
Solved Find Consumer Surplus At The Equilibrium And The Chegg Consumer surplus is the difference between the max unlock this solution for free. There are 3 steps to solve this one. to find the consumer surplus at the equilibrium price using not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly.

Solved The Consumer Surplus At The Equilibrium Point And Chegg Show the area of consumer surplus on the graph, and then determine how much consumer surplus is generated in the market each week. a. price: $250. the graph represents the weekly demand and supply for the game console market. a. what is the equilibrium price and quantity? b. The total of consumer plus producer surplus is greatest at the market equilibrium. refer to the figure above: at equilibrium, consumer surplus is equal to area . Set up the consumer surplus where is the equilibrium quantity and is the equilibrium price. Say the price is $55, what is the consumer surplus? if the price falls from $55 to $45, how much does consumer surplus increase due to more buyers entering the market? use the above figure to answer the below questions! assume: the supply curve intersects the vertical axis at $15 and the demand curve intersects the demand curve at $65.
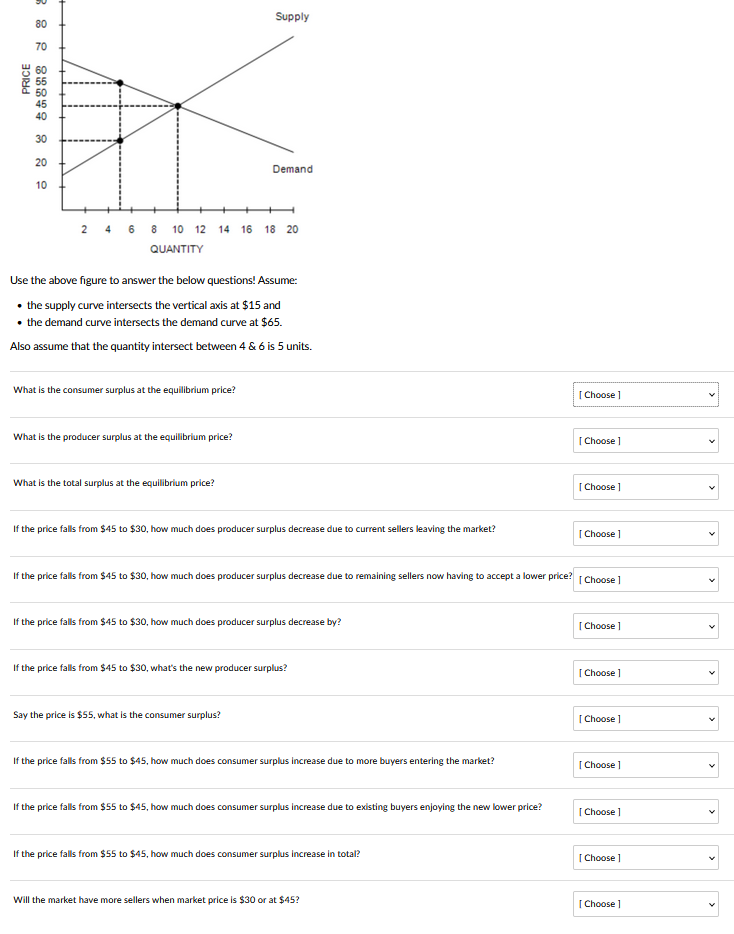
Solved What Is The Consumer Surplus At The Equilibrium Chegg Set up the consumer surplus where is the equilibrium quantity and is the equilibrium price. Say the price is $55, what is the consumer surplus? if the price falls from $55 to $45, how much does consumer surplus increase due to more buyers entering the market? use the above figure to answer the below questions! assume: the supply curve intersects the vertical axis at $15 and the demand curve intersects the demand curve at $65. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price, it results in a surplus of that good or service. in this case, the price floor is set at $9.00, which is above the equilibrium price. this leads to an increase in the producer surplus and the deadweight loss. To calculate consumer surplus at equilibrium, first determine the equilibrium price (p*) and quantity (q*) where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. next, find the demand axis price (p d), which is the price where the demand curve intersects the price axis. Equilibrium consumer surplus producer surplus total surplus in this market is s million. gauth ai solution. 100% (3 rated) answer. the answer is 42750. explanation. the graph shows the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for cameras. Consumer surplus = (1 2) × quantity at equilibrium × (maximum price – equilibrium price) where: quantity → the total market demand for a given good or service at equilibrium.

Solved A What Is The Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Chegg When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price, it results in a surplus of that good or service. in this case, the price floor is set at $9.00, which is above the equilibrium price. this leads to an increase in the producer surplus and the deadweight loss. To calculate consumer surplus at equilibrium, first determine the equilibrium price (p*) and quantity (q*) where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. next, find the demand axis price (p d), which is the price where the demand curve intersects the price axis. Equilibrium consumer surplus producer surplus total surplus in this market is s million. gauth ai solution. 100% (3 rated) answer. the answer is 42750. explanation. the graph shows the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for cameras. Consumer surplus = (1 2) × quantity at equilibrium × (maximum price – equilibrium price) where: quantity → the total market demand for a given good or service at equilibrium.

Solved Consumer Surplus At The Equilibrium Point And C Chegg Equilibrium consumer surplus producer surplus total surplus in this market is s million. gauth ai solution. 100% (3 rated) answer. the answer is 42750. explanation. the graph shows the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for cameras. Consumer surplus = (1 2) × quantity at equilibrium × (maximum price – equilibrium price) where: quantity → the total market demand for a given good or service at equilibrium.
