
Solved 1 Find The Magnitude And Direction For Magnitude Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: problem 1 find the magnitude and the direction of the magnetic force in each case. problem 2 there is a magnetic field of magnitude b in x direction and → a current i traversing the triangular loop in the counter →b clockwise direction. Sample problems include finding the components of a single force, calculating the magnitude and direction of forces based on their components, determining the resultant force of a system of four concurrent forces, and setting up equations to solve for tensions in cables and vertical forces on objects in equilibrium.
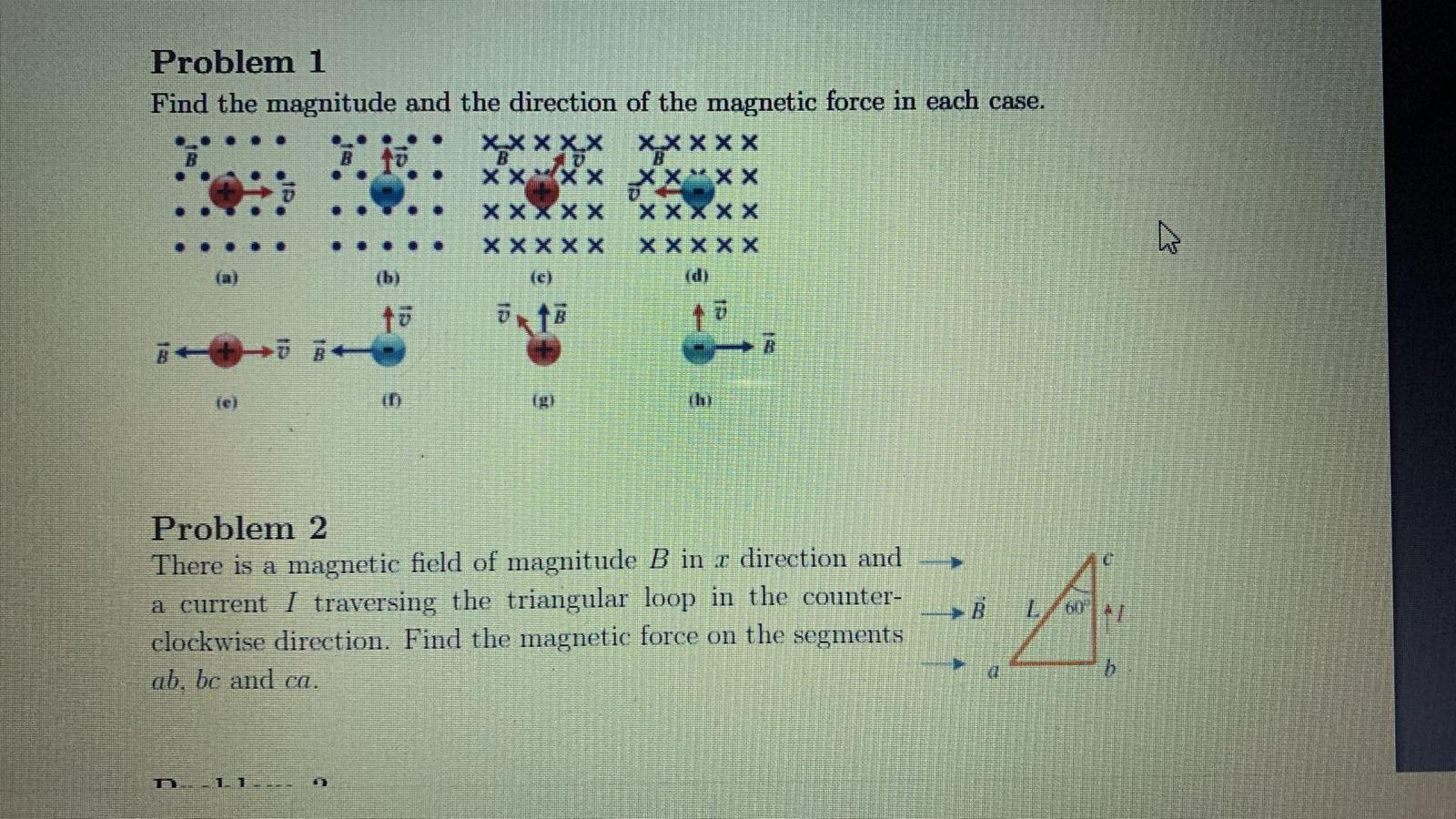
Solved Problem 1 Find The Magnitude And The Direction Of The Chegg Problem (21): as shown in the free body diagram below, a body is subjected to three forces. the body is in equilibrium condition. find the magnitude and direction (the angle $\theta$) of the vector $\vec{f}$ solution: ''equilibrium'' means that the resultant or net force on the object is zero. three forces are acting on the body. To find a unit vector û in the direction of another vector v = (x, y, z), follow these steps: find the magnitude of the vector v: |v| = √(x² y² z²) divide each coefficient of the vector v by the magnitude of v: û = v |v| = (x |v|, y |v|, z |v|) that's it. û is the unit vector in the direction of v. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: problem 1 find the magnitude and the direction of the magnetic force in each case. there are 2 steps to solve this one. the magnetic force on a charged particle q moving with velocity v in a magnetic field b is given by. Coulomb's law practice problems. problem (1): two like and equal charges are at a distance of $d=5\,{\rm cm}$ and exert a force of $f=9\times 10^{ 3}\,{\rm n}$ on each other. (a) find the magnitude of each charge. (b) what is the direction of the electrostatic force between them?.
