Solved If Det A B C 1 1 1 D E F 5 And Det A Chegg
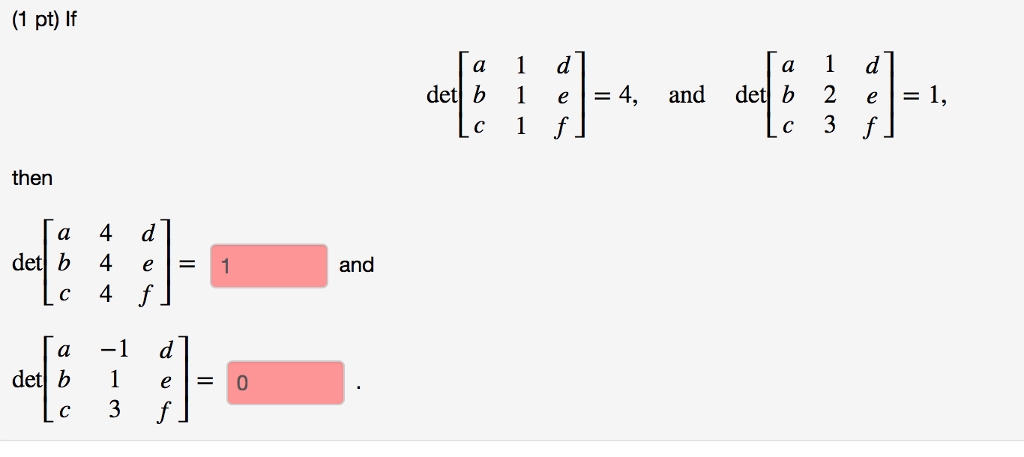
Solved If Det A B C 1 1 1 D E F 4 And Det A B C 1 2 Chegg To start solving the problem, first recognize the procedure when one column of a determinant is multiplied by a scalar, such as the factor of 7 multiplying the second column in the given determinant . let's denot if det [a b c 1 1 1 d e f] = 5 and det [a b c 1 2 3 d e f] = 2, then det [a b c 7 7 7 d e f] = and det [a b c 1 0 1 d e f] = . Given det⎡⎣⎢abc111def⎤⎦⎥=−5, it can be inferred that the middle row is multiplied by '1'. therefore, when it is multiplied by '2' to get det⎡⎣⎢abc222def⎤⎦⎥, the determinant value according to the rule will be 5 * 2 = 10.
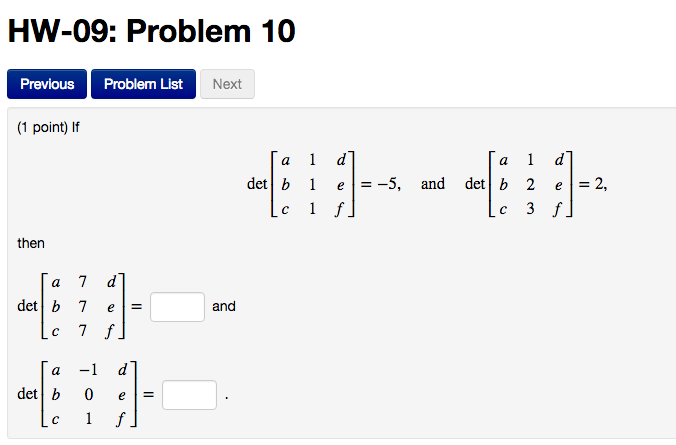
Solved If Det A B C 1 1 1 D E F 5 And Det A Chegg We have that $ ( 5, 7, 9) = 3 (1, 1, 1) 2 (1, 2, 3)$ and so our determinant is $ 3\cdot ( 2) 2\cdot ( 1) = 8$. you must log in to answer this question. find the answer to your question by asking. see similar questions with these tags. Wolfram|alpha is the perfect resource to use for computing determinants of matrices. it can also calculate matrix products, rank, nullity, row reduction, diagonalization, eigenvalues, eigenvectors and much more. use plain english or common mathematical syntax to enter your queries. For large matrices, the determinant can be calculated using a method called expansion by minors. this involves expanding the determinant along one of the rows or columns and using the determinants of smaller matrices to find the determinant of the original matrix. We want to find the determinant of matrix c: c = a −4 d b −6 e c −8 f. we can use the **properties **of determinants to find det (c) by subtracting a multiple of the second row of b from the third row of a to get c: c = a − 3b. now, let's compute det (c): det(c) = det(a − 3b).
