Solving The Bessel Equation For General Order Of Nu Using The Frobenius Method
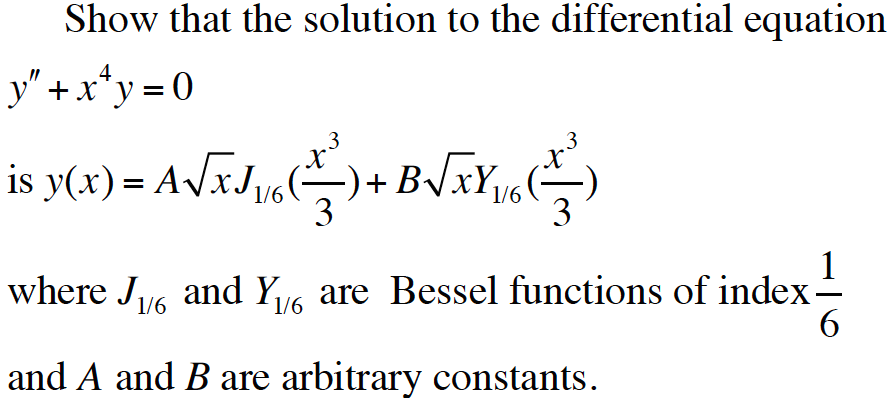
Solved Second Order Differential Equation Applying Chegg In this lecture we will consider the frobenius series solution of the bessel equation, which arises during the process of separation of variables for problems with radial or cylindrical symmetry. Lindrical co ̈ordinates. the bessel equation is solved by series solution methods, in fact, to solve the bessel equation you need to use t. e method of fr ̈obenius. it might be expected that fr ̈obenius is needed because of the singularities at x = 0, however, lets pretend we hadn’t noticed and try to use the ordina. se everything t.
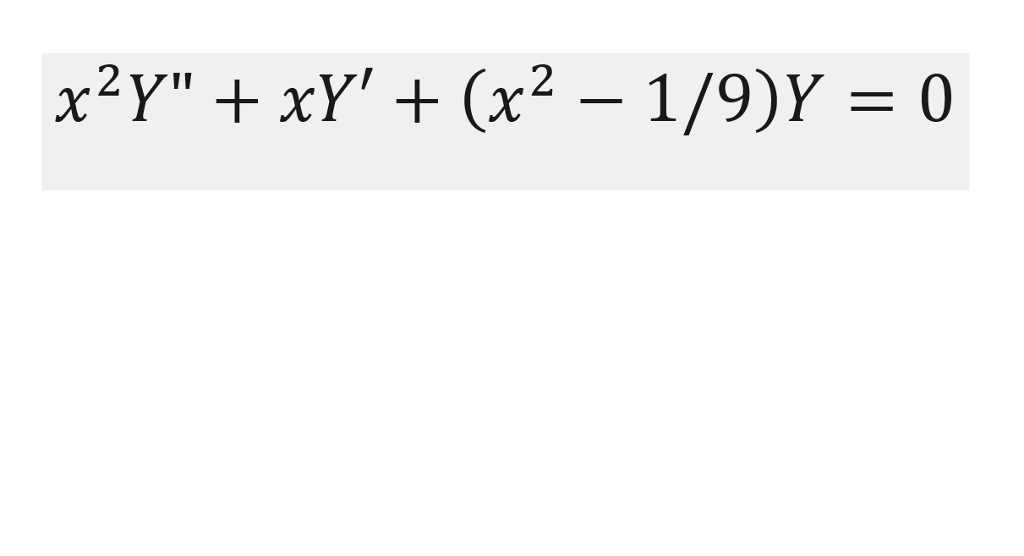
Solved Use The Method Of Frobenius To Solve The Bessel Chegg Bessel equation of order . (1) 0; is called the the point x0 = 0 is a regular singular point. we shall use the method of frobenius to solve this equation. thus, we seek solutions of the form 1 x y(x) = anxn r; x > 0;. Once point (i) has been solved, solve the new differential equation for u(x) u (x). the general solution is what you name y2. this end point (ii). for (iii), look at each of the pieces which compose y2. you know that cos(x) c o s (x) and sin(x) s i n (x) are finite and bounded for all values of x x and that x−1 2 x − 1 2 is defined for ???. The general solution to bessel’s equation is y = c1j (x) c2y (x) where c1 and c2 are constants that are determined by the boundary conditions on the differential equation. The parameter is called the order of the bessel function. bessel’s equation arises when finding solutions to laplace’s equation and the helmholtz equation in cylindrical or spherical coordinates.
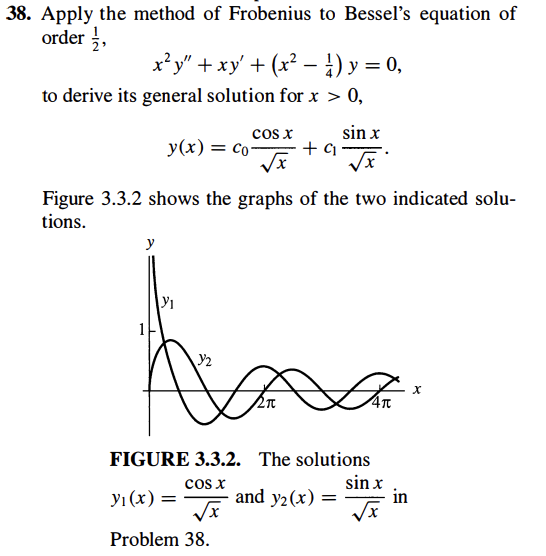
Solved 38 Apply The Method Of Frobenius To Bessel S Chegg The general solution to bessel’s equation is y = c1j (x) c2y (x) where c1 and c2 are constants that are determined by the boundary conditions on the differential equation. The parameter is called the order of the bessel function. bessel’s equation arises when finding solutions to laplace’s equation and the helmholtz equation in cylindrical or spherical coordinates. Bessel’s equation of order ν is given by. clearly x = 0 is a regular singular point, so we can solve by frobenius’ method. the indicial equation is obtained from the lowest power after the substitution y = x γ, and is. so a generalised series solution gives two independent solutions if ν ≠ 1 2 n. Bessel equation and bessel functions of order x2y00 xy0 (x2 2)y = 0; 0 x p0 = lim x = 1; x!0 x2. Determine the indicial equation (solve for r) and the recursion formula. find a basis for the solution space and use this to write the general solution. what is the radius of convergence of each of these two linearly independent solutions?.

Bessels Equation Of Order N Bessel Equation Solution Bessel’s equation of order ν is given by. clearly x = 0 is a regular singular point, so we can solve by frobenius’ method. the indicial equation is obtained from the lowest power after the substitution y = x γ, and is. so a generalised series solution gives two independent solutions if ν ≠ 1 2 n. Bessel equation and bessel functions of order x2y00 xy0 (x2 2)y = 0; 0 x p0 = lim x = 1; x!0 x2. Determine the indicial equation (solve for r) and the recursion formula. find a basis for the solution space and use this to write the general solution. what is the radius of convergence of each of these two linearly independent solutions?.
Comments are closed.