
Solved We Know That An Object In Free Fall Accelerates As It Chegg Question: we know that an object in free fall accelerates as it falls to the earth, today you will be investigating the concepts of free fall, gravity, acceleration and velocity. based on kinematics, we know the following equations can be used to mathematically determine certain values. Question: introduction an object in a free fall accelerates under the effect of the gravitational field, but then the drag force acting on it equilibrates with its weight and the object reaches a constant velocity which is also known as the terminal velocity.
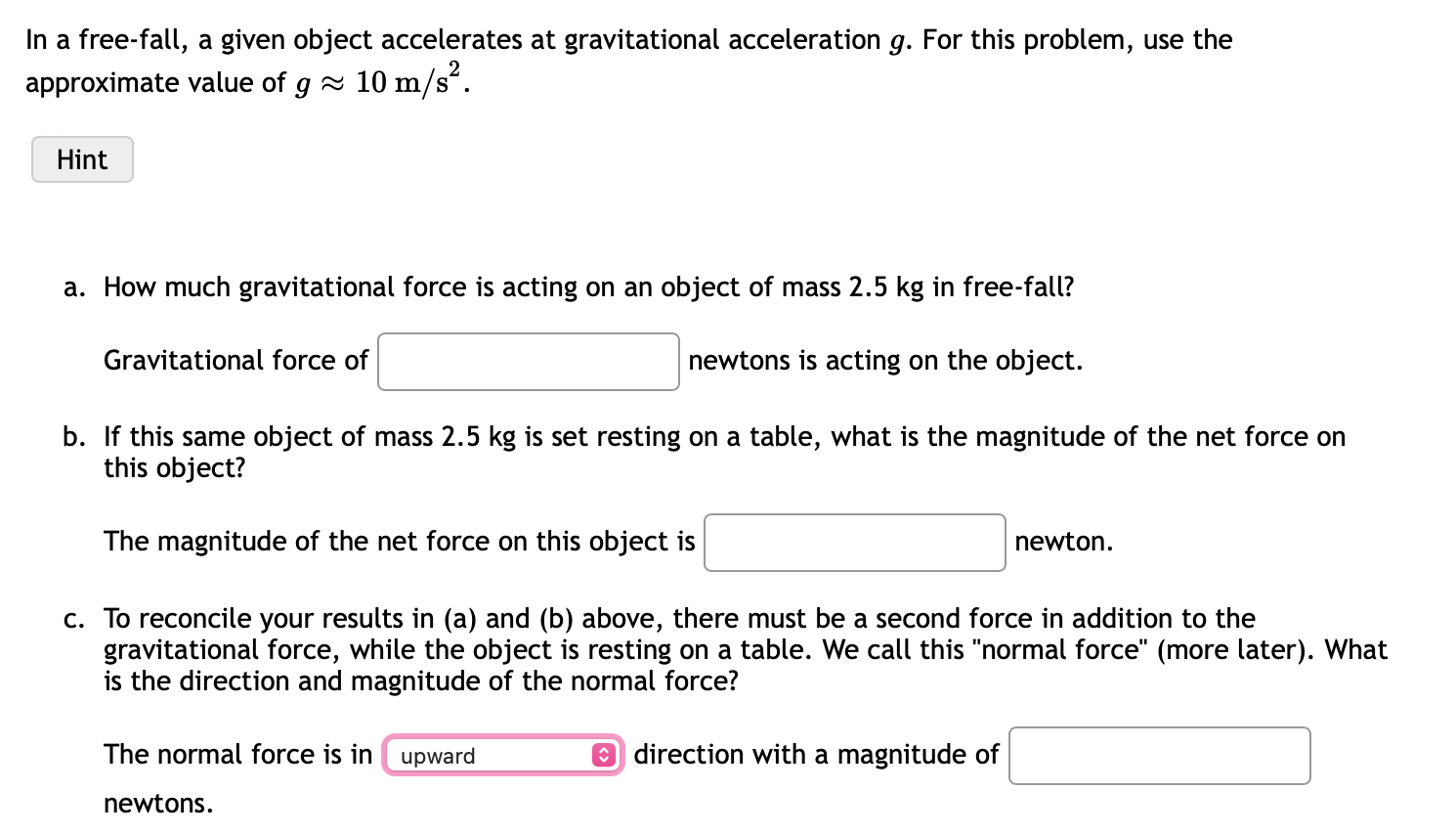
Solved In A Free Fall A Given Object Accelerates At Chegg On earth, all objects in free fall accelerate downward at the rate of gravity or 9.81\text { m s}^2 9.81 m s2. when analyzing free fall motion, we can apply the same kinematic equations as we did for motion on the ground. we can then use these equations to determine properties such as distance, time, and velocity. An object in free fall experiences an acceleration of 9.8 m s s. (the sign indicates a downward acceleration.) whether explicitly stated or not, the value of the acceleration in the kinematic equations is 9.8 m s s for any freely falling object. Aristotle claimed that the speed of a falling object depends on its weight. we now know that objects in free fall, whatever their weights, undergo the same gain in speed. why does weight not aflect acceleration?. Solve for the position, velocity, and acceleration as functions of time when an object is in a free fall. an interesting application of equation 3.3.2 through equation 3.5.22 is called free fall, which describes the motion of an object falling in a gravitational field, such as near the surface of earth or other celestial objects of planetary size.