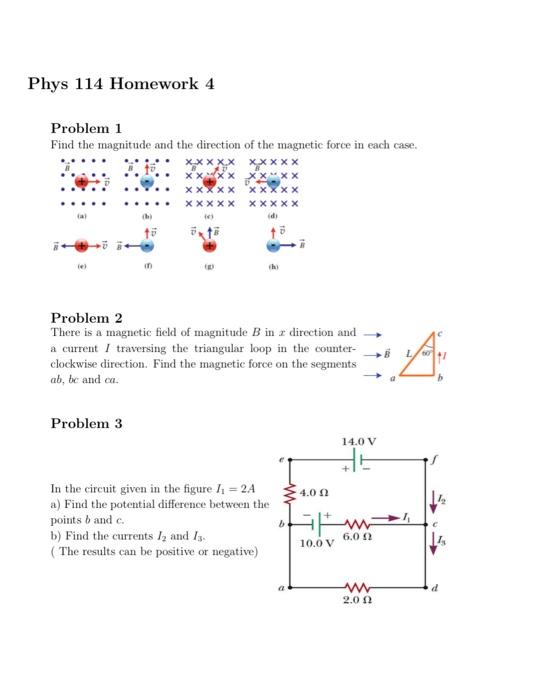
Solved Problem 1 Find The Magnitude And The Direction Of The Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: problem 1 find the magnitude and the direction of the magnetic force in each case. there are 2 steps to solve this one. the magnetic force on a charged particle q moving with velocity v in a magnetic field b is given by. Coulomb's law practice problems. problem (1): two like and equal charges are at a distance of $d=5\,{\rm cm}$ and exert a force of $f=9\times 10^{ 3}\,{\rm n}$ on each other. (a) find the magnitude of each charge. (b) what is the direction of the electrostatic force between them?. The first has a magnitude of 110 cm and makes an angle of 110° with the positive x axis. the resultant displacement has a magnitude of 240 cm and is directed at an angle of 25.0° to the positive x axis. find the magnitude and direction of the second displacement. find the angle with respect to the positive x axis. (c) find the net force on charge q3 due to charges q1 and q2. (a) to find the net force (magnitude and direction) on charge q3 due to charges q1, q2, q4, and q5, we must first find the net electric field at the current location of q3. that require the vector distance r for each case. Find the direction of the vector sum a⃗ b⃗ a → b→. express your answer as counterclockwise angle from x axis to the vector. c. find the magnitude of the vector sum b⃗ a⃗b → a→. To work with a vector, we need to be able to find its magnitude and its direction. we find its magnitude using the pythagorean theorem or the distance formula, and we find its direction using the inverse tangent function. given a position vector v v = a,b = a, b , the magnitude is found by |v|= √a2 b2 | v | = a 2 b 2.
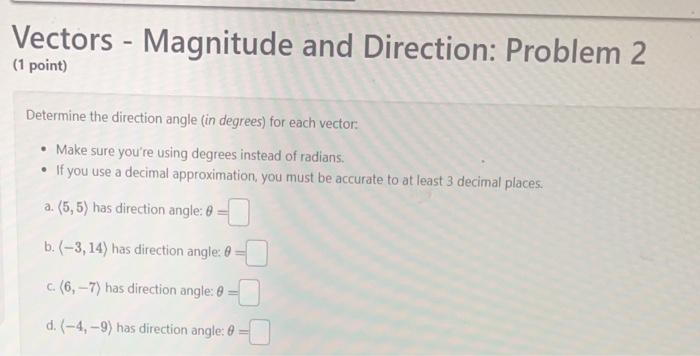
Solved Vectors Magnitude And Direction Problem 2 1 Chegg The first has a magnitude of 110 cm and makes an angle of 110° with the positive x axis. the resultant displacement has a magnitude of 240 cm and is directed at an angle of 25.0° to the positive x axis. find the magnitude and direction of the second displacement. find the angle with respect to the positive x axis. (c) find the net force on charge q3 due to charges q1 and q2. (a) to find the net force (magnitude and direction) on charge q3 due to charges q1, q2, q4, and q5, we must first find the net electric field at the current location of q3. that require the vector distance r for each case. Find the direction of the vector sum a⃗ b⃗ a → b→. express your answer as counterclockwise angle from x axis to the vector. c. find the magnitude of the vector sum b⃗ a⃗b → a→. To work with a vector, we need to be able to find its magnitude and its direction. we find its magnitude using the pythagorean theorem or the distance formula, and we find its direction using the inverse tangent function. given a position vector v v = a,b = a, b , the magnitude is found by |v|= √a2 b2 | v | = a 2 b 2.
