Solved The Figure Given Below Depicts The Equilibrium In The Chegg
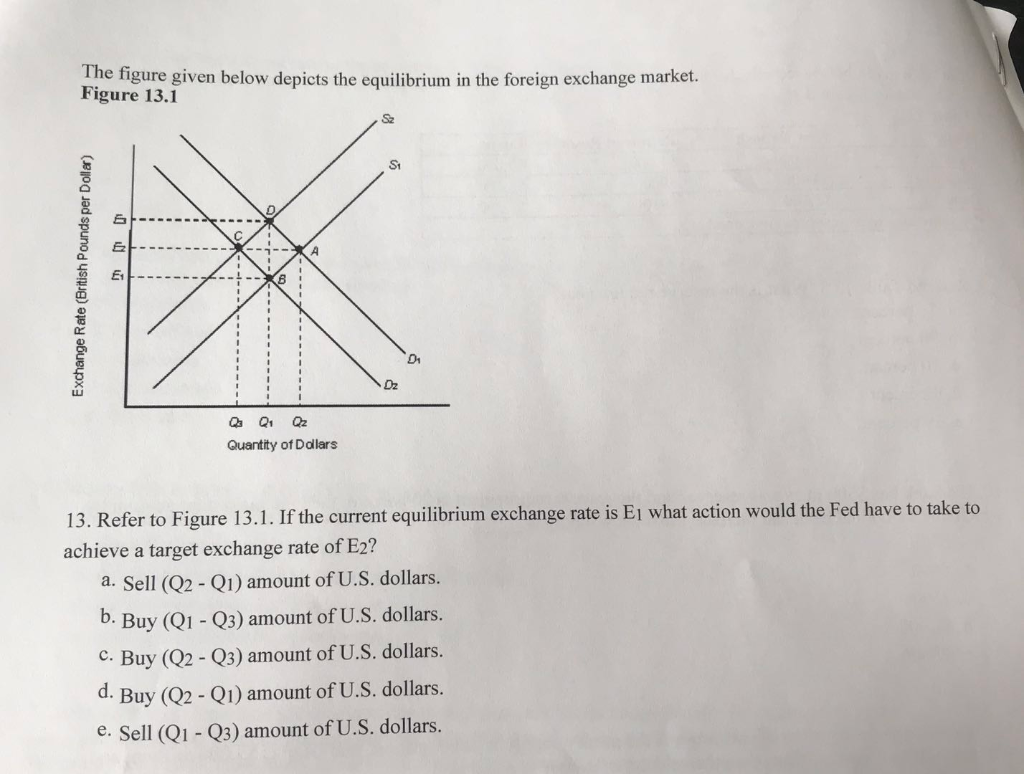
Solved The Figure Given Below Depicts The Equilibrium In The Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: the figure given below depicts the equilibrium in the foreign exchange market. figure 13.1 sz st e a et qa q1 quantity of ddlars 13. refer to figure 13.1. This page discusses using ladder diagrams and algebraic solutions to evaluate and solve equilibrium problems related to chemical reactivity and solubility. it begins with a straightforward example of ….

Solved 19 Consider The Figure Below The Figure Above Chegg Considering the context of long run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market, the most reasonable answer is likely to be the highest quantity that firms can produce sustainably without incurring losses. The figure given below depicts the equilibrium in the foreign exchange market. figure 13.1 sa st a dz q qz quantity of doal lars 13. refer to figure 13.1. if the current equilibrium exchange rate is el what action would the fed have to take to. The table given below shows the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded for a good at different prices. if the price of the good described in the table given below is $1.60, then there is a surplus of 30 units. a price floor set below the cquilibrium price will result in a surplus. The figure given below depicts the long run equilibrium in an aggregate demand aggregate supply model.

Solved The Drawing Below Depicts The Following Reaction At Chegg The table given below shows the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded for a good at different prices. if the price of the good described in the table given below is $1.60, then there is a surplus of 30 units. a price floor set below the cquilibrium price will result in a surplus. The figure given below depicts the long run equilibrium in an aggregate demand aggregate supply model. The consumer surplus is the area between the demand curve and the price level up to the point of equilibrium. it represents the difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and what they actually pay. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: the figure given below depicts the equilibrium in the foreign exchange market. figure 13.1 sa st a dz q qz quantity of doal lars 13. refer to figure 13.1. The figure given below depicts long run equilibrium in the aggregate demand aggregate supply model. which of the following changes is depicted by the movement from y 1 to y 2?. The figure given below depicts long run equilibrium in the aggregate demand aggregate supply model. the movement from y1 to y2in this figure could have been caused by a: figure 10.9 a. positive level of net investment.

The Figure Given Below Represents The Equilibrium In Chegg The consumer surplus is the area between the demand curve and the price level up to the point of equilibrium. it represents the difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and what they actually pay. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: the figure given below depicts the equilibrium in the foreign exchange market. figure 13.1 sa st a dz q qz quantity of doal lars 13. refer to figure 13.1. The figure given below depicts long run equilibrium in the aggregate demand aggregate supply model. which of the following changes is depicted by the movement from y 1 to y 2?. The figure given below depicts long run equilibrium in the aggregate demand aggregate supply model. the movement from y1 to y2in this figure could have been caused by a: figure 10.9 a. positive level of net investment.
Comments are closed.