Solved Given The Matrix I A 1 2 1 0 2 1 1 1 2 Chegg
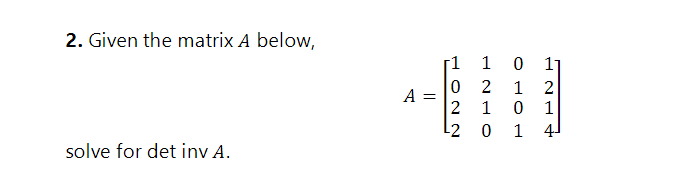
Solved 2 Given The Matrix A Below а 1 1 0 2 2 1 2 0 0 1 Chegg We can start solving this question by first performing row operations on the given matrix a, for example, you could subtract 2 times the first row from the second row. Solution: since square a matrix is invertible if and only if elimination yields the same number of pivots as rows, we just need to do elimination on a and b and see what conditions on their entries ensure that we get a pivot in every row.

Solved Given The Matrix 1 0 1 A 0 2 1 2 2 4 I Apply Chegg To invert a 3 by 3 matrix a, we have to solve three systems of equations: ax1 = e1 and ax2 = e2 = (0, 1, 0) and ax3 = e3 = (0, 0, 1). gauss jordan finds a−1 this way. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 1. let a = 1 −1 2 0 1 −3 . find a vector x in n (a) and verify that it is orthogonal to the rows of a. 2. let a 1 = 1 0 1 , a2 = 1 2 −1 . find a unit vector ˆx that is orthogonal to both a 1 and a 2 . 3. Using the square matrices in problem a.8, and the column matrices a = (i 2i 2), b = (2 (1 i) 0). find: (a) aa, (b) your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. By the way, you should remove the subscript of 3 3 from the identity matrix since that was an error in the original question (it's meaningless if you think about it).
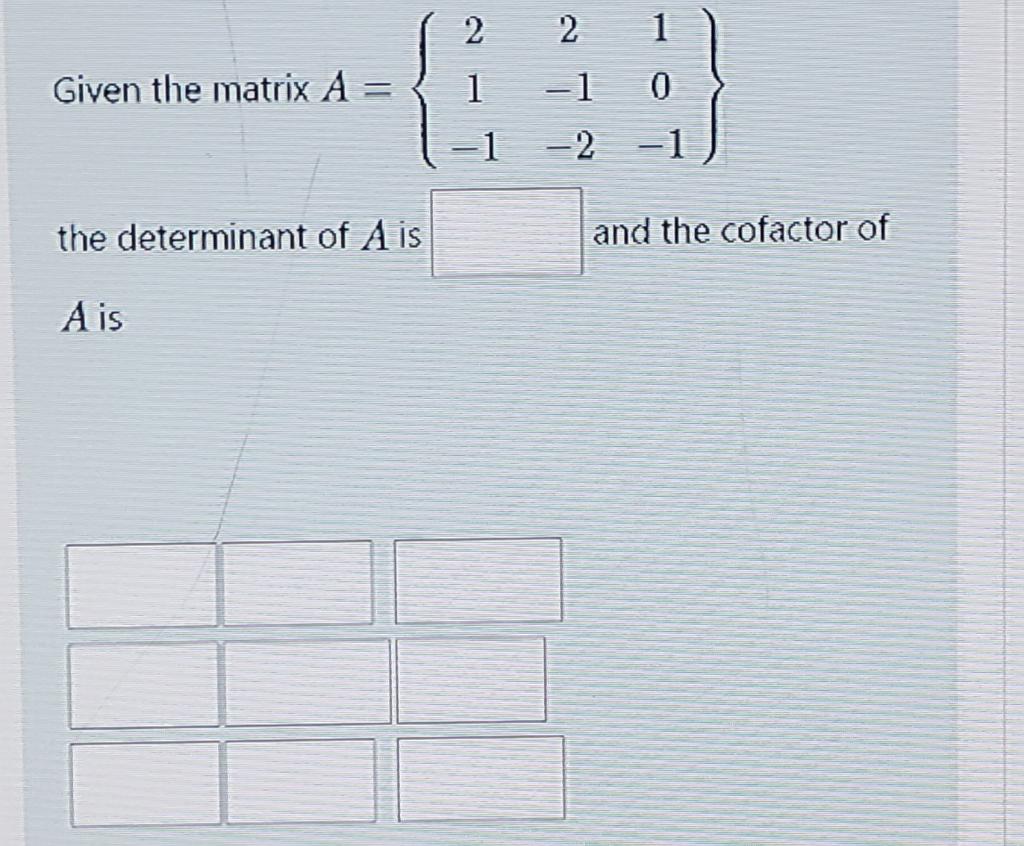
Solved 2 2 1 Given The Matrix A 1 1 0 2 2 1 The Chegg Using the square matrices in problem a.8, and the column matrices a = (i 2i 2), b = (2 (1 i) 0). find: (a) aa, (b) your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. By the way, you should remove the subscript of 3 3 from the identity matrix since that was an error in the original question (it's meaningless if you think about it). A matrix calculator is designed to rapidly and precisely simplify difficult matrix operations, a matrix calculator is either online application. it eliminates mistakes, removes hand computations, and boosts mathematical problem solving efficiency. Since a−1 is the matrix of q−1 and a is the matrix of q, it follows that a−1 = a. of course this conclusion is clear by simply observing directly that a2 = i, but the geometric method can often work where these other methods may be less straightforward. To show that (i a) (i a)^ { 1} is a unitary matrix, we confirm that a is invertible and then find the inverse of a. afterward, we show that this expression multiplied by its conjugate transpose equals the identity matrix, satisfying the condition of a unitary matrix. Free calculator to perform matrix operations on one or two matrices, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, determinant, inverse, or transpose.

Solved 2 2 1 Given The Matrix A 1 1 0 2 2 1 The Chegg A matrix calculator is designed to rapidly and precisely simplify difficult matrix operations, a matrix calculator is either online application. it eliminates mistakes, removes hand computations, and boosts mathematical problem solving efficiency. Since a−1 is the matrix of q−1 and a is the matrix of q, it follows that a−1 = a. of course this conclusion is clear by simply observing directly that a2 = i, but the geometric method can often work where these other methods may be less straightforward. To show that (i a) (i a)^ { 1} is a unitary matrix, we confirm that a is invertible and then find the inverse of a. afterward, we show that this expression multiplied by its conjugate transpose equals the identity matrix, satisfying the condition of a unitary matrix. Free calculator to perform matrix operations on one or two matrices, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, determinant, inverse, or transpose.

Solved Given Matrix A 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 4 And Matrix Chegg To show that (i a) (i a)^ { 1} is a unitary matrix, we confirm that a is invertible and then find the inverse of a. afterward, we show that this expression multiplied by its conjugate transpose equals the identity matrix, satisfying the condition of a unitary matrix. Free calculator to perform matrix operations on one or two matrices, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, determinant, inverse, or transpose.
Comments are closed.