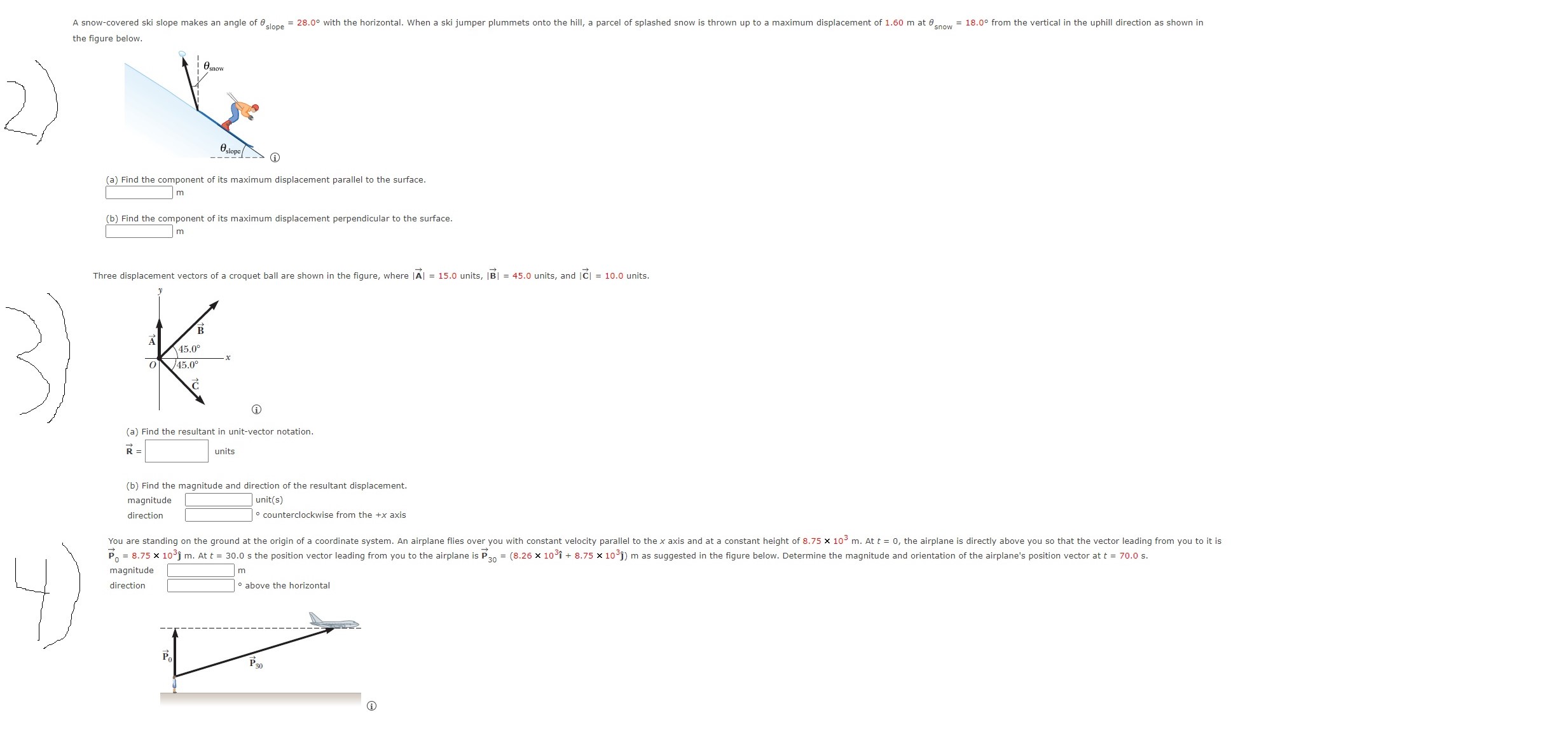
Solved B Find The Magnitude And Direction Of The Resultant Chegg Find the direction of the vector sum a⃗ b⃗ a → b→. express your answer as counterclockwise angle from x axis to the vector. c. find the magnitude of the vector sum b⃗ a⃗b → a→. To work with a vector, we need to be able to find its magnitude and its direction. we find its magnitude using the pythagorean theorem or the distance formula, and we find its direction using the inverse tangent function. given a position vector v v = a,b = a, b , the magnitude is found by |v|= √a2 b2 | v | = a 2 b 2.
