
Solved Prove The Following Identities Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: question 4. prove the following identities. (a) (a b)× (a−b)=−2 (a×b). (b) (a×b)⋅ (c×d)=∣∣a⋅ba⋅db⋅cb⋅d∣∣. please answer clearly for ease of understanding. here’s the best way to solve it. question 4. prove the following identities. To prove that this expression equals zero under certain conditions, we can use the properties of the gradient (∇), the vector cross product (∇x), and the divergence (∇ ·) operators. here's we can prove it: start with the expression ∇ · (∇xw). use the vector identity for the divergence of a cross product:.

Solved Prove The Following Identities Chegg Ex 8.3, 4 prove the following identities, where the angles involved are acute angles for which the expressions are defined. (i) (cosec θ – cot θ)2 = (1 − 𝑐𝑜𝑠" " θ) (1 cosθ ) solving l.h.s (cosec θ – cot θ)2 we need to make it in terms of cos θ & sin θ = (1 sin𝜃 − cos𝜃 sin𝜃 )^2 =. Sure, i'd be happy to help you understand how to use venn diagrams to verify these identities. identity 1: (a ∩ b) \ c = (a \ c) ∩ (b \ c) let's start with the first identity. draw three overlapping circles, each representing a set (a, b, and c). shade the area representing (a ∩ b) \ c. Use sum or difference identities to verify the following: 1. sin (x – y) sin (x y) = 2 sin x cos y 2. cos (x – y) cos (x y) = 2 cos x cos y 4.08 practice:. Prove the following identities (show your complete solution): (a) ∇×(ϕ∇ϕ)=0, with ϕ=ϕ(x,y,z) (b) a×(∇×a)=21∇(a2)−(a⋅∇)a your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.
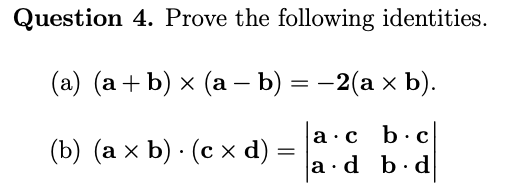
Solved Question 4 Prove The Following Identities A Chegg Use sum or difference identities to verify the following: 1. sin (x – y) sin (x y) = 2 sin x cos y 2. cos (x – y) cos (x y) = 2 cos x cos y 4.08 practice:. Prove the following identities (show your complete solution): (a) ∇×(ϕ∇ϕ)=0, with ϕ=ϕ(x,y,z) (b) a×(∇×a)=21∇(a2)−(a⋅∇)a your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. here’s the best way to solve it. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Let $f$, $g$ and $h$ be any $c^{2}$ scalar functions. using the standard identities of vector calculus, prove that; $$ \nabla \cdot \left( f\nabla g \times \nabla h \right) = \nabla f \cdot \left(\nabla g \times \nabla h \right)$$. Prove the following identities, show your steps for full marks.(6 marks)a) cosx(1 secx)(cosx 1)= sin2xb) 1 cot2xcsc2x=1 question: prove the following identities, show your steps for full marks.(6 marks)a) cosx(1 secx)(cosx 1)= sin2xb) 1 cot2xcsc2x=1. Prove the following identities (a) $2 \sec a=\frac {\cos a} {1 \sin a} \frac {1 \sin a} {\cos a}$ 🤔 not the exact question you’re looking for? this problem has been solved! you'll receive a detailed solution to help you. master the concepts. the first term is . to simplify, multiply the numerator and the denominator by : the second term is .

Solved Question 4 Prove The Following Identities A Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. here’s the best way to solve it. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Let $f$, $g$ and $h$ be any $c^{2}$ scalar functions. using the standard identities of vector calculus, prove that; $$ \nabla \cdot \left( f\nabla g \times \nabla h \right) = \nabla f \cdot \left(\nabla g \times \nabla h \right)$$. Prove the following identities, show your steps for full marks.(6 marks)a) cosx(1 secx)(cosx 1)= sin2xb) 1 cot2xcsc2x=1 question: prove the following identities, show your steps for full marks.(6 marks)a) cosx(1 secx)(cosx 1)= sin2xb) 1 cot2xcsc2x=1. Prove the following identities (a) $2 \sec a=\frac {\cos a} {1 \sin a} \frac {1 \sin a} {\cos a}$ 🤔 not the exact question you’re looking for? this problem has been solved! you'll receive a detailed solution to help you. master the concepts. the first term is . to simplify, multiply the numerator and the denominator by : the second term is .
