
Solved Let U 3 2 3 And A 2 3 3 Find The Vector Chegg Let u = (3, 2, 3) and a = (2, 3, − 3). find the vector component of u orthogonal to a. enter your answer symbolically, as in these enter your answer in the form a, b, c examples. Free online vector calculator solve vector operations and functions step by step.
Solved Let U 3 2 3 V 1 1 3 A Find U B Chegg If $\bar{u} = (3,3, 1)$ and $\bar{a} =( 3,3, 2)$ find the vector component of $\bar{u}$ orthogonal to $\bar{a}$ ok, so pretty straight forward i found the projection $\bar{u}\cdot$ $\bar{a}$. Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step by step explanations. You can add, subtract, find length, find vector projections, and find the dot and cross product of two vectors. for each operation, the calculator writes a step by step, easy to understand explanation of how the work has been done. Given a unit vector u u, is it possible to find a vector v v such that u ⋅ v = −3 u ⋅ v = − 3 and ∥v∥ = 2 ‖ v ‖ = 2? give an example or explain why this can't be done. hint: |u ⋅ v| ≤ ∥u∥∥v∥ | u ⋅ v | ≤ ‖ u ‖ ‖ v ‖ by the cauchy schwarz inequality.
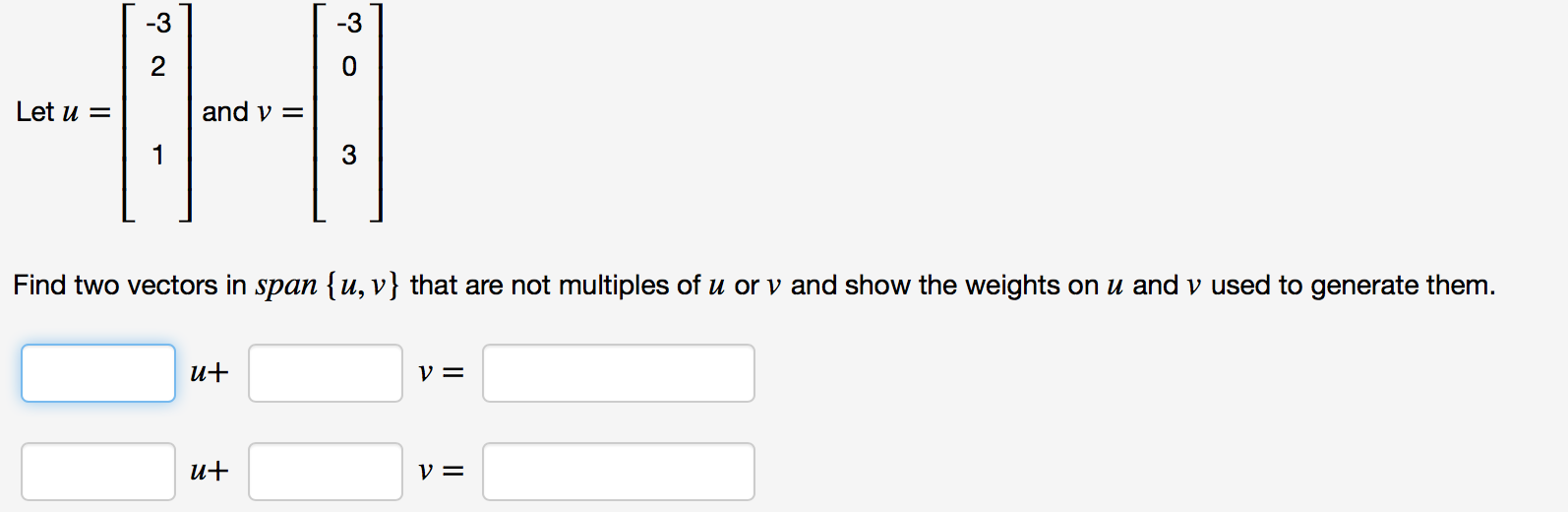
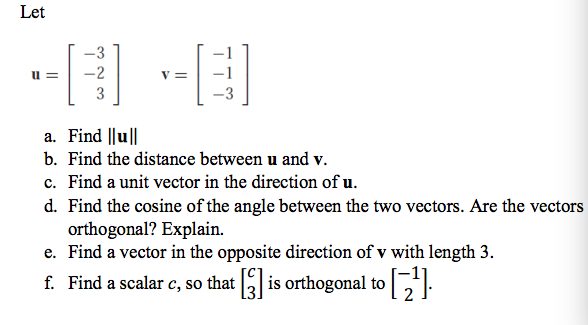
Solved Let U 3 2 1 And V 3 0 3 Find Two Vectors Chegg You can add, subtract, find length, find vector projections, and find the dot and cross product of two vectors. for each operation, the calculator writes a step by step, easy to understand explanation of how the work has been done. Given a unit vector u u, is it possible to find a vector v v such that u ⋅ v = −3 u ⋅ v = − 3 and ∥v∥ = 2 ‖ v ‖ = 2? give an example or explain why this can't be done. hint: |u ⋅ v| ≤ ∥u∥∥v∥ | u ⋅ v | ≤ ‖ u ‖ ‖ v ‖ by the cauchy schwarz inequality. Let u = (3, − 3, − 1) and a = (2, 3, 3). find the vector component of u orthogonal to a. problem \#7: enter your answer symbolically, in the form a, b, c as in these examples. Answer to solved let u = ( 3, 2, 3) and a = ( 2, 3, 3). find the | chegg. Let u = (−2,3, 1), v = (−1, −1, 2), and 3u − 2v − 4w = (3, 2, −3). a. the vector w. b. −2u 3v − 5w. to find the vector w, we calculated it to be (−47,− 413, 21). then, we found −2u 3v − 5w = (439, 429, 23). this problem demonstrates how to handle vector equations and find linear combinations, useful in physics and engineering applications. Question: let u = [ 3 2 3] v = [ 1 1 3] a. find ||u|| b. find the distance between u and v. c. find a unit vector in the direction of u. d. find the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. are the vectors orthogonal? explain. e. find a vector in the opposite direction of v with length 3. f. find a scalar c, so that [c 3] is orthogonal.
