
27 1 Force On Charged Particles Moving In Magnetic Field Pdf Magnetic force on charged particles conceptual question 1 of 15 > a review for each of the situations below, a charged particle enters a region of uniform magnetic field. determine the direction of the force on each charge due to the magnetic field. 1) which particle (if any) is neutral? 2) which particle (if any) is negatively charged? 3) which particle (if any) is positively charged? 4) now assume that particles a, b, c, and e all have the same magnitude of electric charge. rank the particles a, b, c, and e on the basis of their speed from largest to smallest explain your reason in each.

Solved Magnetic Force On Charged Particles Conceptual Que Chegg Consider the expression for the force acting on a charged particle, f=b q v \sin \theta f = b qvsinθ. consider the first case, \theta=180^ {\circ} θ = 180∘. hence magnetic force acting, \begin {aligned} f &=b q v \sin 180^ {\circ} \\ &=0 \end {aligned} f = b qvsin180∘ = 0. that is, the magnetic force acting is zero in this case. part b. When the charged particle of incoming cosmic rays enters into earth's magnetic field, earth's magnetic field exerts a force on charged particle of rays. earth moves from west to east. the magnetic force exerted on the charges particle is more than the poles that deflect them away from the earth. There are 2 steps to solve this one. magnetic force on charged particles conceptual question 28 of 36 parta determine the direction of the force on the charge due to the magnetic field. (figure 1) view available hint (s) f points into the page. f points out of the page. f points neither into nor out of the page and f =0 f =0. Calculate the radius of curvature of the path of a charge that is moving in a magnetic field. magnetic force can cause a charged particle to move in a circular or spiral path. cosmic rays are energetic charged particles in outer space, some of which approach the earth. they can be forced into spiral paths by the earth’s magnetic field.
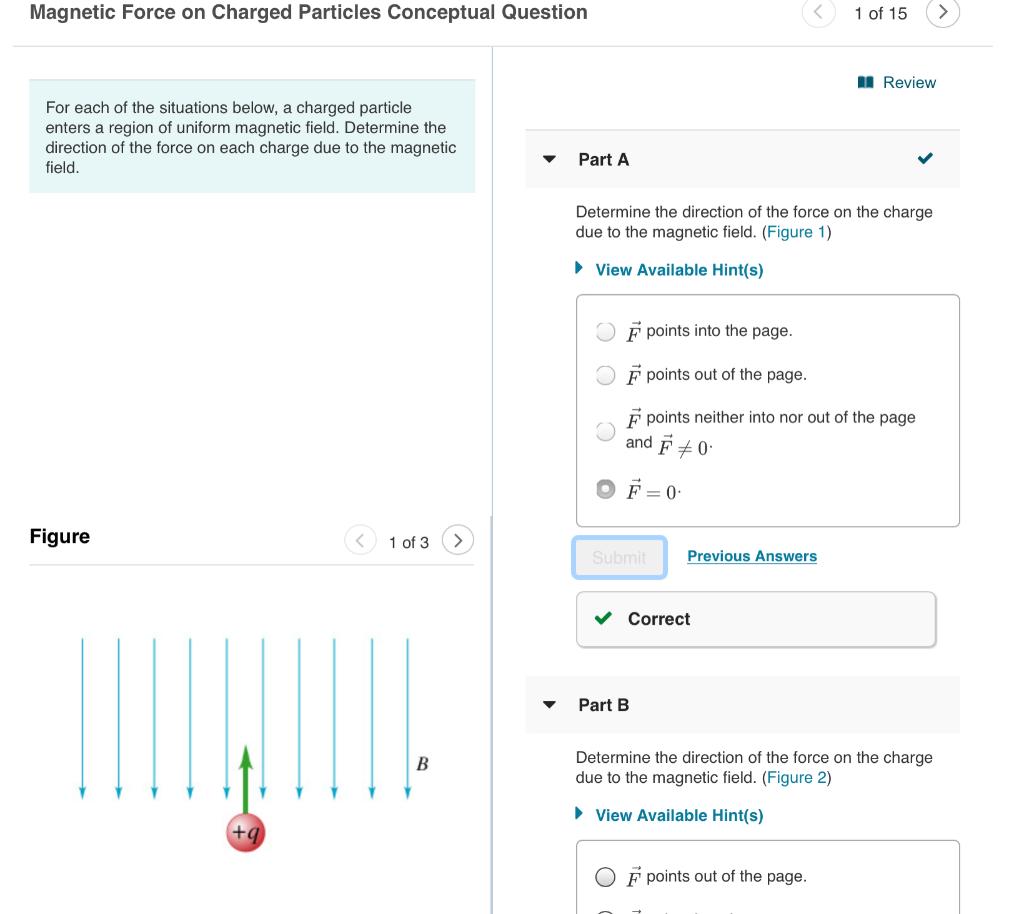
Solved Magnetic Force On Charged Particles Conceptual Chegg There are 2 steps to solve this one. magnetic force on charged particles conceptual question 28 of 36 parta determine the direction of the force on the charge due to the magnetic field. (figure 1) view available hint (s) f points into the page. f points out of the page. f points neither into nor out of the page and f =0 f =0. Calculate the radius of curvature of the path of a charge that is moving in a magnetic field. magnetic force can cause a charged particle to move in a circular or spiral path. cosmic rays are energetic charged particles in outer space, some of which approach the earth. they can be forced into spiral paths by the earth’s magnetic field. Magnets exert forces on each other just like charges. you can draw magnetic field lines just like you drew electric field lines. magnetic north and south pole’s behavior is not unlike electric charges. for magnets, like poles repel and opposite poles attract. a permanent magnet will attract a metal like iron with either the north or south pole. Solution: a magnetic force will not change the magnitude of a charged particle's velocity. what it will change is the direction of a moving, charged particle's velocity. that is, magnetic forces act centripetally. 16.7) you put a stationary positive charge in a magnetic field whose direction is upwards toward the top of the page. Phys 1200 1250 lab manual nicholas cummings, section 3 1 27a magnetic fields and forces 1) the force that a magnetic field exerts on a charged particle is given by 𝑭 = 𝑞𝒗 ⃑ × ? . for a given charge q = 7.1 nc, velocity 6000 m s, and field strengths of 1.2 t. 1) which particle (if any) is neutral? 2) which particle (if any) is negatively charged? 3) which particle (if any) is positively charged? 4) now assume that particles a, b, c, and e all have the same magnitude of electric charge. rank the particles a, b, c, and e on the basis of their speed from largest to smallest. explain your reason in each.

