Structure Of Bone Tissue Bone Structure Anatomy Components Of Bones
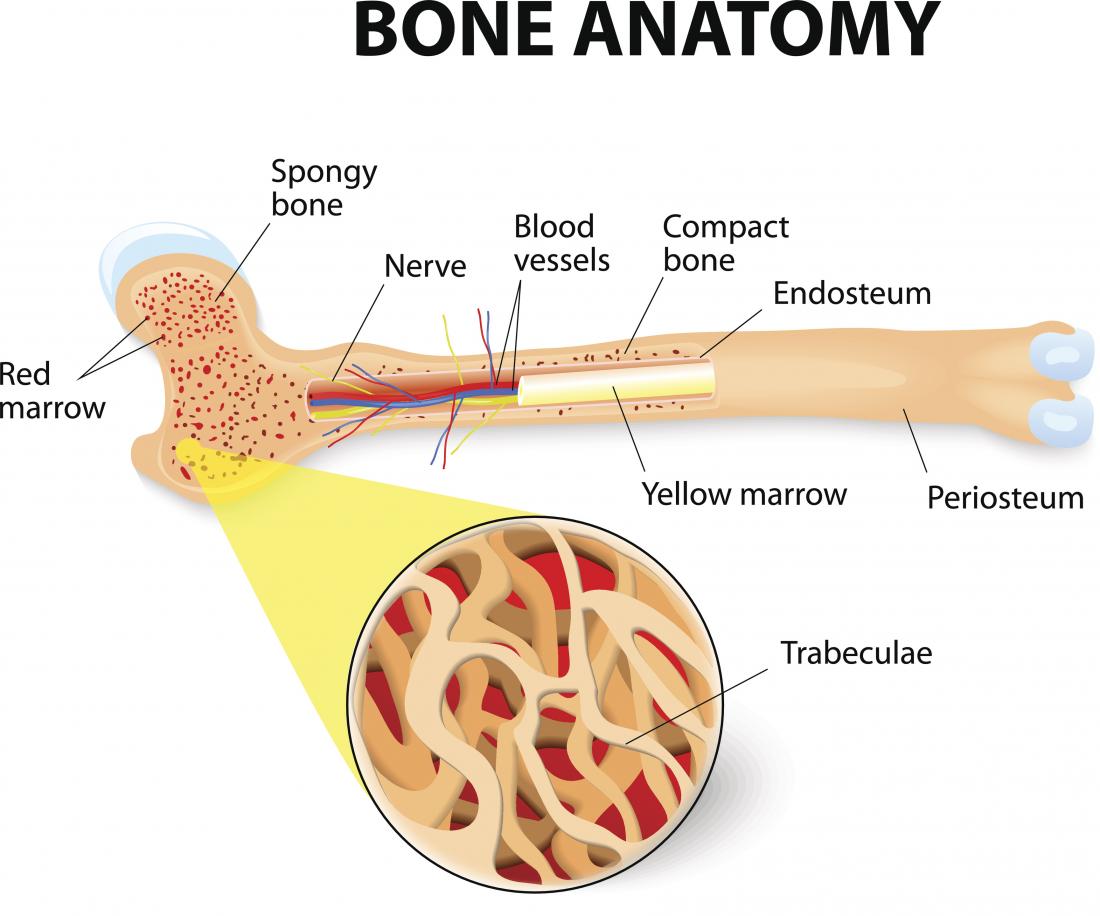
Structure Of Bone Science Online In this video we discuss the structure of bone tissue and the components of bones. we also discuss what are osteons, what are canaliculi, what are trabeculae, and the components of. In this article, we shall look at the ultrastructure of bone – its components, structure and development. we shall also examine how disease can affect its structure.
Solved Human Anatomy Bone Cells And Tissue Structure 1 What Chegg This detailed anatomical illustration provides a clear view of a typical long bone’s internal structure, demonstrating the various tissue types that contribute to its unique properties and functions, from mechanical support to hematopoiesis. Osteoblasts are bone forming cell, osteoclasts resorb or break down bone, and osteocytes are mature bone cells. an equilibrium between osteoblasts and osteoclasts maintains bone tissue. compact bone consists of closely packed osteons or haversian systems. Bone is a rigid body tissue consisting of cells embedded in an abundant hard intercellular material. bone tissue makes up the individual bones of the skeletons of vertebrates. its two principle components are collagen and calcium phosphate. From a histological perspective, bones are highly specialized connective tissues that can remodel based on exogenous demand. the cell primarily responsible for building bones is the osteoblast, which secretes a collagen rich fluid known as osteoid.