Solved In A Free Fall A Given Object Accelerates At Chegg Aristotle claimed that the speed of a falling object depends on its weight. we now know that objects in free fall, whatever their weights, undergo the same gain in speed. why does weight not aflect acceleration?. Solve for the position, velocity, and acceleration as functions of time when an object is in a free fall. an interesting application of equation 3.3.2 through equation 3.5.22 is called free fall, which describes the motion of an object falling in a gravitational field, such as near the surface of earth or other celestial objects of planetary size. What can you say about the relative speeds of the two objects at any instant after both objects are in free fall? in other words, will ball b be moving faster, slower, or at the same speed as ball a? why?. For the ideal situations of these first few chapters, an object falling without air resistance or friction is defined to be in free fall. the force of gravity causes objects to fall toward the center of earth. the acceleration of free falling objects is therefore called the acceleration due to gravity. Definition of free fall. free fall is the movement of an object or body only under the influence of gravity. the acceleration is caused by this external force on the object, hence the motion of the object will be accelerated. thus, free fall motion is also popularly known as acceleration due to gravity. An object in a free fall accelerates under the effect of the gravitational field, but then the drag force acting on it equilibrates with its weight and the object reaches a constant velocity which is also known as the terminal velocity.

Solved The Rate Of Acceleration Of An Object In Free Fall Chegg What can you say about the relative speeds of the two objects at any instant after both objects are in free fall? in other words, will ball b be moving faster, slower, or at the same speed as ball a? why?. For the ideal situations of these first few chapters, an object falling without air resistance or friction is defined to be in free fall. the force of gravity causes objects to fall toward the center of earth. the acceleration of free falling objects is therefore called the acceleration due to gravity. Definition of free fall. free fall is the movement of an object or body only under the influence of gravity. the acceleration is caused by this external force on the object, hence the motion of the object will be accelerated. thus, free fall motion is also popularly known as acceleration due to gravity. An object in a free fall accelerates under the effect of the gravitational field, but then the drag force acting on it equilibrates with its weight and the object reaches a constant velocity which is also known as the terminal velocity.

Acceleration Due To Gravity Free Fall Theory In Chegg Definition of free fall. free fall is the movement of an object or body only under the influence of gravity. the acceleration is caused by this external force on the object, hence the motion of the object will be accelerated. thus, free fall motion is also popularly known as acceleration due to gravity. An object in a free fall accelerates under the effect of the gravitational field, but then the drag force acting on it equilibrates with its weight and the object reaches a constant velocity which is also known as the terminal velocity.

Solved Probleman Object Does Free Fall Motion It Hits The Chegg
