Supported Protocols On An Irb Interface In Evpn Vxlan Junos Os

Vxlan Evpn An Introduction To Virtual Extensible Lan Pdf Networks When configuring an esi interface for multihomed devices, junos os only supports routing protocols that are configured on an irb in the all active multihoming mode in a centrally routed bridging overlay evpn vxlan network. Note on the s4248 on switch, ipv6 overlay routing between virtual networks is not supported with static vxlan. ipv6 overlay routing is, however, supported with bgp evpn asymmetric irb. each tenant is assigned a vrf and each virtual network interface is assigned an ip subnet in the tenant vrf.
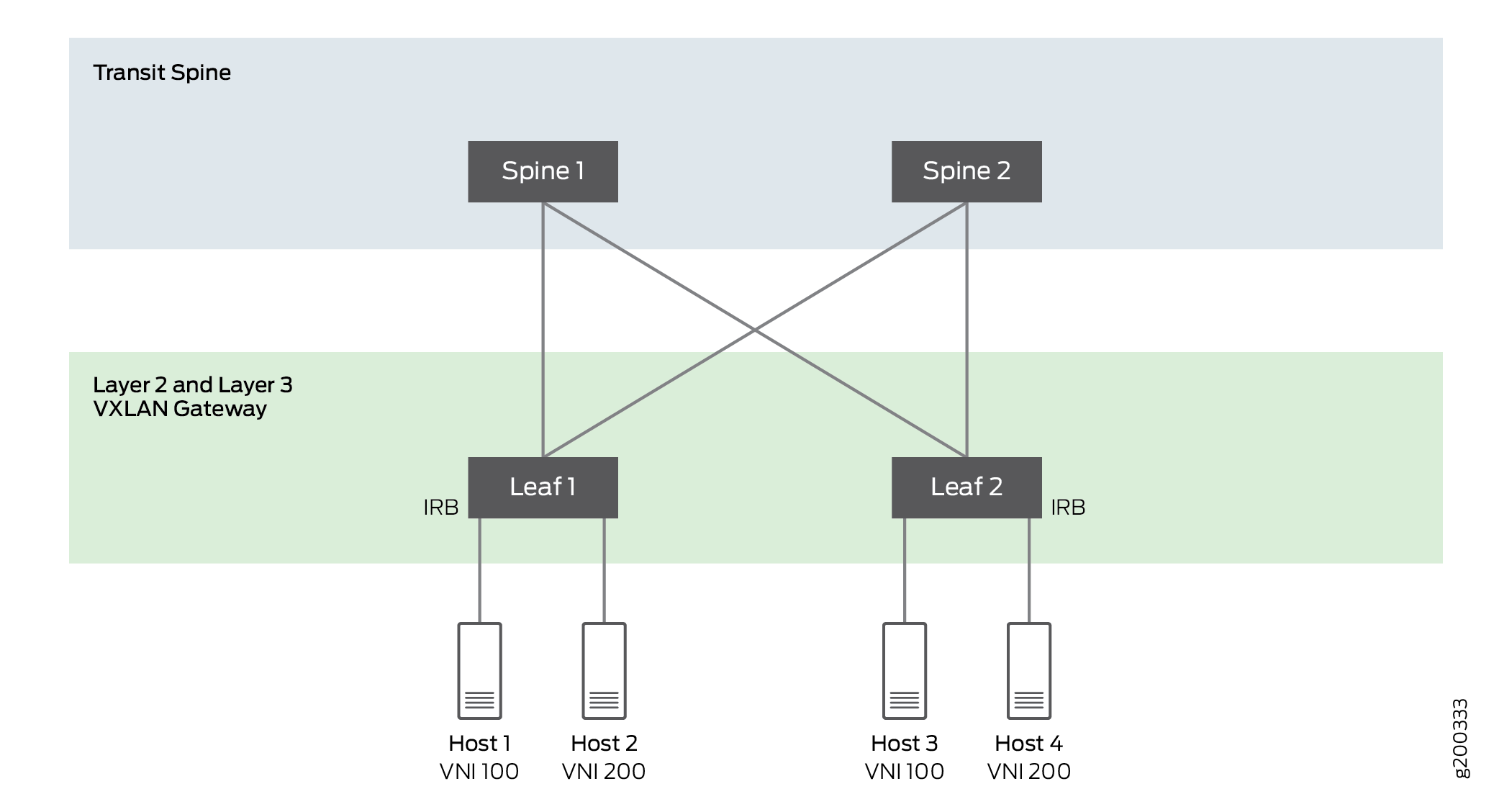
Supported Protocols On An Irb Interface In Evpn Vxlan Junos Os In this case, a given vtep needs to learn the arp and mac address entries only for tenant systems (tss) across the tenant vxlan network belonging to vnids attached to that vtep. in this mode, the ingress vtep perform layer 2 and layer 3 lookups and egress vteps perform layer 2 lookups only. This page provides an overview of symmetric integrated routing and bridging (irb) with evpn over virtual extensible lan (vxlan) tunnels. we also introduce the elements you configure to enable symmetric evpn type 2 routing. Note: symmetric irb is recommended, as it does not require that all vlans and vrfs exist everywhere to guarantee host reachability. additionally, with symmetric irb, remote arp entries are maintained in software instead of consuming hardware resources. Configure symmetric irb for vxlan bgp evpn before you start follow the procedure in configure vxlan to: configure the vxlan overlay network. enable routing for vxlan virtual networks. integrated routing and bridging (irb) is automatically enabled. enable an overlay routing profile with the number of reserved arp table entries for vxlan overlay routing. follow the procedure in configure bgp.

