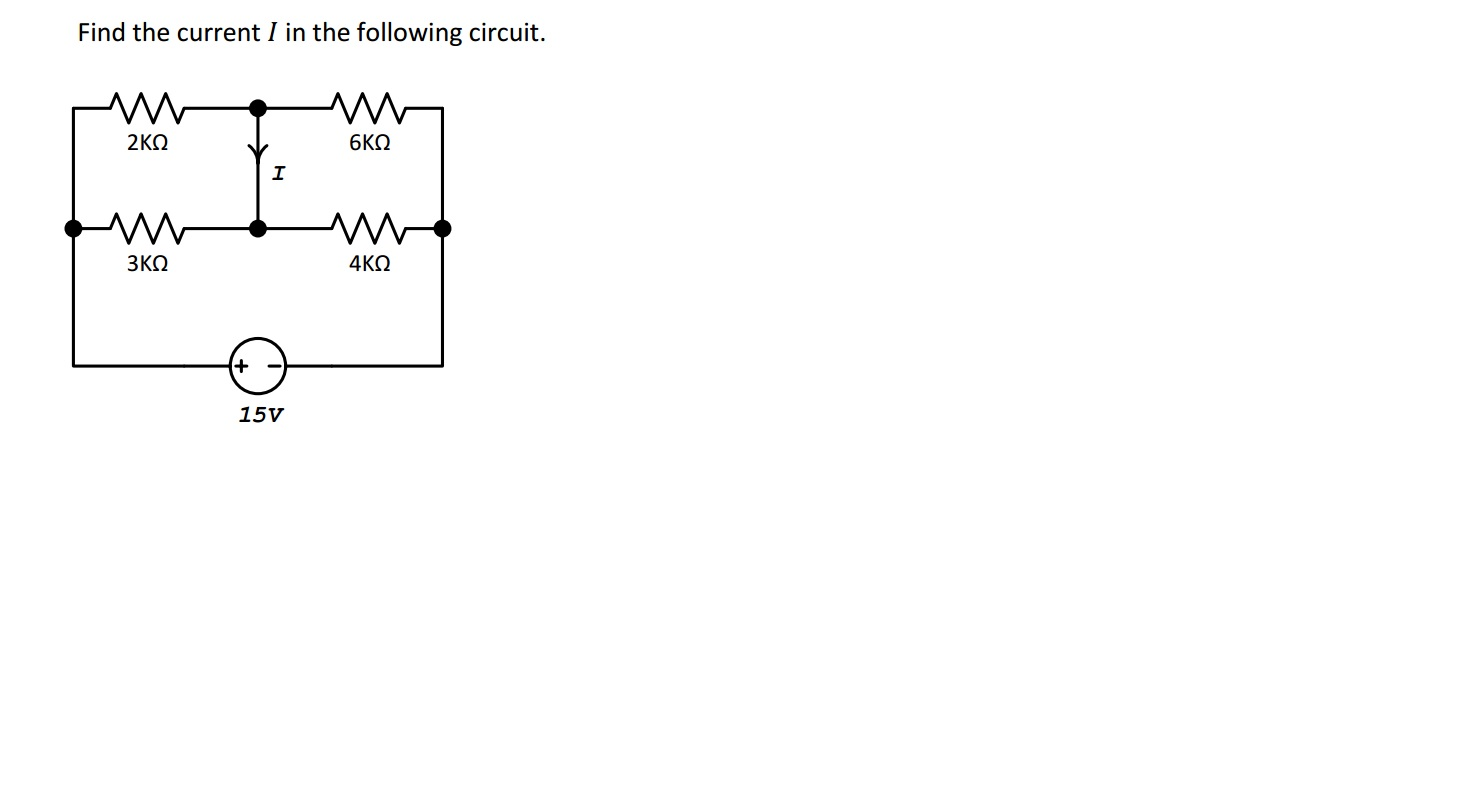
Solved Find The Current I In The Following Circuit Chegg Find the current i in the following circuit. hint: we need to understand the circuital laws which govern the electrical circuits in order to find the current through the arm indicated in a circuit. the current through the circuit is dependent on the kirchhoff’s laws and the type of combination of resistors. Consider a circuit with resistors r1 = 1 Ω and r2 = 9 Ω are connected parallelly with a battery. if the current through the resistor r2 is 2.5 a find the current through resistor one. Calculate current i in the following circuit using superposition theorem. superposition theorem is used to solve a circuit that contains multiple current and or voltage sources acting together. Find the current i in the following circuit. according to kirchhoff’s voltage law (kvl), the algebraic sum of voltage in a closed loop is zero. it is also known as the loop current method of analysis. last updated on apr 14, 2025. > the pgcil diploma trainee answer key 2025 has been released on 12th april.
