
Solved 4 Let R1 And R2 Be Relations On A Set A 1 2 3 4 Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. let r 1 = 1 ohm, r 2 = 4 ohm, r 3 = 1 ohm, and r 4 = 5 ohm. if i s = 6a, find the value of i 1. i 1 = a (within three significant digits) not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. answer to let r1=1?r1=1?, r2=4?r2=4?, r3=1?r3=1?, and. Definition: let a and b be sets. a binary relation from a to b is. example: let a={a,b,c} and b={1,2,3}. if a r b then draw an arrow from a to b. | u v or. | x. | 0. | 1 2 | x 0. a relation r is reflexive if and only if mr has 1 in every position on its main diagonal. r≠ on a={1,2,3,4}, such that a r≠ b if and only if a ≠ b.

Solved Let R Be The Relation On 1 2 3 4 Given By Chegg Let a = {1,2,3} b={w,x,y,z} c = {4,5,6} define the relations r1⊆ axb , r2 ⊆bxc and r3 ⊆bxc where, r1={(1,w) (3,w) (2,x)(1,y)} r2= {(w,5)(x,6)(y,4)(y,6)} problems: 2. for the relation r1 and r2 on set a to b and b to c. find m(r1) ,m(r2) and m(r1 ∘r2) and verify that m(r1 ∘r2) = m(r1) . m(r2) m(r1) . m(r2) = 0 0 0 0 0 0. There are 3 steps to solve this one. let r1 and r2 be relations on a set a represented by the matrices mr1 =⎣⎡ 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 ⎦⎤ and mr2 =⎣⎡ 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 ⎦⎤. find the matrices that represent a) r1∪ r2. b) r1∩r2. d) r1∘r1. e) r1⊕r2. c) r2∘r1. 3. let r be the relation r ={ (a,b)∣a

Solved 6 Let A 1 2 3 4 And Let R 1 1 1 2 2 4 And Chegg To solve the problem, we will compute the union, intersection, and difference of the two given relations, . let's start by noting the two relations: a. union (: the union of two sets includes all elements that are in either set. therefore: b. intersection (: the intersection includes only the elements that are common to both sets:. Solution for problem 3.1 cs 5515, f all 1997 loop: lw r1, 0(r2) addi r1, r1, #1 sw r1, 0(r2) addi r2, r2, #4 sub r4, r3, r2 bnz r4, loop 3.1(a) assume that al l data hazar ds c ause a stal l in the pip eline, and that ther ear e no structur al hazar ds. however, assume that the r e gister le is written in the rst half of a clo ck cycle and a r. Part (a) i) draw the directed graphs for the relations r1,r2,r3,r4r 1, r 2, r 3, r 4. relation r1r 1: given r1={(1,1),(3,3),(2,2),(4,4)}r 1 = \{(1, 1), (3, 3), (2, 2), (4, 4)\}, the graph would have loops at each of the elements 1, 2, 3, and 4. these represent self loops, showing that each element is related to itself. relation r2r 2:. Let r1 and r2 be the “congruent modulo 3” and the “congruent modulo 4” relations, respectively, on the set of integers. that is, r1 = {(a, b)|a ≡ b (mod 3)} and r2 = {(a, b)|a ≡ b (mod 4)}. Definition: let r be a relation from a set a to a set b and s a relation from b to a set c. the composite of r and s is the relation consisting of the ordered pairs (a,c) where a ∈ a and c ∈ c, and for which there is a b ∈ b such that (a,b) ∈ r and (b,c) ∈ s. we denote the composite of r and s by s o r. let a = {1,2,3}, b = {0,1,2} and c = {a,b}. There are 2 steps to solve this one. 4) let r1 and r2 be relations on a set a = {1,2,3,4}. in particular, let r1 = { (1, 3), (1,4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 4), (3, 4), (4, 3) (4,4)} and r2 = { (1,2), (1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4), (4, 1)} determine the following: a) whether or not rį is reflexive, irreflexive, symmetric, anti symmetric and transitive or not.

