Suppose That F 4 3 G 4 2 F 4 5 I And G 4 4 Chegg
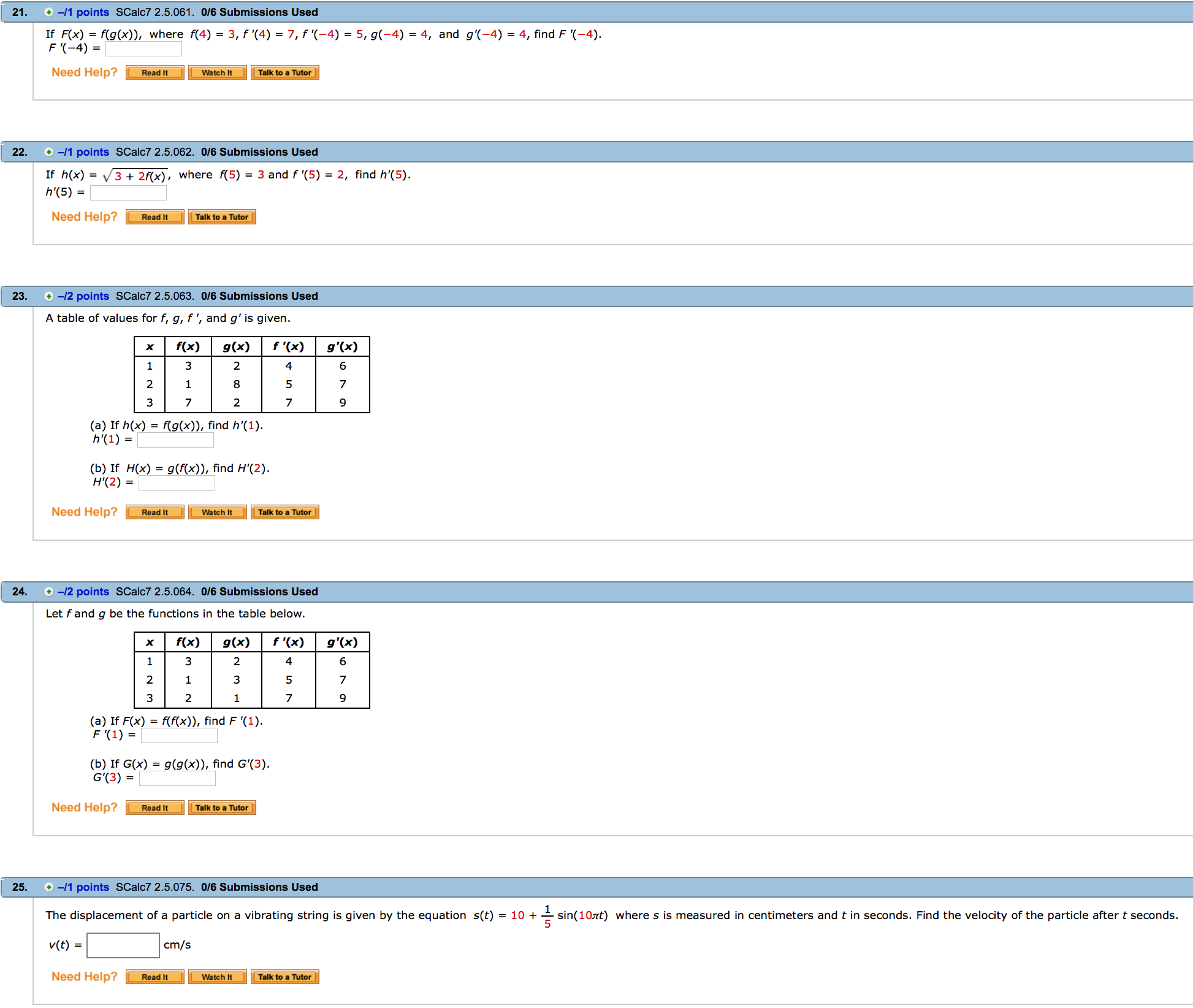
Solved If F X F G X Where F 4 3 F 4 7 F Chegg Suppose that f (4) = 3, g (4) = 5, f' (4) = 4, and g' (4) = 2. find h' (4). (a) h (x) = 2f (x) 5g (x) h' (4) = (b) h (x) = f (x)g (x) h' (4) = = f (x) (c) h (x) g (x) h' (4) = (d) h (x) g (x) f (x) g (x) h' (4) your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. To find h' (4) for each function, we need to use the rules of differentiation and the given** information **about f (x) and g (x). (a) for h (x) = 4f (x) 5g (x), we can** differentiate** each term separately.