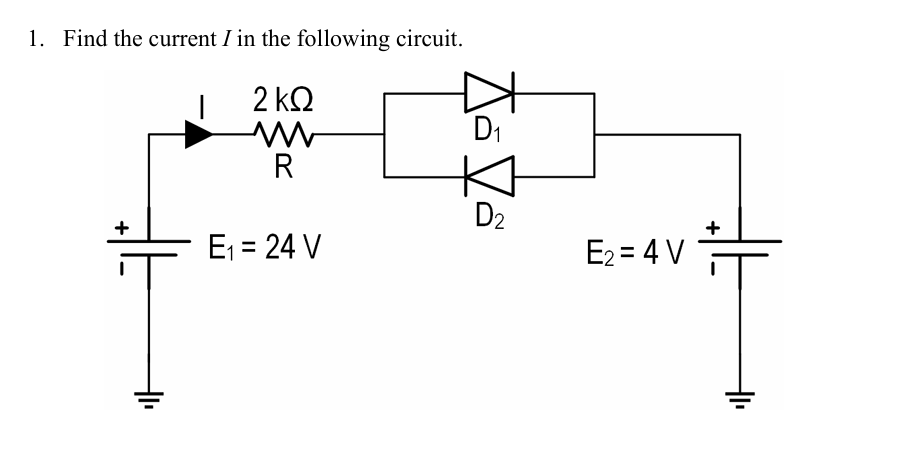
Solved Find The Current I In The Following Circuit Chegg Calculate current i in the following circuit using superposition theorem. superposition theorem is used to solve a circuit that contains multiple current and or voltage sources acting together. Find the current i in the following circuit. according to kirchhoff’s voltage law (kvl), the algebraic sum of voltage in a closed loop is zero. it is also known as the loop current method of analysis. last updated on apr 14, 2025. > the pgcil diploma trainee answer key 2025 has been released on 12th april. Here’s the best way to solve it. a) for the circuit: i) the current in resistor r is $$i = \frac {28\text { v}. Use mesh analysis to find the current i 0 in the circuit of fig. 15. (ml) fig.15. for prob. 15. solution: for loop 1, 16i 1 – 10i 2 – 2i 3 = 0 which leads to 8i 1 – 5i 2 – i 3 = 0 (1) for the. All elements are in parallel, so we can redraw circuit to get one current source and two resistors in parallel. one resistor is the 3 Ω so we can find the current in it. the other is the effective resistance of the other resistors added in parallel. the effective current source is 2 a 1.5 a – 0.5 a since the 2 and 1.5 a sources go to the left. Then you must have covered some other method(s). how about current dividers? kvl around a loop? or, if you answered part (b) first and found the voltage ##v o##, could you then find the currents?.
