
Solved Let A 1 3 5 7 9 B 0 3 6 9 12 Find An B Chegg Let a = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}, b = {3, 6, 9}, and c = {2, 4, 6, 8}. find each of the following. (enter your answer in set roster notation. enter empty or ∅ for the empty set.) (a) a ∪ b (b) a ∩ b (c) a ∪ c (d) a ∩ c (e) a − b (f) b − a (g) b ∪. To find the set a u b, we need to combine the elements of sets a and b. the union of two sets is the set of all elements that are in either set. in this case, a = {1,3,5,7,9} and b = {3,6,9}. combining these sets, we get a u b = {1,3,5,6,7,9}.
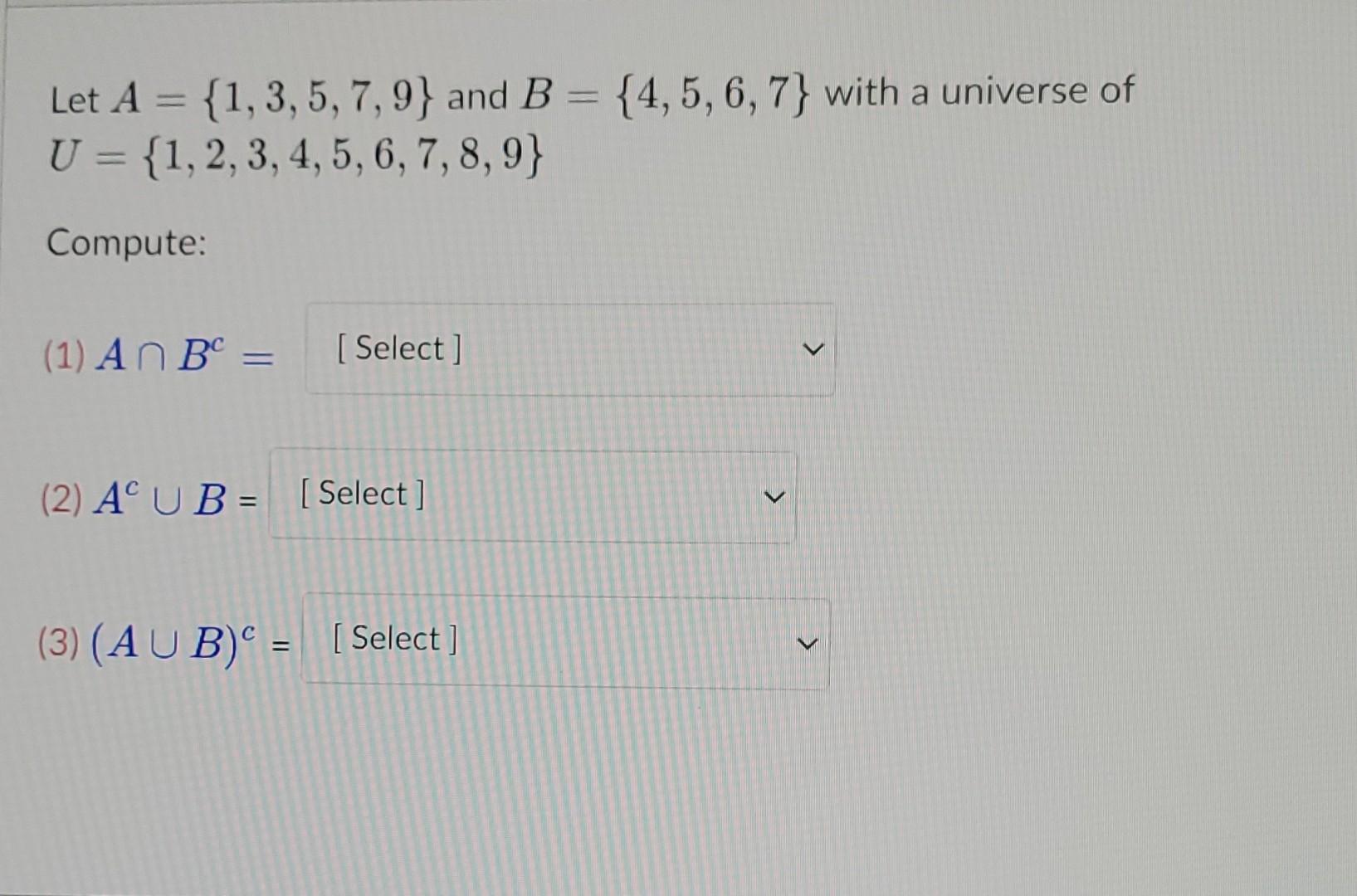
Solved Let A 1 3 5 7 9 And B 4 5 6 7 With A Universe Of Chegg The union of sets a and b, denoted as a ∪ b, includes all distinct elements from both sets. therefore, a ∪ b = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}. no elements were duplicated in this union. First use the extended euclidean algorithm to find the greatest common divisor of 660 and 73 and express it as a linear combination of 660 and 73. 0 ≤ r 1 < 73. r 1 = 660 − 73 · q 1 = . 0 ≤ r 2 < r 1. · q 2 = . 0 ≤ r 3 < r 2. · q 3 = . step 4: select the correct statement from the options below. because r 3 = 1, gcd (660, 73) = r 1 − r 2 · q 3 = 0. Here’s the best way to solve it. let a = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}, b = {4, 5, 6, 7}, c = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}, d = {1, 2, 3} and let the universal set be u = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}. what are: |a| a intersection b (a union b) c (b intersection a) union (b intersection c) p (d) d times (b intersection c) |p (a)|. not the question you’re looking for?. A b = {1, 5, 7} b a = {6} b u c = {2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9 } b ∩ c = {6} the given values are. a = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9} b = {3, 6, 9} c = {2, 4, 6, 8} then find the each given terms in** set roaster notation** union of the set, intersection of the set and the difference of the set are the basic operations of set . a ∪ b = {1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9} a ∩ b.

Solved Let 4 1 3 5 6 7 And B 0 3 5 6 9 11 Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. let a = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}, b = {4, 5, 6, 7}, c = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}, d = {1, 2, 3} and let the universal set be u = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}. what are: |a| a intersection b (a union b) c (b intersection