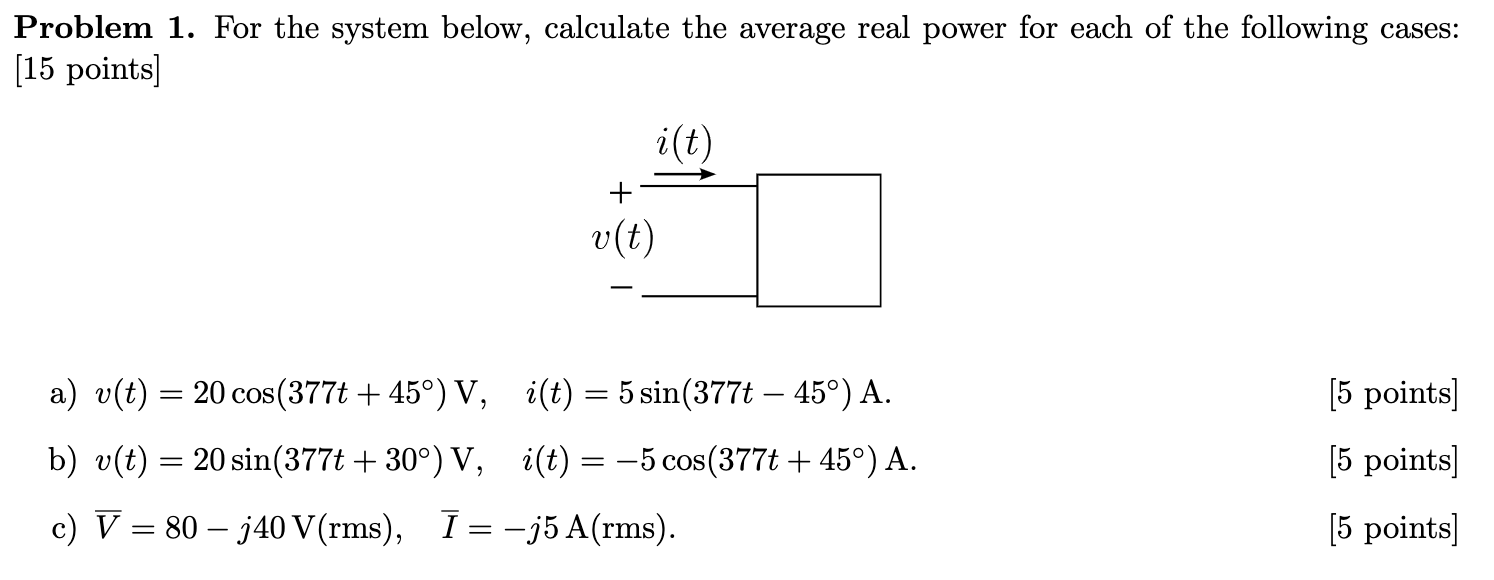
Solved Problem 1 For The System Below Calculate The Chegg There are 2 steps to solve this one. problem 1. for the system below, calculate the average real power for each of the following cases: [15 points] a) v(t)=20cos(377t 45∘)v, i(t)= 5sin(377t−45∘)a. [5 points] b) v(t)=20sin(377t 30∘)v, i(t)=−5cos(377t 45∘)a. [5 points] c) v ˉ =80−j40 v(rms), i ˉ= −j5 a(rms). [5 points]. Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step by step explanations.