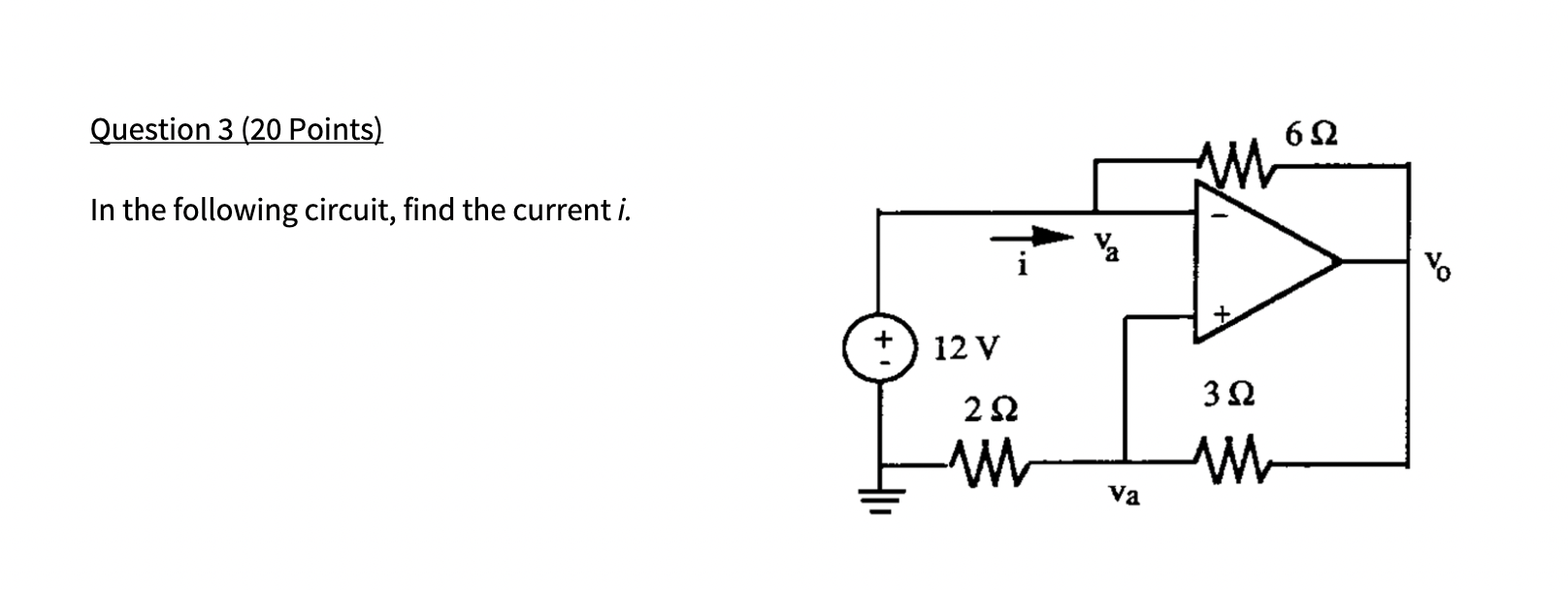
Solved In The Following Circuit Find The Current I Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. a) for the circuit: i) the current in resistor r is $$i = \frac {28\text { v}. Use mesh analysis to find the current i 0 in the circuit of fig. 15. (ml) fig.15. for prob. 15. solution: for loop 1, 16i 1 – 10i 2 – 2i 3 = 0 which leads to 8i 1 – 5i 2 – i 3 = 0 (1) for the. All elements are in parallel, so we can redraw circuit to get one current source and two resistors in parallel. one resistor is the 3 Ω so we can find the current in it. the other is the effective resistance of the other resistors added in parallel. the effective current source is 2 a 1.5 a – 0.5 a since the 2 and 1.5 a sources go to the left. Then you must have covered some other method(s). how about current dividers? kvl around a loop? or, if you answered part (b) first and found the voltage ##v o##, could you then find the currents?.

Solved Q2 Find The Current I In The Following Circuit Chegg All elements are in parallel, so we can redraw circuit to get one current source and two resistors in parallel. one resistor is the 3 Ω so we can find the current in it. the other is the effective resistance of the other resistors added in parallel. the effective current source is 2 a 1.5 a – 0.5 a since the 2 and 1.5 a sources go to the left. Then you must have covered some other method(s). how about current dividers? kvl around a loop? or, if you answered part (b) first and found the voltage ##v o##, could you then find the currents?.