Solved Suppose That F 4 3 G 4 4 F 4 2 And Chegg Suppose g is the inverse function of f and f (4) = 5, f (5) = 2, f' (4) = 3 4 , and f' (5) = 2 3. find g' (5). Suppose that f (4) = 3, g (4) = 5, f' (4) ~4, and g' (4) 2 find h' (4). (a) h (x) 2f (x) sg (x) h' (4) = (b) h (x) = fx)g (x) h' (4) = f (x) (c) h (x) = g (x) h' (4) = h (x) g (x) (d) f (x) g (x) h' (4) = 03:09. Find step by step calculus solutions and the answer to the textbook question suppose that f (4) = 2, g (4) = 5, f' (4) = 6, and g' (4) = 3. find h' (4). $h (x)=\frac {f (x)} {g (x)}$. Given that h (x) is defined as 5f (x) 3g (x), where f (x) and g (x) are functions, we can find h' (x) by taking the derivatives of f (x) and g (x) and multiplying them by their respective coefficients.
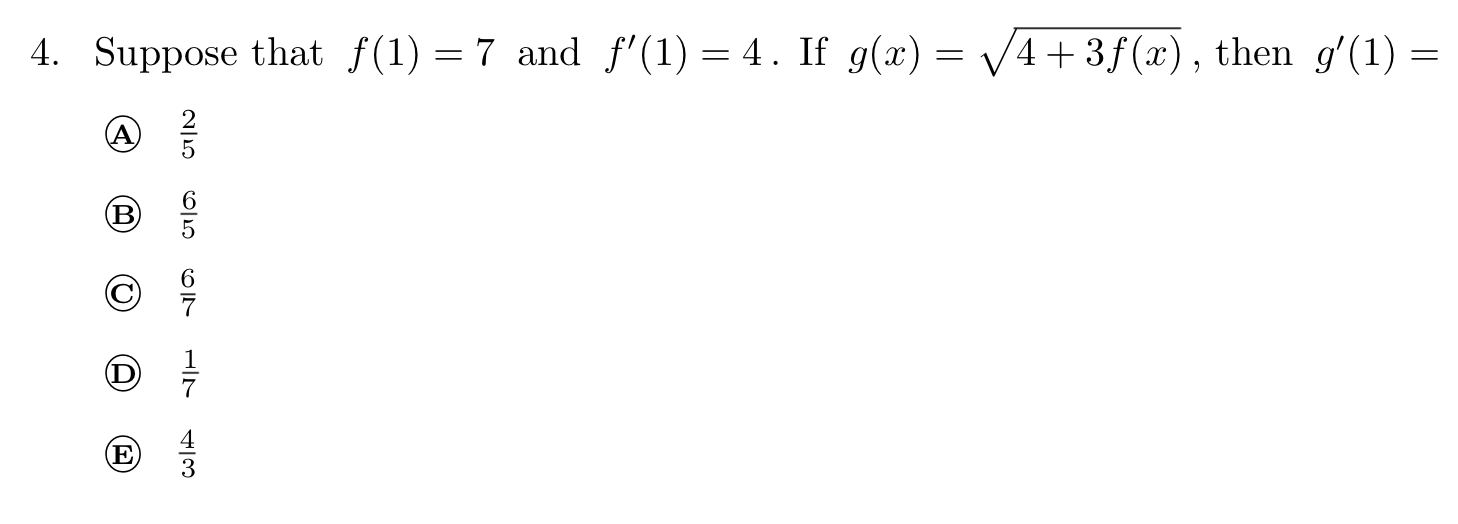
Solved 4 Suppose That F 1 7 And F 1 4 If G X 4 3f X Chegg Find step by step calculus solutions and the answer to the textbook question suppose that f (4) = 2, g (4) = 5, f' (4) = 6, and g' (4) = 3. find h' (4). $h (x)=\frac {f (x)} {g (x)}$. Given that h (x) is defined as 5f (x) 3g (x), where f (x) and g (x) are functions, we can find h' (x) by taking the derivatives of f (x) and g (x) and multiplying them by their respective coefficients. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: suppose that f (4) = 2, g (4) = 3, f ′ (4) = −5, and g ′ (4) = 4. find h ′ (4). Video answer: fine edge, primal four. so here we take for party edge. prime force should just be three of prime for plus eight g prime before and this one will be three times two plus eight times five. so that's ah. This formula helps you to find the derivative by considering both the numerator f (x) and the denominator g (x). it's particularly useful when directly differentiating such functions seems challenging. We're given the function h (x) = 2f (x) 5g (x) and asked to find h' (4). here's how we'll do it; since h (x) is a sum of two functions we use the sum rule, and because those functions are being multiplied by constants, we’ll also the constant rule.

