Solved Consider The Simply Supported Beam Shown Below Vrogue Co Problem 1: for the simply supported beam shown below, complete the following using the conjugate beam method. determine the values of ea, oc, and vmax as functions of e, i, l, and mo. the value of vmax can be determined from your shear diagram of the conjugate beam. clearly indicate both magnitude and direction for all values. Analyze the beam shown using influence line. a. determine the maximum reaction at roller support due to 8 kn concentrated moving load only. b. determine the maximum positive shear at b due to 15 kn m moving uniform load only. c. determine the moment at b due to 10 kn m uniform dead load only.
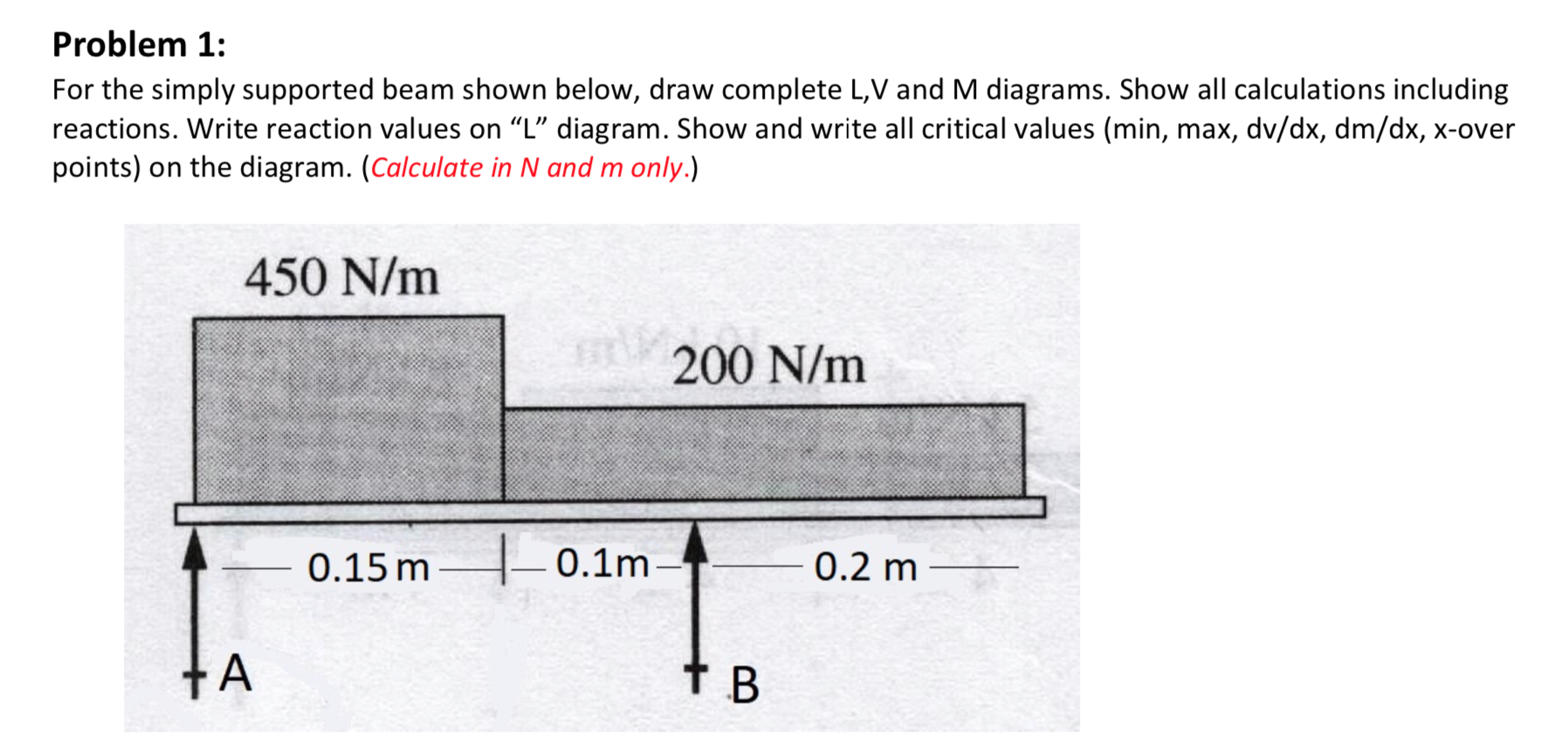
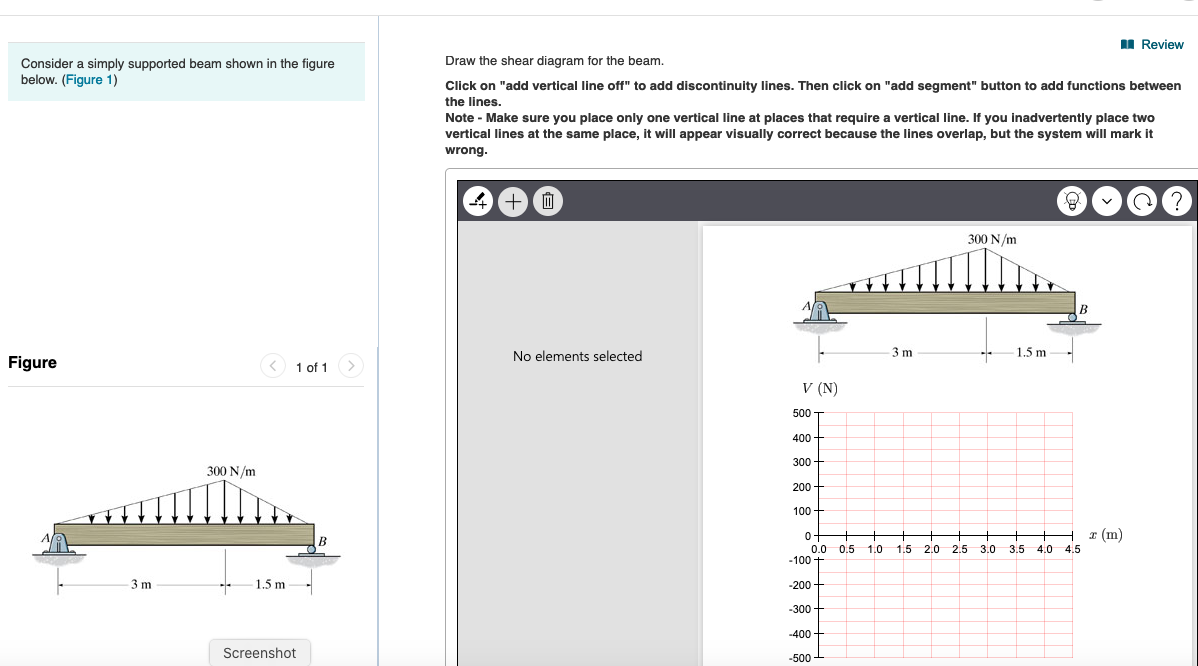
Solved Problem 1 For The Simply Supported Beam Shown Below Chegg The simply supported beam as shown in figure below carries two concentrated loads. a) derive the expressions for the shear force and the bending moment for each segment of the beam. b) sketch the shear force and bending moment diagrams. Question: problem 1: for the simply supported beam shown below, draw complete l, v and m diagrams. show all calculations including reactions. write reaction values on “l” diagram. show and write all critical values (min, max, dv dx, dm dx, x over points) on the diagram. (calculate in n and m only.) 450 n m 200 n m 0.15 m | 0.1m 0.2 m ha ТВ. Identify the points of interest where loads are applied and the reactions occur at the supports of the beam. Draw the shear diagram for the beam. click on "add vertical line off" to add discontinuity lines. then click on "add segment" button to add functions between the lines. note make sure you place only one vertical line at places that require a vertical line.

1 For The Simply Supported Beam Solved In Problem 2 Chegg Identify the points of interest where loads are applied and the reactions occur at the supports of the beam. Draw the shear diagram for the beam. click on "add vertical line off" to add discontinuity lines. then click on "add segment" button to add functions between the lines. note make sure you place only one vertical line at places that require a vertical line. Sample problems include determining stress in a cantilever beam carrying a uniformly distributed load, a simply supported beam with a concentrated load, and minimum beam height needed to limit stress to a specified value. Given below are solved examples for calculation of shear force and bending moment and plotting of the diagrams sfd and bmd for different load conditions of simply supported beam, cantilever and overhanging beam. The primary structure is a simply supported beam as shown in fig.1.11. now, compute the deflection at b, in the released structure due to uniformly distributed load and concentrated load. 1. the beam is simply supported over 8m with udl of 10kn m over the first 4m from the left support. 2. the left support reaction is 40kn and right support is 20kn. 3. the shear force diagram shows v reducing linearly from 40kn to 0kn over 0 4m and then constant at 20kn from 4 8m. 4.
