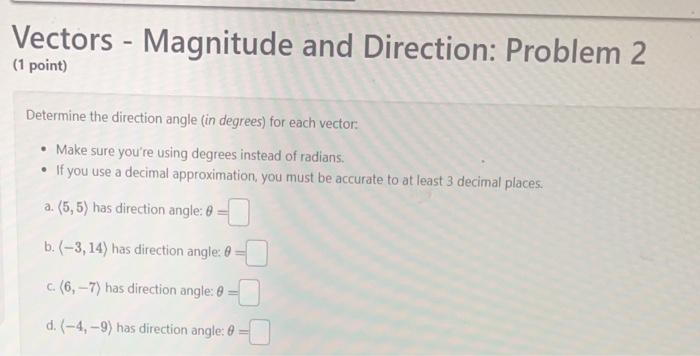
Solved Vectors Magnitude And Direction Problem 2 1 Chegg Vectors magnitude and direction: problem 2 (1 point) determine the direction angle (in degrees) for each vector: make sure you're using degrees instead of radians. if you use a decimal approximation, you must be accurate to at least 3 decimal places. Vectors unit vectors: problem 2 (1 point) drag v into one of the four quadrants, then give the magnitude and direction angle for the unit vector, u. ∥ u ∥ = θ = you must complete.

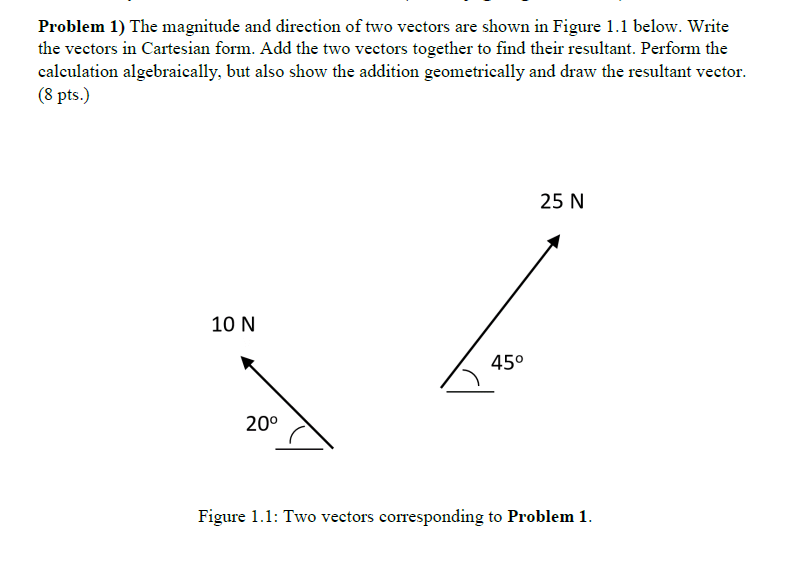
Solved Problem 1 On Vectors In 2d Consider Vector A Of Chegg Question: problem 1) the magnitude and direction of two vectors are shown in figure 1.1 below. write the vectors in cartesian form. add the two vectors together to find their resultant. perform the calculation algebraically, but also show the addition geometrically and draw the resultant vector. Hw1: problem 2.2 determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force of the two forces shown if the resultant force is to be 530 n directed along the positive y axis. This video presents the solution to example problem 2.1: finding the magnitude and direction of the resultant force. before attempting to solve this problem, i recommend reviewing. If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the bracket is 400 lb directed along the positive x axis, determine the magnitude of f 1 and its direction .
Solved Problem 1 The Magnitude And Direction Of Two Vectors Chegg This video presents the solution to example problem 2.1: finding the magnitude and direction of the resultant force. before attempting to solve this problem, i recommend reviewing. If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the bracket is 400 lb directed along the positive x axis, determine the magnitude of f 1 and its direction . Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force, $\mathbf{f} {r}$ measured counterclockwise from the positive $x$ axis. solve the problem by first finding the resultant $\mathbf{f}^{\prime}=\mathbf{f} {2} \mathbf{f} {3}$ and then forming $\mathbf{f} {r}=\mathbf{f}^{\prime} \mathbf{f} {1}$. Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force, fr measured counterclockwise from the positive x axis. solve the problem by first finding the resultant f0 = f1 f2 and then forming fr = f0 f3. draw the triangle that f1 and f2 and their resultant f0 make. Find the magnitude and direction of the second displacement. find the angle with respect to the positive x axis. i started by measuring 110 degrees and drew my vector starting at the origin (origin is point a). Chapter 2 force vectors chapter objectives to show how to add forces and resolve them into components using the parallelogram law. to express force and position in cartesian vector form and explain how to determine the vector’s magnitude and direction. to introduce the dot product in order to determine the angle between two vectors or the.