Solved Magnetic Force On Charged Particles Conceptual Chegg Magnets exert forces on each other just like charges. you can draw magnetic field lines just like you drew electric field lines. magnetic north and south pole’s behavior is not unlike electric charges. for magnets, like poles repel and opposite poles attract. a permanent magnet will attract a metal like iron with either the north or south pole. Solution: a magnetic force will not change the magnitude of a charged particle's velocity. what it will change is the direction of a moving, charged particle's velocity. that is, magnetic forces act centripetally. 16.7) you put a stationary positive charge in a magnetic field whose direction is upwards toward the top of the page. Phys 1200 1250 lab manual nicholas cummings, section 3 1 27a magnetic fields and forces 1) the force that a magnetic field exerts on a charged particle is given by 𝑭 = 𝑞𝒗 ⃑ × ? . for a given charge q = 7.1 nc, velocity 6000 m s, and field strengths of 1.2 t. 1) which particle (if any) is neutral? 2) which particle (if any) is negatively charged? 3) which particle (if any) is positively charged? 4) now assume that particles a, b, c, and e all have the same magnitude of electric charge. rank the particles a, b, c, and e on the basis of their speed from largest to smallest. explain your reason in each.

Solved Magnetic Force On Charged Particles Conceptual Chegg Phys 1200 1250 lab manual nicholas cummings, section 3 1 27a magnetic fields and forces 1) the force that a magnetic field exerts on a charged particle is given by 𝑭 = 𝑞𝒗 ⃑ × ? . for a given charge q = 7.1 nc, velocity 6000 m s, and field strengths of 1.2 t. 1) which particle (if any) is neutral? 2) which particle (if any) is negatively charged? 3) which particle (if any) is positively charged? 4) now assume that particles a, b, c, and e all have the same magnitude of electric charge. rank the particles a, b, c, and e on the basis of their speed from largest to smallest. explain your reason in each.
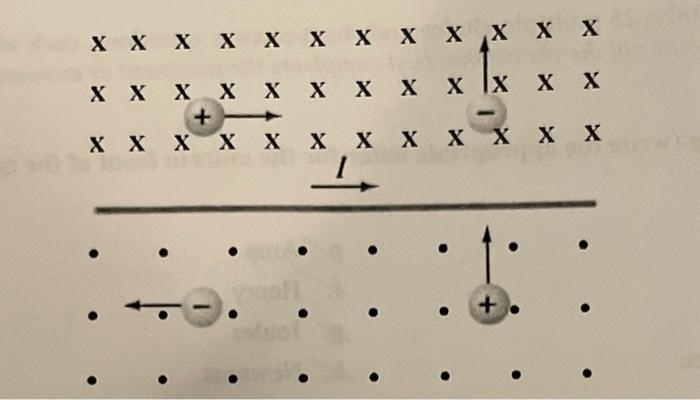
Solved Illustrate The Force On Each Of The Charged Particles Chegg
