
Solved Part 2 A What Is The Net Force On Each Wire Shown At Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. here’s the best way to solve it. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Wire 2 experiences force wire by 1 and 3 and both have current in the same direction, so the force that is exerted on wire 2 is the difference of the both wires. π f 2 = μ 0 l 2 π i 2 i 1 d 12 i 2 i 3 d 23. where localid="1649247642224" d 12 = 2 c m and localid="1650882416742" d 23 = 2 c m.

Solved Part 2 A What Is The Net Force On Each Wire Shown At Chegg In the context of magnetic forces on current carrying wires, the net magnetic field at a point is the vector sum of the fields produced by each wire, and consequently, the net force on a wire is the sum of the forces due to each of these individual magnetic fields. In c the current is opposite to the current in a and b. the wires are equally spaced. each wire experiences a net force due to the other two wires. which wire experiences a net force with the greatest magnitude? (a) a (b) b (c) c (d) all three wires experience a net force that has the same magnitude. And the key concept here is that if the two wires the two parallel wires carrying a current in the same direction, they will attract each other and if they are carrying current in opposite direction, they will repel each other. What is the net force (magnitude and direction) on each wire in figure ex29.36? your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.
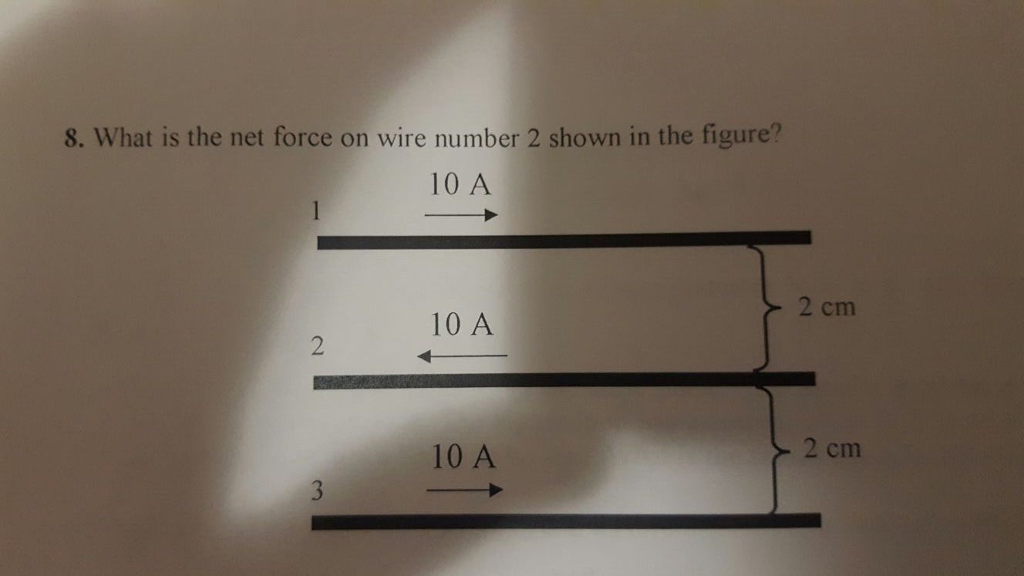
Solved What Is The Net Force On Wire Number 2 Shown In The Chegg And the key concept here is that if the two wires the two parallel wires carrying a current in the same direction, they will attract each other and if they are carrying current in opposite direction, they will repel each other. What is the net force (magnitude and direction) on each wire in figure ex29.36? your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Find the direction and magnitude of the force that each wire experiences in figure 22.58(b), using vector addition. Formula used: the magnetic force exerted by one wire on the other is given by f = μ₀li₁i₂ 2πd, where: μ₀ = permeability constant = 4π × 10⁻⁷ t·m a, l = length of the wire, i₁ = current through the first wire, i₂ = current through the second wire, d = separation between the wires. Q3. a long straight wire carries a current i1 = 30a, and a rectangular loop carries currenti2 = 20a. the loop is 30cm long and 8cm on the side. its side nearest to the wire is 1cm from the wire. what is the net force on the loop due to i1? solution : the magnetic eld along the two sides of the loop that. Two parallel wires carrying current in the same direction attract each other due to the magnetic fields they create. the force on wire 2 due to wire 1 is attractive, pulling wire 2 towards wire 1. this force can be calculated using the formula f l = 2 π r μ 0 i 1 i 2 .
