Solved Solve The Polynomial Equation X3 5×2 2x 8 0 Question Chegg

Solved Solve The Polynomial Equation X3 5x2 2x 8 0 Question Chegg Express the improper fraction below as a series of partial fractions: x2−4x3−3x2−x 2 question 9. write the equation y=x2−2x−3 in the form y=(x−a)2 b. After changing the signs, add the last dividend from the multiplied polynomial to find the new dividend.
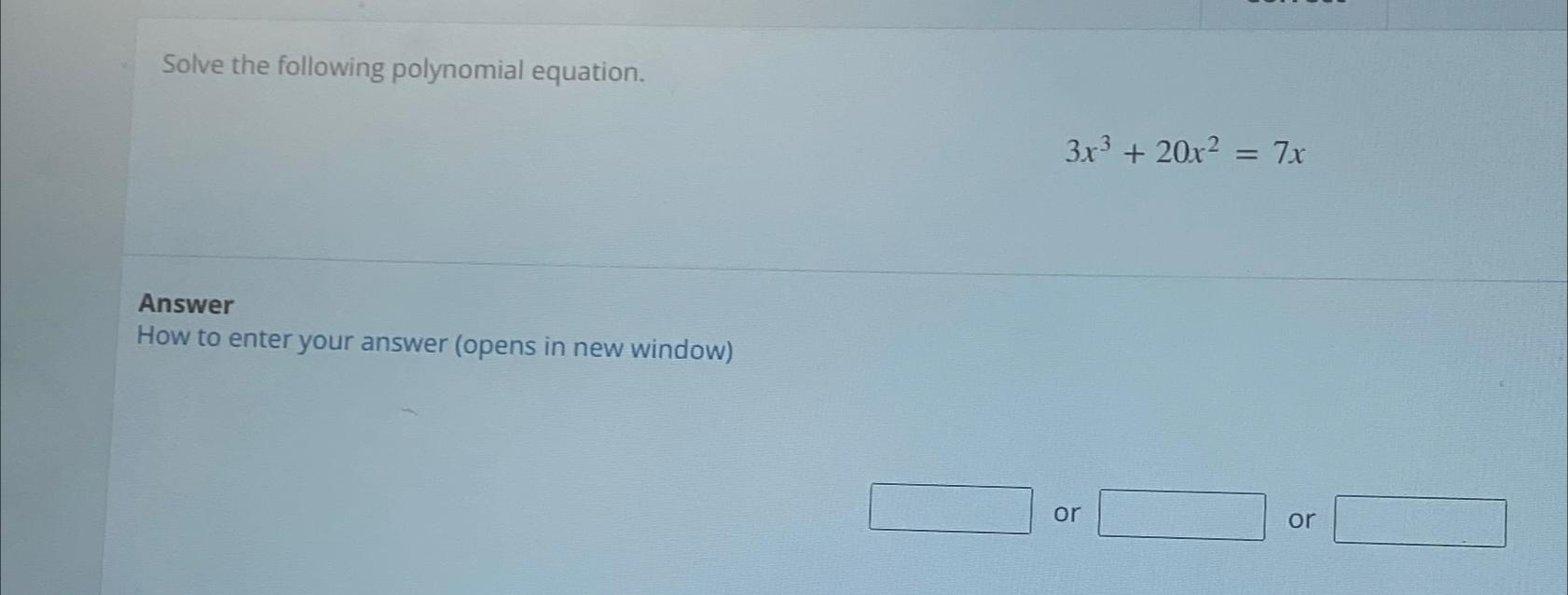
Solved Solve The Following Polynomial Chegg The equation x3 −5x2 2x 8 = 0 can be solved by confirming that −1 is a root, then using synthetic division to find the quadratic factor x2 −6x 8. this factors further into (x − 4)(x − 2), leading to the complete roots of −1,2, and 4. Tiger algebra solver x^3 5x^2 2x 8=0 free solver simplifier that shows steps. helps you solve your homework assignments". In this case, we use the given zero to perform synthetic division, which helps us factorize the polynomial and find its roots. this process is crucial in solving polynomial equations and understanding the behavior of polynomial functions. Solve the equation x3−5x2 2x 8=0 given that 1 is a zero of f (x)=x3−5x2 2x 8 the solution set is (use a comma to separate answers as needed.) your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.

