
Solved U A B C D E F G H I J K A A C E Chegg 2 of the plaintext and the keystream. the keystream is produced from an initial key (l1; l2; l3. rresponds to the ciphertext 01101100. dete. e encryption function is not one one. for example 2 2 p, 2 2 p, 3 . and 12 = 2 6 0 so gcd(26; 14) = 2. since gcd(26; 14) 6= 1, 14 does not. war. s from part . ultipli. Encrypt the message “be happy” using the following simple substitution ciper: plain: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z cipher: z n q v i f b j w p e s c x h t m y a u o l r g k d. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.

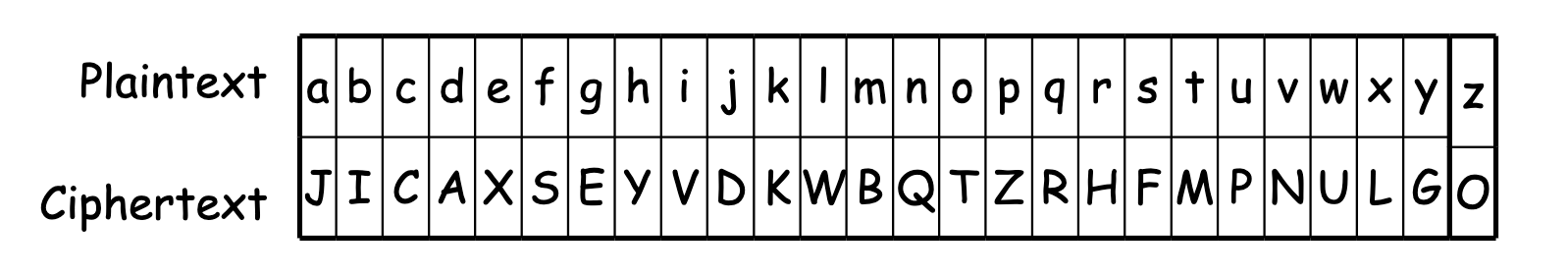
Question Chegg Here is the ciphertext and plaintext juxtaposed, followed by the method jim used to solve the problem:. A monoalphabetic, or simple substitution, cipher is one in which the ciphertext alphabet is a rearrangement of the plaintext alphabet. substitution ciphers, despite having 26! possible permutations, are actually very insecure and are easily solved using letter frequencies. Decode the message “rmij’u uamu xyj.” (30 points) plaintext letter: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z ciphertext letter: m n b v c x z a s d f g h j k l p o i u y t r e w q. your solution’s ready to go! enhanced with ai, our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: p1. How is the original (plaintext) message recovered from the ciphertext if the encryption key is known? the following ciphertext was produced using an affine cipher with encryption key (3,7): qtorhg. to decrypt it (i.e., to recover the plaintext message), we can reverse the steps in the encryption: first add 19 (.
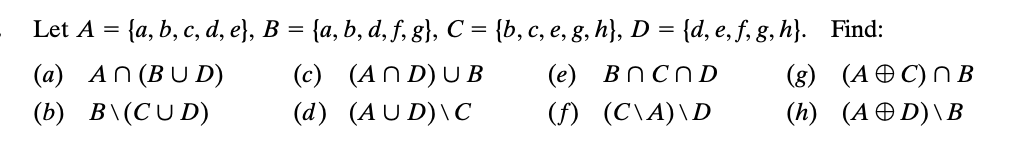
Solved Let Chegg Decode the message “rmij’u uamu xyj.” (30 points) plaintext letter: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z ciphertext letter: m n b v c x z a s d f g h j k l p o i u y t r e w q. your solution’s ready to go! enhanced with ai, our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: p1. How is the original (plaintext) message recovered from the ciphertext if the encryption key is known? the following ciphertext was produced using an affine cipher with encryption key (3,7): qtorhg. to decrypt it (i.e., to recover the plaintext message), we can reverse the steps in the encryption: first add 19 (. Here is how one common version of the keyword cipher works. cryptography. the key has two parts – a word or phrase and a letter of the alphabet. 1. select a keyword or phrase. 2. reading from left to right, write the word or phrase without duplicating letters. 3. Cryptanalysis is based upon finding the ghosts of patterns of the plaintext. we have seen that an important technique of doing this is frequency analysis. so, cryptographers try to develop ciphers that are not easily attacked by frequency analysis. Consider the two caesar ciphers, c1 and c2, below. plaintext letter: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z c1 (k=5): f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z a b c d e c2 (k=19): t u v w x y z a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s use these ciphers in the repeating pattern c2, c1, c1, c2 to encrypt the following word: cyber. Cnt 4403: 20.january.2015 14 plaintext is encrypted two letters at a time 1. if a pair is a repeated letter, insert filler like 'x’ 2. if both letters fall in the same row, replace each with letter.
Solved Plaintext A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T Here is how one common version of the keyword cipher works. cryptography. the key has two parts – a word or phrase and a letter of the alphabet. 1. select a keyword or phrase. 2. reading from left to right, write the word or phrase without duplicating letters. 3. Cryptanalysis is based upon finding the ghosts of patterns of the plaintext. we have seen that an important technique of doing this is frequency analysis. so, cryptographers try to develop ciphers that are not easily attacked by frequency analysis. Consider the two caesar ciphers, c1 and c2, below. plaintext letter: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z c1 (k=5): f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z a b c d e c2 (k=19): t u v w x y z a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s use these ciphers in the repeating pattern c2, c1, c1, c2 to encrypt the following word: cyber. Cnt 4403: 20.january.2015 14 plaintext is encrypted two letters at a time 1. if a pair is a repeated letter, insert filler like 'x’ 2. if both letters fall in the same row, replace each with letter.

Solved Let U A B C D E F G H I J K Let A A Chegg Consider the two caesar ciphers, c1 and c2, below. plaintext letter: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z c1 (k=5): f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z a b c d e c2 (k=19): t u v w x y z a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s use these ciphers in the repeating pattern c2, c1, c1, c2 to encrypt the following word: cyber. Cnt 4403: 20.january.2015 14 plaintext is encrypted two letters at a time 1. if a pair is a repeated letter, insert filler like 'x’ 2. if both letters fall in the same row, replace each with letter.