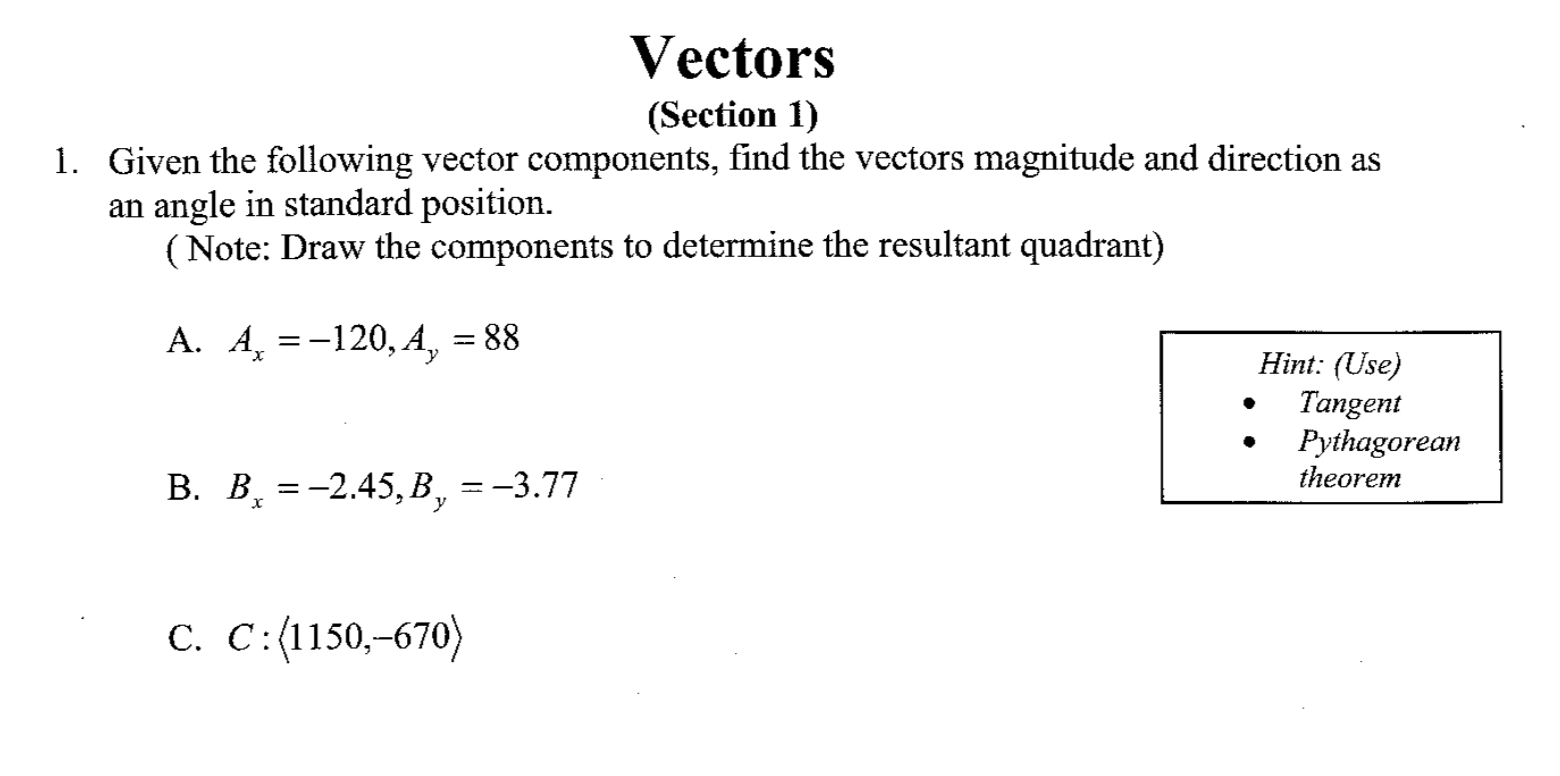
Solved Vectors Section 1 1 Given The Following Vector Chegg Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force, $\mathbf{f} {r}$ measured counterclockwise from the positive $x$ axis. solve the problem by first finding the resultant $\mathbf{f}^{\prime}=\mathbf{f} {2} \mathbf{f} {3}$ and then forming $\mathbf{f} {r}=\mathbf{f}^{\prime} \mathbf{f} {1}$. Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force, fr measured counterclockwise from the positive x axis. solve the problem by first finding the resultant f0 = f1 f2 and then forming fr = f0 f3. draw the triangle that f1 and f2 and their resultant f0 make. Find the magnitude and direction of the second displacement. find the angle with respect to the positive x axis. i started by measuring 110 degrees and drew my vector starting at the origin (origin is point a). Chapter 2 force vectors chapter objectives to show how to add forces and resolve them into components using the parallelogram law. to express force and position in cartesian vector form and explain how to determine the vector’s magnitude and direction. to introduce the dot product in order to determine the angle between two vectors or the.

Solved Problem 2 Determine Magnitude And The Direction Of Chegg Find the magnitude and direction of the second displacement. find the angle with respect to the positive x axis. i started by measuring 110 degrees and drew my vector starting at the origin (origin is point a). Chapter 2 force vectors chapter objectives to show how to add forces and resolve them into components using the parallelogram law. to express force and position in cartesian vector form and explain how to determine the vector’s magnitude and direction. to introduce the dot product in order to determine the angle between two vectors or the.