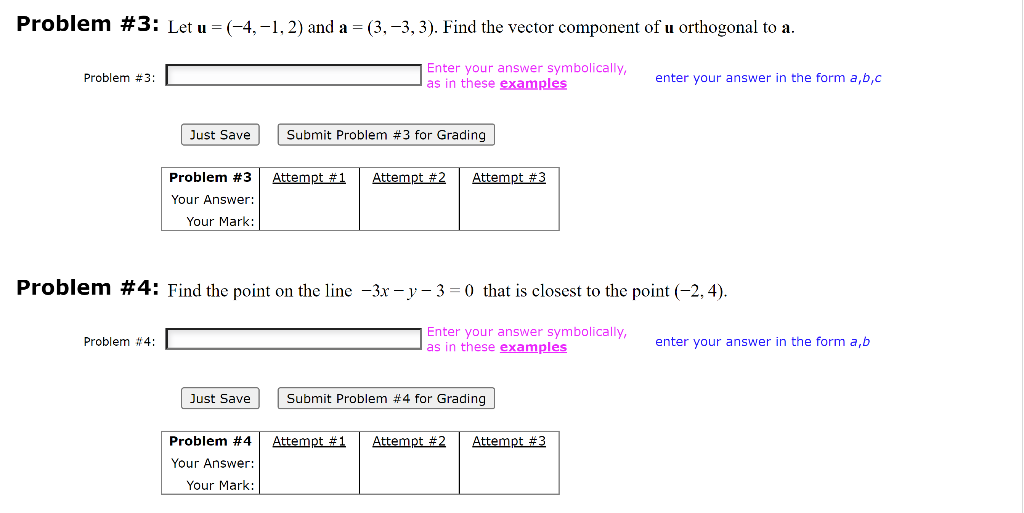
Solved Problem 3 Let U 4 1 2 And A 3 3 3 Find The Chegg Let u = (3, − 3, − 1) and a = (2, 3, 3). find the vector component of u orthogonal to a. problem \#7: enter your answer symbolically, in the form a, b, c as in these examples. Answer to solved let u = ( 3, 2, 3) and a = ( 2, 3, 3). find the | chegg. Let u = (−2,3, 1), v = (−1, −1, 2), and 3u − 2v − 4w = (3, 2, −3). a. the vector w. b. −2u 3v − 5w. to find the vector w, we calculated it to be (−47,− 413, 21). then, we found −2u 3v − 5w = (439, 429, 23). this problem demonstrates how to handle vector equations and find linear combinations, useful in physics and engineering applications. Question: let u = [ 3 2 3] v = [ 1 1 3] a. find ||u|| b. find the distance between u and v. c. find a unit vector in the direction of u. d. find the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. are the vectors orthogonal? explain. e. find a vector in the opposite direction of v with length 3. f. find a scalar c, so that [c 3] is orthogonal.

Solved Let U 3 2 5 V 0 1 2 W 2 6 3 Are Vectors Chegg Let u = (−2,3, 1), v = (−1, −1, 2), and 3u − 2v − 4w = (3, 2, −3). a. the vector w. b. −2u 3v − 5w. to find the vector w, we calculated it to be (−47,− 413, 21). then, we found −2u 3v − 5w = (439, 429, 23). this problem demonstrates how to handle vector equations and find linear combinations, useful in physics and engineering applications. Question: let u = [ 3 2 3] v = [ 1 1 3] a. find ||u|| b. find the distance between u and v. c. find a unit vector in the direction of u. d. find the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. are the vectors orthogonal? explain. e. find a vector in the opposite direction of v with length 3. f. find a scalar c, so that [c 3] is orthogonal.
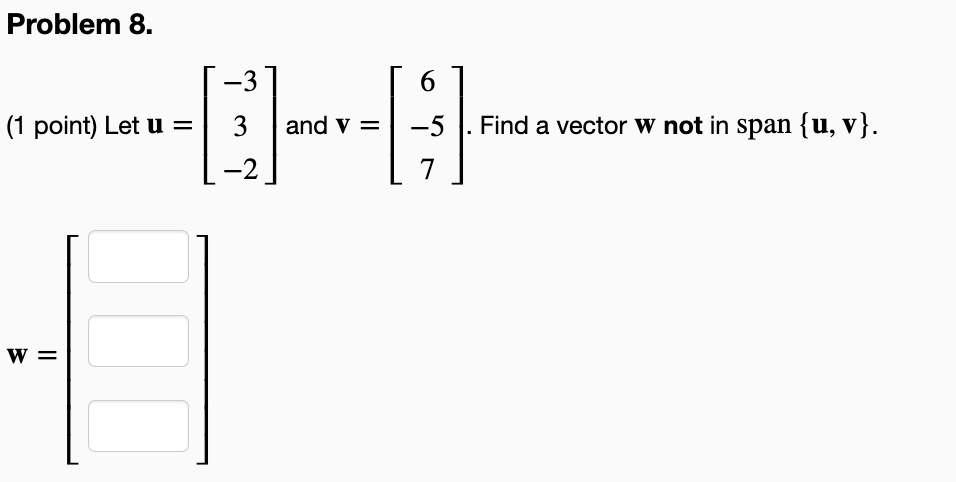
Solved Problem 8 1 ï Point ï Let U 33 2 ï And V 6 57 Chegg