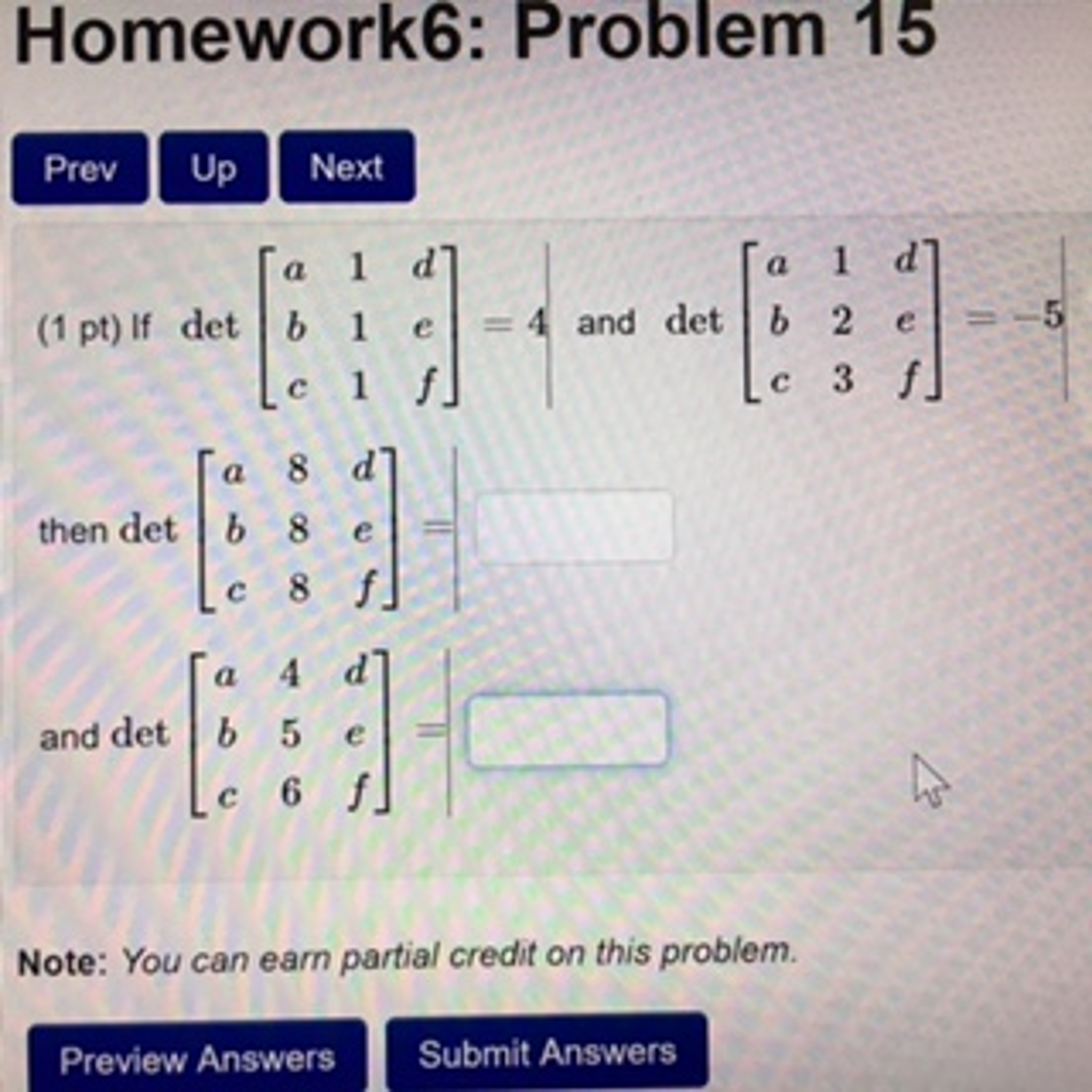
Solved It Det A B C 1 1 1 D E F 4 And Det A B Chegg For large matrices, the determinant can be calculated using a method called expansion by minors. this involves expanding the determinant along one of the rows or columns and using the determinants of smaller matrices to find the determinant of the original matrix. We want to find the determinant of matrix c: c = a −4 d b −6 e c −8 f. we can use the **properties **of determinants to find det (c) by subtracting a multiple of the second row of b from the third row of a to get c: c = a − 3b. now, let's compute det (c): det(c) = det(a − 3b). Det⎣⎡abc111def⎦⎤=5, and det⎣⎡abc123def⎦⎤=−2, then det⎣⎡abc444def⎦⎤=∣ and det⎣⎡abc234def⎦⎤= hint: transposing a matrix has no effect on its determinant. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. These are easily verified directly: write a = a b d , b = ( r s ), etc. the third property benefits from a little expansion: writing a matrix in terms of its columns, determinant can be thought of as a function. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. det⎡⎣⎢abc468def⎤⎦⎥=det [ 4 6 8 ]= . there’s just one step to solve this. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. If det [a 1 d b 1 e c 1 f]=5, and det [a 1 d b 2 e c 3 f]=4,then det [a 8 d b 8 e c 8 f]= and det [a 1 d b −1 e c −3 f]= . your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.

Solved Show That Det 1 1 1 1 A B C D A 2 B 2 C 2 D 2 Chegg Det⎣⎡abc111def⎦⎤=5, and det⎣⎡abc123def⎦⎤=−2, then det⎣⎡abc444def⎦⎤=∣ and det⎣⎡abc234def⎦⎤= hint: transposing a matrix has no effect on its determinant. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. These are easily verified directly: write a = a b d , b = ( r s ), etc. the third property benefits from a little expansion: writing a matrix in terms of its columns, determinant can be thought of as a function. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. det⎡⎣⎢abc468def⎤⎦⎥=det [ 4 6 8 ]= . there’s just one step to solve this. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. If det [a 1 d b 1 e c 1 f]=5, and det [a 1 d b 2 e c 3 f]=4,then det [a 8 d b 8 e c 8 f]= and det [a 1 d b −1 e c −3 f]= . your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.
Comments are closed.