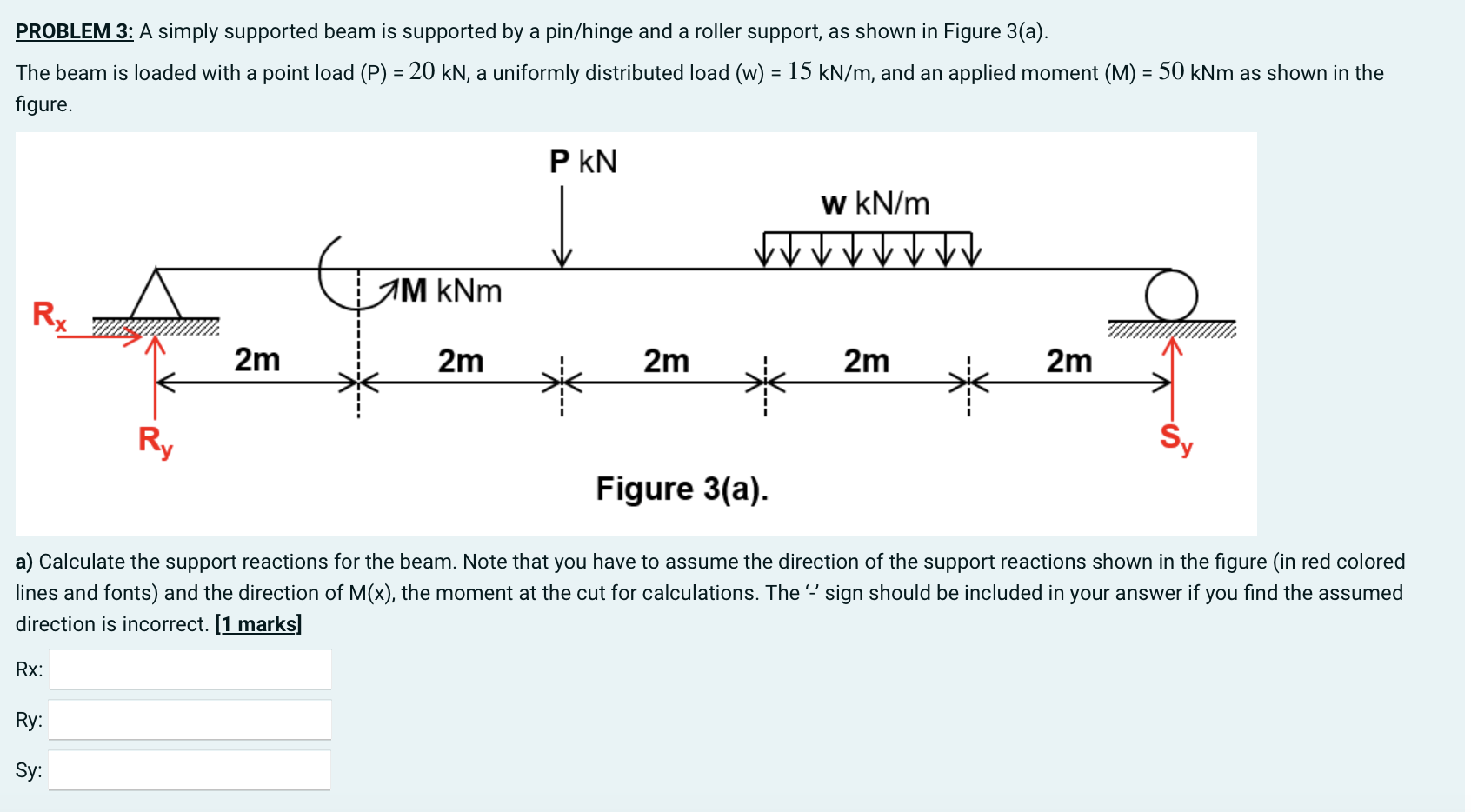
Solved Problem 3 A Simply Supported Beam Is Supported By A Chegg Sample problems include determining stress in a cantilever beam carrying a uniformly distributed load, a simply supported beam with a concentrated load, and minimum beam height needed to limit stress to a specified value. Given below are solved examples for calculation of shear force and bending moment and plotting of the diagrams sfd and bmd for different load conditions of simply supported beam, cantilever and overhanging beam. The primary structure is a simply supported beam as shown in fig.1.11. now, compute the deflection at b, in the released structure due to uniformly distributed load and concentrated load. 1. the beam is simply supported over 8m with udl of 10kn m over the first 4m from the left support. 2. the left support reaction is 40kn and right support is 20kn. 3. the shear force diagram shows v reducing linearly from 40kn to 0kn over 0 4m and then constant at 20kn from 4 8m. 4.