Solved 1 Let A1 1 2 3 4 A2 4 5 6 And A3 6 7 8 Let Chegg Part (a) i) draw the directed graphs for the relations r1,r2,r3,r4r 1, r 2, r 3, r 4. relation r1r 1: given r1={(1,1),(3,3),(2,2),(4,4)}r 1 = \{(1, 1), (3, 3), (2, 2), (4, 4)\}, the graph would have loops at each of the elements 1, 2, 3, and 4. these represent self loops, showing that each element is related to itself. relation r2r 2:. Let r1 and r2 be the “congruent modulo 3” and the “congruent modulo 4” relations, respectively, on the set of integers. that is, r1 = {(a, b)|a ≡ b (mod 3)} and r2 = {(a, b)|a ≡ b (mod 4)}. Definition: let r be a relation from a set a to a set b and s a relation from b to a set c. the composite of r and s is the relation consisting of the ordered pairs (a,c) where a ∈ a and c ∈ c, and for which there is a b ∈ b such that (a,b) ∈ r and (b,c) ∈ s. we denote the composite of r and s by s o r. let a = {1,2,3}, b = {0,1,2} and c = {a,b}. There are 2 steps to solve this one. 4) let r1 and r2 be relations on a set a = {1,2,3,4}. in particular, let r1 = { (1, 3), (1,4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 4), (3, 4), (4, 3) (4,4)} and r2 = { (1,2), (1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4), (4, 1)} determine the following: a) whether or not rį is reflexive, irreflexive, symmetric, anti symmetric and transitive or not.
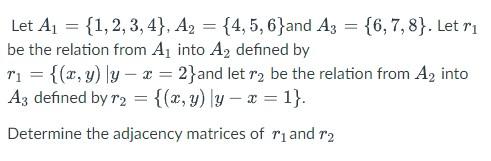
Solved Let A1 1 2 3 4 A2 4 5 6 And A3 6 7 8 Let R1 Be Chegg Definition: let r be a relation from a set a to a set b and s a relation from b to a set c. the composite of r and s is the relation consisting of the ordered pairs (a,c) where a ∈ a and c ∈ c, and for which there is a b ∈ b such that (a,b) ∈ r and (b,c) ∈ s. we denote the composite of r and s by s o r. let a = {1,2,3}, b = {0,1,2} and c = {a,b}. There are 2 steps to solve this one. 4) let r1 and r2 be relations on a set a = {1,2,3,4}. in particular, let r1 = { (1, 3), (1,4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 4), (3, 4), (4, 3) (4,4)} and r2 = { (1,2), (1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4), (4, 1)} determine the following: a) whether or not rį is reflexive, irreflexive, symmetric, anti symmetric and transitive or not.
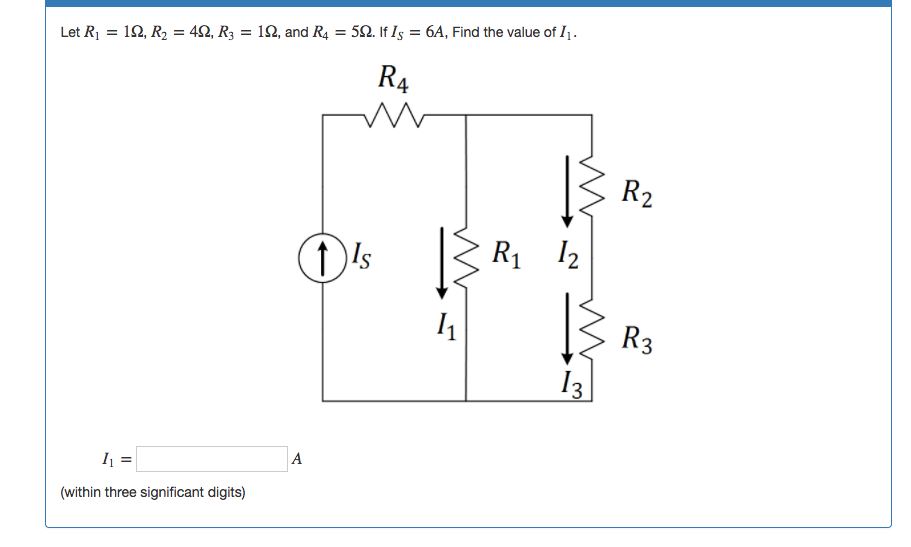
Solved Let R1 1 R1 1 R2 4 R2 4 R3 1 R3 1 And Chegg
