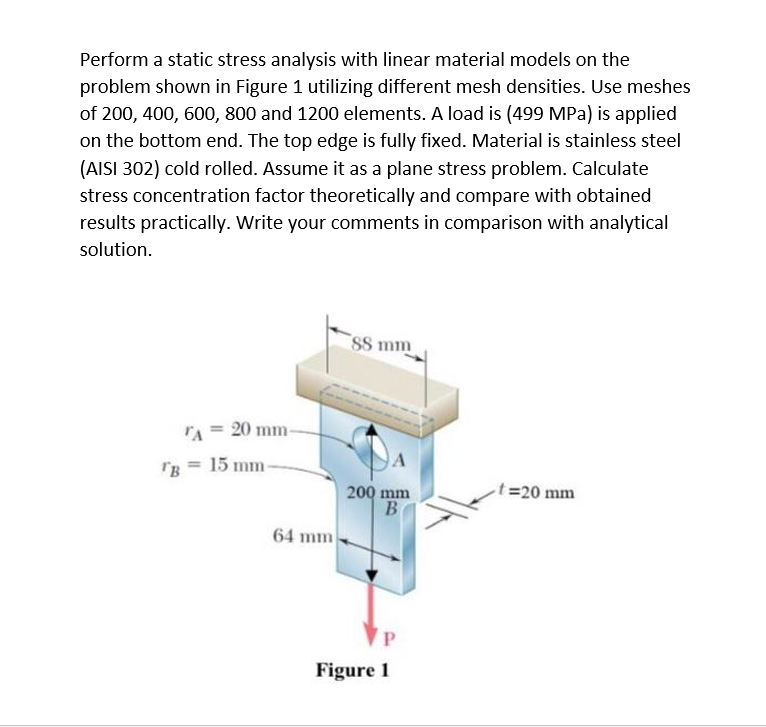
Solved Perform A Static Stress Analysis With Linear Material Chegg Perform a static stress analysis with linear material models on the problem shown in figure 1 utilizing different mesh densities. use meshes of 200, 400, 600, 800 and 1200 elements. a load of 587mpa is applied on the bottom end, the top edge is fully fixed. Young’s modulus and poisson’s ratio are always required for linear static structural analyses: •density is required if any inertial loads are present. •thermal expansion coefficient is required if a temperature load is applied. •stress limits are needed if a stress tool result is present.
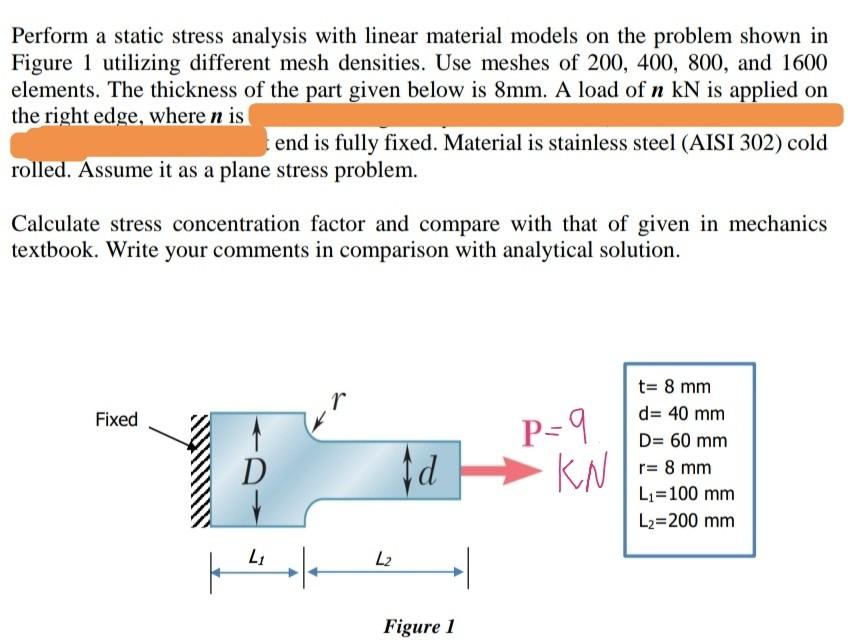
Solved Perform A Static Stress Analysis With Linear Material Chegg In this section we outline a general technique for solving 2d static linear elasticity problems. the technique is known as the `airy stress function’ method. a typical plane elasticity problem is illustrated in the picture. By comparing the ansys solution with simple beam theory, you will be able to understand the accuracy of your model. a schematic of a statically determinate beam with distributed load is shown below. we will use the gui to solve this problem. follow along. For linear static analysis where the deformations are in the elastic range, that is, the stresses, σ , are assumed to be linear functions of the strains, ε , hooke's law can be used to calculate the stresses. hooke's law can be stated as: σ = c ε with the elasticity matrix c of the material. In this chapter, you will perform various case studies of linear static analysis. in this case study, you will perform the linear static analysis of a rectangular plate shown in figure 3.1 and determine the stress under a tensile load.