Solved Suppose That F 4 2 G 4 4 F 4 3 And Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: suppose that f (4) = 2, g (4) = 3, f ′ (4) = −5, and g ′ (4) = 4. find h ′ (4). Video answer: fine edge, primal four. so here we take for party edge. prime force should just be three of prime for plus eight g prime before and this one will be three times two plus eight times five. so that's ah. This formula helps you to find the derivative by considering both the numerator f (x) and the denominator g (x). it's particularly useful when directly differentiating such functions seems challenging. We're given the function h (x) = 2f (x) 5g (x) and asked to find h' (4). here's how we'll do it; since h (x) is a sum of two functions we use the sum rule, and because those functions are being multiplied by constants, we’ll also the constant rule.
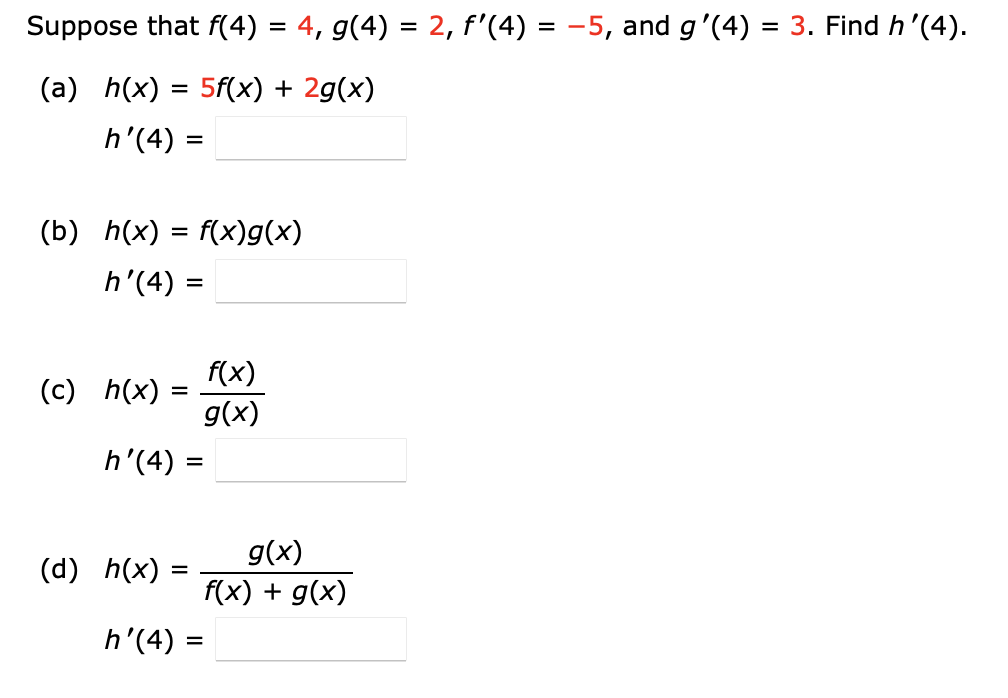
Solved Suppose That F 5 1 F 5 2 G 5 6 And G 5 4 Chegg This formula helps you to find the derivative by considering both the numerator f (x) and the denominator g (x). it's particularly useful when directly differentiating such functions seems challenging. We're given the function h (x) = 2f (x) 5g (x) and asked to find h' (4). here's how we'll do it; since h (x) is a sum of two functions we use the sum rule, and because those functions are being multiplied by constants, we’ll also the constant rule.

Solved Suppose That F 4 3 G 4 2 F 4 5 ï And G 4 4 Chegg
Comments are closed.