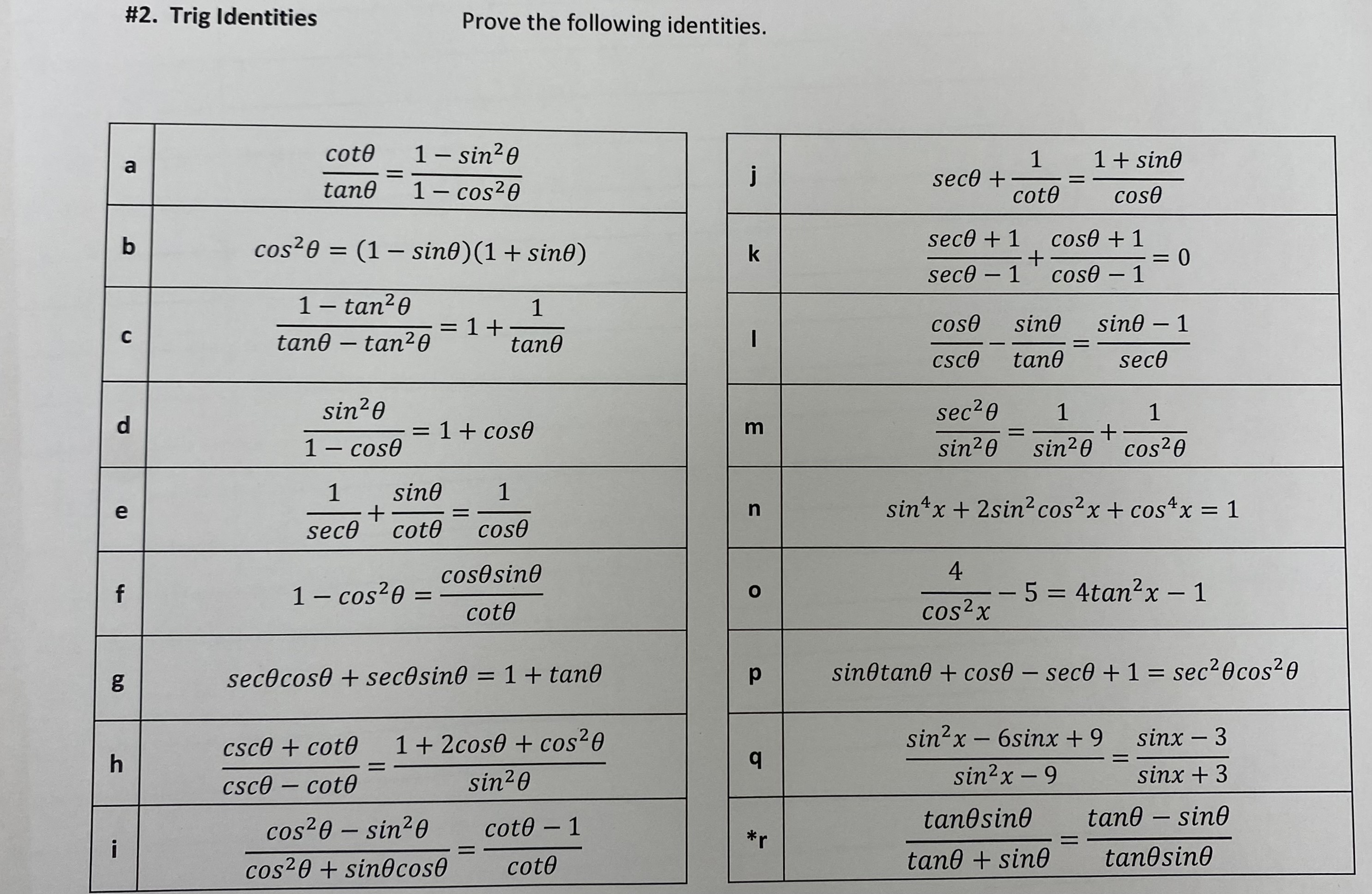
Solved 2 Trig Identities Prove The Following Identities Chegg Prove the following identities, show your steps for full marks.(6 marks)a) cosx(1 secx)(cosx 1)= sin2xb) 1 cot2xcsc2x=1 question: prove the following identities, show your steps for full marks.(6 marks)a) cosx(1 secx)(cosx 1)= sin2xb) 1 cot2xcsc2x=1. Prove the following identities (a) $2 \sec a=\frac {\cos a} {1 \sin a} \frac {1 \sin a} {\cos a}$ 🤔 not the exact question you’re looking for? this problem has been solved! you'll receive a detailed solution to help you. master the concepts. the first term is . to simplify, multiply the numerator and the denominator by : the second term is .
