Solved Problem 3 For The Matrix A 1 2 0 3 2 4 1 2 1 2 Chegg
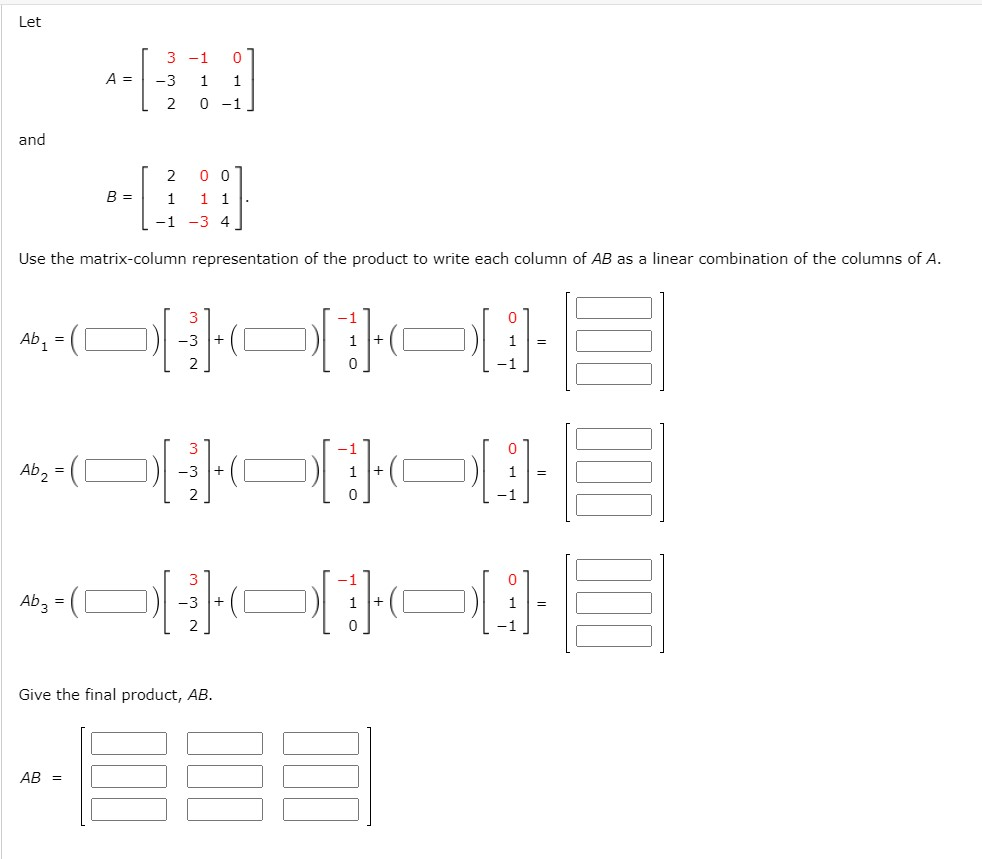
Solved Let A 3 1 0 3 1 1 2 0 1 And 2 0 0 B 1 1 1 1 3 Chegg For the matrix a= (1 2 0 3 2 4 1 2 1 2 1 1 3 6 2 1 (a) find a matrix b such that r (a) = n (b). 1 1 1 1 0 1 Ꮎ : b 2 0 1 0 ſi 1 1 0 0] 12: b = 1 2 0 11 1 1 1 0 t: b= 1 2 0 1 v: none of the other answers. here’s the best way to solve it. this ai generated tip is based on chegg's full solution. sign up to see more!. Define the term identity matrix (unit matrix). all elements are ones. ones on one of the diagonals and zeros elsewhere. ones on the first row and column and zeros elsewhere. ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. write the following system of equations as an augmented matrix. what is the sum of the matrices?.

Solved Given The Matrix A 1 2 3 4 2 4 6 8 3 5 7 9 Chegg With help of this calculator you can: find the matrix determinant, the rank, raise the matrix to a power, find the sum and the multiplication of matrices, calculate the inverse matrix. Free math problem solver answers your linear algebra homework questions with step by step explanations. Determine whether b can be written as a linear combination of a 1, a 2, and a 3. in other words, determine whether weights x 1, x 2, and x 3 exist, such that x 1 a 1 x 2 a 2 x 3 a 3 = b. 4 4 matrices and higher dimensional matrices the sarrus map does not provide the determinant of the given matrix. find the condition on 4 4 matrix a such that det(a) = s(a).

Solved Find The Solution To The Matrix Problem 4 2 4 3 Chegg Determine whether b can be written as a linear combination of a 1, a 2, and a 3. in other words, determine whether weights x 1, x 2, and x 3 exist, such that x 1 a 1 x 2 a 2 x 3 a 3 = b. 4 4 matrices and higher dimensional matrices the sarrus map does not provide the determinant of the given matrix. find the condition on 4 4 matrix a such that det(a) = s(a). Ai may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent symbolab's views. save to notebook!. There are 2 steps to solve this one. perform the row operation r 2 = r 2 2 r 1 to make the entry at 2, 1 a 0 . problem 1. let a= [1 2 0 31 2 4 1 2 1 2 1 1 3 6 2 1 (a) find a matrix b such that r (a) = n (b). (b) find a matrix c such that n (a) = r (c). Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step by step explanations, just like a math tutor. The matrix a is diagonalizable if and only if the sum of the dimensions of the distinct eigenspaces equals n, and this happens if and only if the dimension of the eigenspace for each k equals the multiplicity of k.

Solved 1 A 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 3 1 4 For The Matrix A2 3a 41 Chegg Ai may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent symbolab's views. save to notebook!. There are 2 steps to solve this one. perform the row operation r 2 = r 2 2 r 1 to make the entry at 2, 1 a 0 . problem 1. let a= [1 2 0 31 2 4 1 2 1 2 1 1 3 6 2 1 (a) find a matrix b such that r (a) = n (b). (b) find a matrix c such that n (a) = r (c). Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step by step explanations, just like a math tutor. The matrix a is diagonalizable if and only if the sum of the dimensions of the distinct eigenspaces equals n, and this happens if and only if the dimension of the eigenspace for each k equals the multiplicity of k.

Solved A 3 4 1 2 1 0 3 1 2 5 4 0 B 1 0 0 1 1 1 Chegg Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step by step explanations, just like a math tutor. The matrix a is diagonalizable if and only if the sum of the dimensions of the distinct eigenspaces equals n, and this happens if and only if the dimension of the eigenspace for each k equals the multiplicity of k.

Solved Problem 3 For The Matrix A 1 2 0 3 2 4 1 2 1 2 Chegg
Comments are closed.