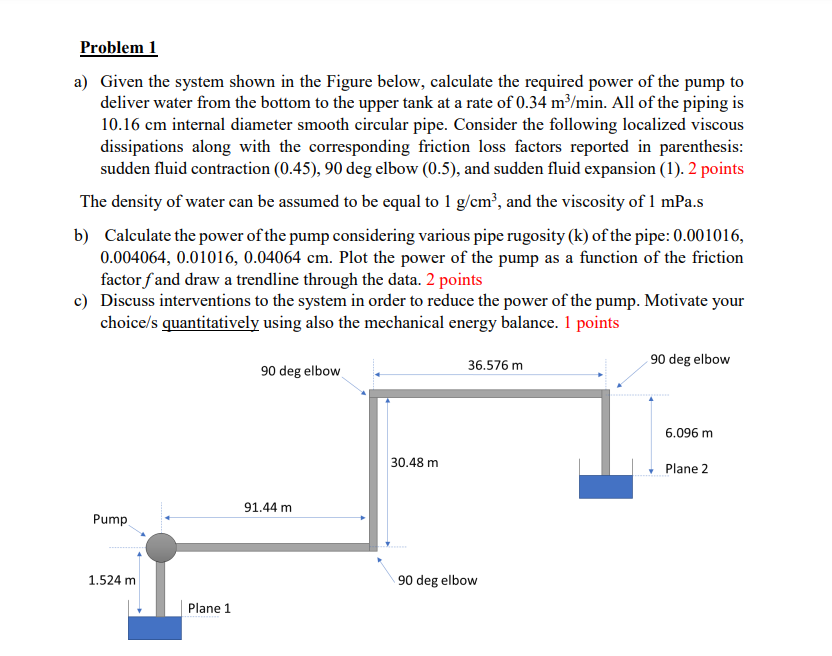
Solved Problem 1a ï Given The System Shown In The Figure Chegg To solve a system of equations by elimination, write the system of equations in standard form: ax by = c, and multiply one or both of the equations by a constant so that the coefficients of one of the variables are opposite. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. problem 1. stiffness. there are 2 steps to solve this one. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. A. assemble the system global stiffness matrix and calculate the global displacements of the unconstrained node; b. compute the reaction forces and check the equilibrium conditions; c. check the energy balance. is the strain energy in balance with the mechanical work of the applied force? d. compute the strain and stress in each bar. figure 2. This calculator solves systems of linear equations with steps shown, using gaussian elimination method, inverse matrix method, or cramer's rule. also you can compute a number of solutions in a system (analyse the compatibility) using rouché–capelli theorem .
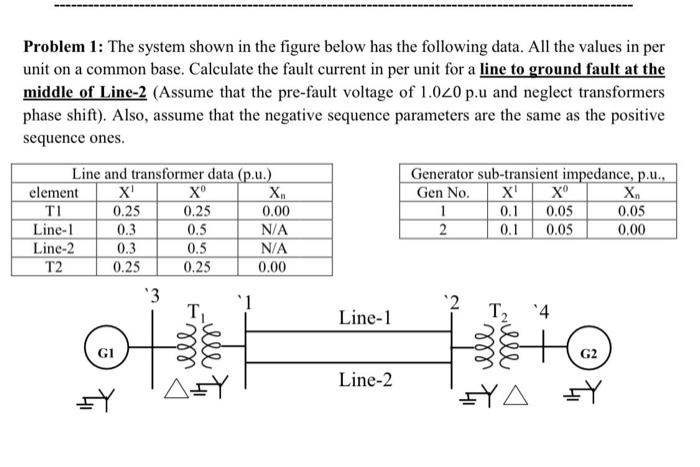
Solved Problem 1 The System Shown In The Figure Below Has Chegg A. assemble the system global stiffness matrix and calculate the global displacements of the unconstrained node; b. compute the reaction forces and check the equilibrium conditions; c. check the energy balance. is the strain energy in balance with the mechanical work of the applied force? d. compute the strain and stress in each bar. figure 2. This calculator solves systems of linear equations with steps shown, using gaussian elimination method, inverse matrix method, or cramer's rule. also you can compute a number of solutions in a system (analyse the compatibility) using rouché–capelli theorem . Determine the transfer function of a linear time invariant system given the following information: 4.1.1 the system has relative degree 3. 4.1.2 it has 3 poles of which 2 are at 2 and 4. 4.1.3 the impulse response resembles a step response for a stable linear system with a steady state value of 0.25. solved problem 4.2. Shows you step by step how to solve systems of equations! this calculator will solve your problems. Problem #1: obtain the bus admittance matrix for the admittance network shown aside by the rule of inspection. problem #2: obtain ybus and zbus matrices for the impedance network shown aside by the rule of inspection. also, determine ybus for the reduced network after eliminating the eligible unwanted node. Problem 1 consider the system below: (system input = raw materials system output = finished products) (a) calculate the line yield of the given system. (b) calculate the average cost to process one unit of material in the system.

Solved This Problem Is Solved By Chegg And I Put It Below Chegg Determine the transfer function of a linear time invariant system given the following information: 4.1.1 the system has relative degree 3. 4.1.2 it has 3 poles of which 2 are at 2 and 4. 4.1.3 the impulse response resembles a step response for a stable linear system with a steady state value of 0.25. solved problem 4.2. Shows you step by step how to solve systems of equations! this calculator will solve your problems. Problem #1: obtain the bus admittance matrix for the admittance network shown aside by the rule of inspection. problem #2: obtain ybus and zbus matrices for the impedance network shown aside by the rule of inspection. also, determine ybus for the reduced network after eliminating the eligible unwanted node. Problem 1 consider the system below: (system input = raw materials system output = finished products) (a) calculate the line yield of the given system. (b) calculate the average cost to process one unit of material in the system.