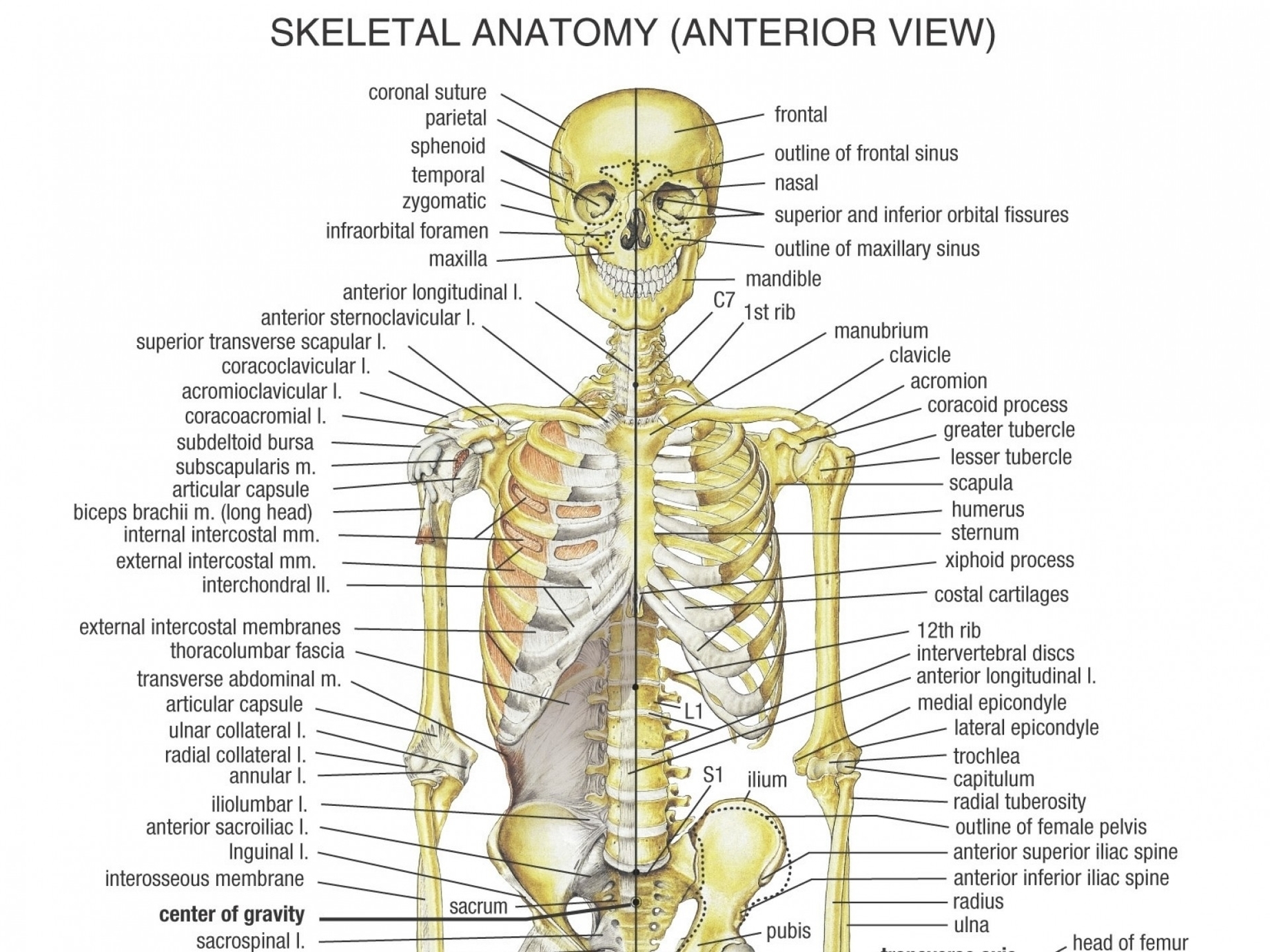
Human Bone Structure Explanation Anatomy System Human Body Anatomy Bone is a rigid body tissue consisting of cells embedded in an abundant hard intercellular material. bone tissue makes up the individual bones of the skeletons of vertebrates. its two principle components are collagen and calcium phosphate. From a histological perspective, bones are highly specialized connective tissues that can remodel based on exogenous demand. the cell primarily responsible for building bones is the osteoblast, which secretes a collagen rich fluid known as osteoid. A typical bone in your body contains 3 types of tissue—a hard outer tissue, a sponge like inner tissue, and smooth tissue at the ends. Bones are organs that consist primarily of bone tissue, also called osseous tissue. bone tissue is a type of connective tissue consisting mainly of a collagen matrix that is mineralized with calcium and phosphorus crystals. the combination of flexible collagen and hard mineral crystals makes bone tissue hard, without making it brittle. In this guide, we break down bone structure, naming each part, its function, and how it contributes to overall skeletal health — perfect for biology students, medical aspirants, or curious learners. Bone tissue (osseous tissue) differs greatly from other tissues in the body. bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness. later discussions in this chapter will show that bone is also dynamic in that its shape adjusts to accommodate stresses.
Comments are closed.