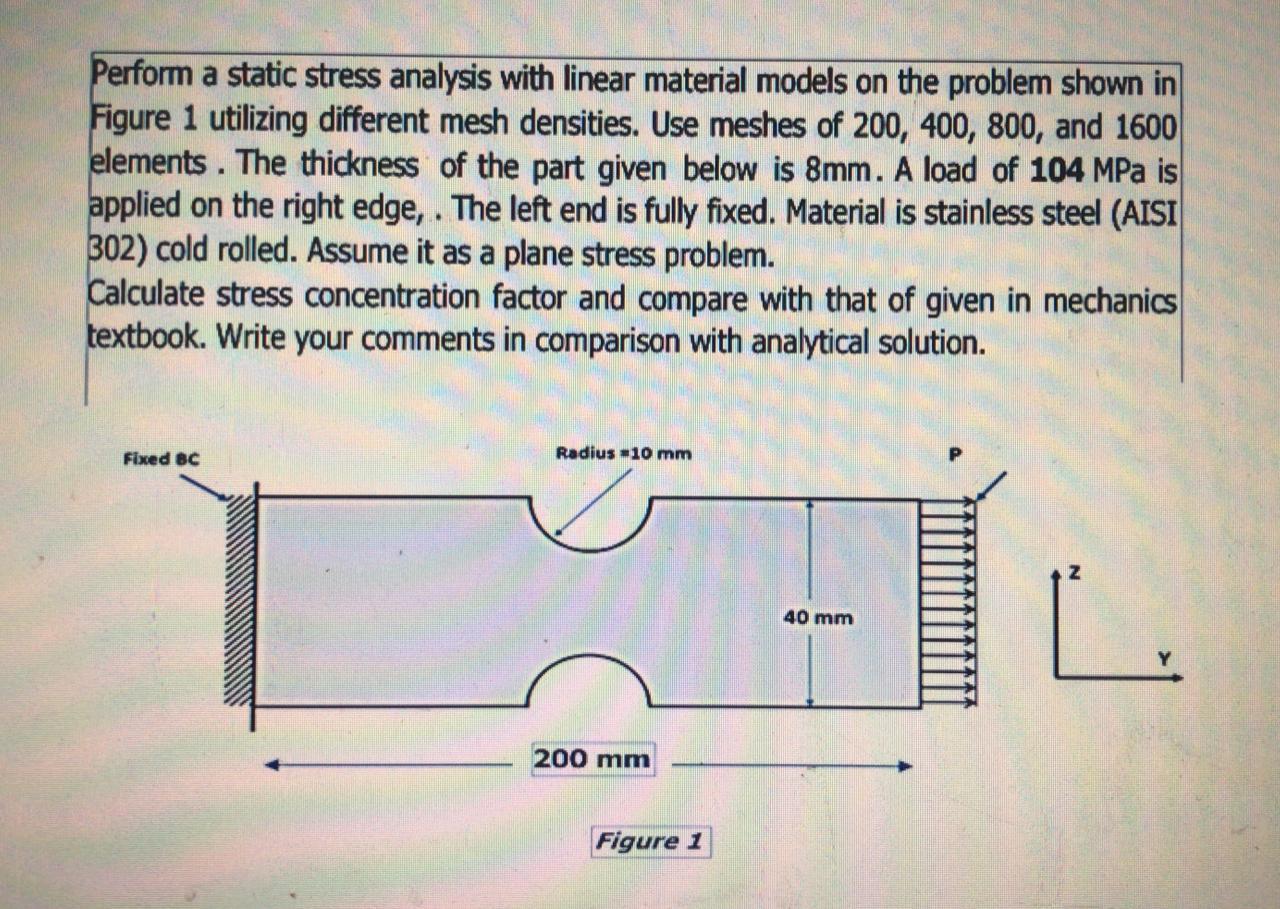
Solved Perform A Static Stress Analysis With Linear Material Chegg For linear static analysis where the deformations are in the elastic range, that is, the stresses, σ , are assumed to be linear functions of the strains, ε , hooke's law can be used to calculate the stresses. hooke's law can be stated as: σ = c ε with the elasticity matrix c of the material. In this chapter, you will perform various case studies of linear static analysis. in this case study, you will perform the linear static analysis of a rectangular plate shown in figure 3.1 and determine the stress under a tensile load. Perform a static stress analysis with linear material models on the problem shown in figure 1 utilizing different mesh densities. use meshes of 200, 400, 600, 800 and 1200 elements. a load is (499 mpa) is applied on the bottom end. the top edge is fully fixed. material is stainless steel (aisi 302) cold rolled. assume it as a plane stress problem. A static structural analysis can be either linear or nonlinear. all types of nonlinearities are allowed large deformations, plasticity, stress stiffening, contact (gap) elements, hyperelasticity and so on. this chapter focuses on linear static analyses, with brief references to nonlinearities. The simplest and most common static structural model can be solved with just the isotropic elasticity material model, which requires two property values: young's modulus and poisson's ratio. with those two values, you can calculate stress and deformation. You can use a static analysis to perform inertia relief calculations (irlf command) that compute the accelerations to exactly counterbalance the applied loads, thus simulating a minimally constrained structure.