Vxlan Evpn Irb Overview Fabricplane Note: symmetric irb is recommended, as it does not require that all vlans and vrfs exist everywhere to guarantee host reachability. additionally, with symmetric irb, remote arp entries are maintained in software instead of consuming hardware resources. Configure symmetric irb for vxlan bgp evpn before you start follow the procedure in configure vxlan to: configure the vxlan overlay network. enable routing for vxlan virtual networks. integrated routing and bridging (irb) is automatically enabled. enable an overlay routing profile with the number of reserved arp table entries for vxlan overlay routing. follow the procedure in configure bgp. This is an example of an evpn vxlan ip fabric based on a centrally routed bridging (crb) architecture. integrated routing and bridging (irb) interfaces provide layer 3 (l3) connectivity to servers and vms that belong to different vlans and networks. these irb interfaces serve as the default gateway for inter vlan traffic within a fabric. You configure irb interfaces irb.101, irb.102, and irb.103 to function as default l3 gateways that handle server inter vlan traffic. to that end, in each irb interface configuration, you also include a virtual gateway address (vga), which configures an irb interface as a default l3 gateway. The vtep acts as the l3 gateway that routes traffic from one tenant subnet to another in the overlay before encapsulating it in the vxlan header and transporting it over the underlay fabric. on virtual networks that associate with evis, evpn irb is enabled only after you create a virtual network interface. To support this use case in releases prior to 22.4r1, you can configure the irb interface in a routing instance of type vrf instead of in the default routing instance.

Vxlan Evpn Irb Overview Fabricplane This is an example of an evpn vxlan ip fabric based on a centrally routed bridging (crb) architecture. integrated routing and bridging (irb) interfaces provide layer 3 (l3) connectivity to servers and vms that belong to different vlans and networks. these irb interfaces serve as the default gateway for inter vlan traffic within a fabric. You configure irb interfaces irb.101, irb.102, and irb.103 to function as default l3 gateways that handle server inter vlan traffic. to that end, in each irb interface configuration, you also include a virtual gateway address (vga), which configures an irb interface as a default l3 gateway. The vtep acts as the l3 gateway that routes traffic from one tenant subnet to another in the overlay before encapsulating it in the vxlan header and transporting it over the underlay fabric. on virtual networks that associate with evis, evpn irb is enabled only after you create a virtual network interface. To support this use case in releases prior to 22.4r1, you can configure the irb interface in a routing instance of type vrf instead of in the default routing instance.
Comments are closed.