Solved Solve The Polynomial Equation X 3 5x 2 6x 2 0 Chegg In this case, we use the given zero to perform synthetic division, which helps us factorize the polynomial and find its roots. this process is crucial in solving polynomial equations and understanding the behavior of polynomial functions. Solve the equation x3−5x2 2x 8=0 given that 1 is a zero of f (x)=x3−5x2 2x 8 the solution set is (use a comma to separate answers as needed.) your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. To solve the equation x3 − 5x2 2x 8 = 0 given that −1 is a zero, we will perform polynomial division to factor the cubic polynomial using (x 1) since a known zero means that this factor is valid. The rational root theorem states that if a polynomial zeroes for a rational number p q then p is a factor of the trailing constant and q is a factor of the leading coefficient. Question 37 solve the polynomial equation: x3 5x2 9x 45 = 0 a x = 3i, 3i, and 5 b x = 3i, 3i, and 5 С x = 3,3, and 5 x = 3,3, and 5. The rational root theorem states that if a polynomial zeroes for a rational number p q then p is a factor of the trailing constant and q is a factor of the leading coefficient.

Solved Solve The Equation X3 5x2 2x 8 0 Given That 1 Chegg To solve the equation x3 − 5x2 2x 8 = 0 given that −1 is a zero, we will perform polynomial division to factor the cubic polynomial using (x 1) since a known zero means that this factor is valid. The rational root theorem states that if a polynomial zeroes for a rational number p q then p is a factor of the trailing constant and q is a factor of the leading coefficient. Question 37 solve the polynomial equation: x3 5x2 9x 45 = 0 a x = 3i, 3i, and 5 b x = 3i, 3i, and 5 С x = 3,3, and 5 x = 3,3, and 5. The rational root theorem states that if a polynomial zeroes for a rational number p q then p is a factor of the trailing constant and q is a factor of the leading coefficient.
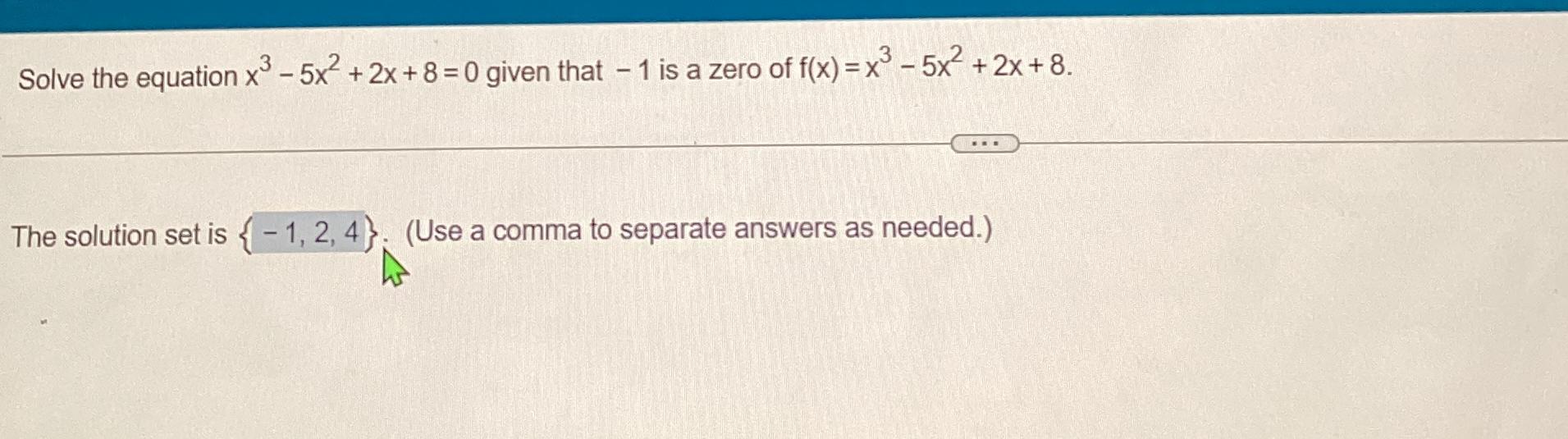
Solved Solve The Equation X3 5x2 2x 8 0 ï Given That 1 ï Is A Chegg Question 37 solve the polynomial equation: x3 5x2 9x 45 = 0 a x = 3i, 3i, and 5 b x = 3i, 3i, and 5 С x = 3,3, and 5 x = 3,3, and 5. The rational root theorem states that if a polynomial zeroes for a rational number p q then p is a factor of the trailing constant and q is a factor of the leading coefficient.
Comments are closed.