a) union (b intersection c) p (d) d times (b intersection c) |p (a)|. not the question you’re looking for?. A b = {1, 5, 7} b a = {6} b u c = {2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9 } b ∩ c = {6} the given values are. a = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9} b = {3, 6, 9} c = {2, 4, 6, 8} then find the each given terms in** set roaster notation** union of the set, intersection of the set and the difference of the set are the basic operations of set . a ∪ b = {1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9} a ∩ b. $a = \{1,3,5,7,9\}; b = \{3,6,9\}$ $\cup = $ "union" means to the set that contains the combined elements of both sets. $a \cup b = \{1,3,5,6,7,9\}$ because 1,3,5,6,7,9 are all the elements in the two sets. Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of math problems, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and linear algebra. it shows you the solution, graph, detailed steps and explanations for each problem. Determine whether the sequence is arithmetic, geometric, or neither. let u= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}, a= {1, 3, 5, 7}, b= {1, 2, 3}, c= {2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. find each of the following sets. ′ a b′) solve the inequality and sketch the solution on the real number line. use a graphing utility to verify your solution graphically. x ≤ x. Question 14 options: a) a ∩ (b ∪ c) = {3,5,6,7,9} your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.
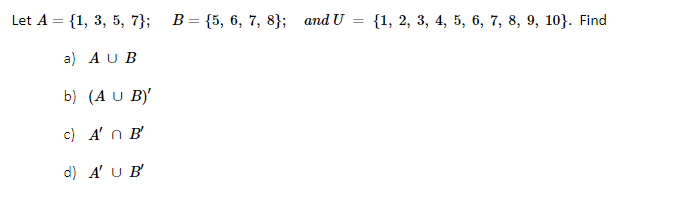
Solved Let A 1 3 5 7 B 5 6 7 8 And Chegg $a = \{1,3,5,7,9\}; b = \{3,6,9\}$ $\cup = $ "union" means to the set that contains the combined elements of both sets. $a \cup b = \{1,3,5,6,7,9\}$ because 1,3,5,6,7,9 are all the elements in the two sets. Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of math problems, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and linear algebra. it shows you the solution, graph, detailed steps and explanations for each problem. Determine whether the sequence is arithmetic, geometric, or neither. let u= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}, a= {1, 3, 5, 7}, b= {1, 2, 3}, c= {2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. find each of the following sets. ′ a b′) solve the inequality and sketch the solution on the real number line. use a graphing utility to verify your solution graphically. x ≤ x. Question 14 options: a) a ∩ (b ∪ c) = {3,5,6,7,9} your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.
