The Overview Of Fermentation Processes Pdf Metabolism Fermentation

The Overview Of Fermentation Processes Pdf Metabolism Fermentation Batch fermentation is defined as the fermentation process is carried out in defined volume at a particular period of time. in batch fermentation six phases of the microbial growth [lag phase, acceleration phase, log phase, deceleration phase, stationary and death] is observed. Simple classification of fermentation based on the nature of the process (criteria: processes based on traditional procedures vs. processes based on technological facilities).
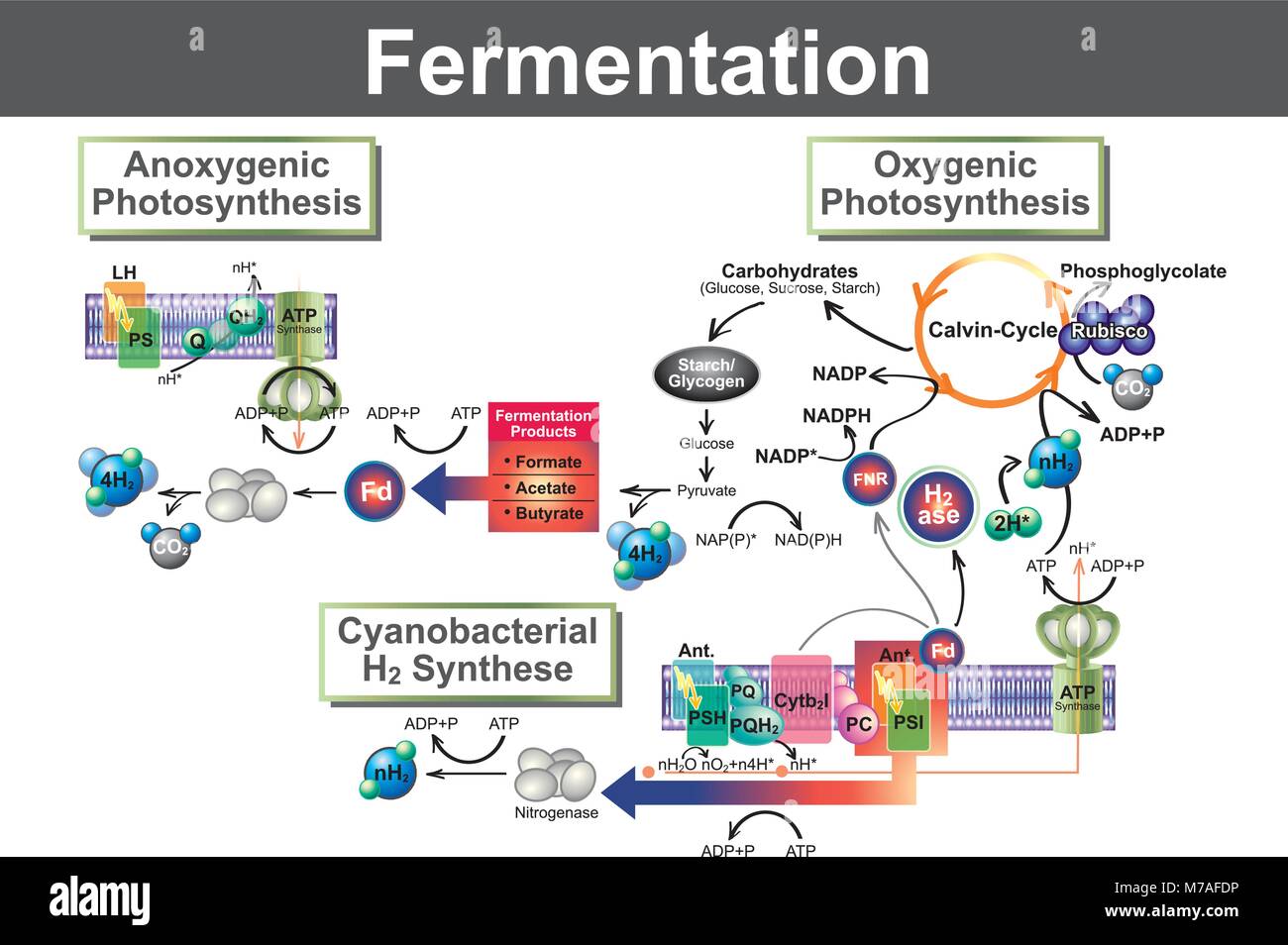
Effizienz Der Fermentation The overview of fermentation processes free download as powerpoint presentation (.ppt .pptx), pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Fermentation is a metabolic process that converts sugar to acids, gases or alcohol. it occurs in yeast and bacteria, and also in oxygen starved muscle cells, as in the case of lactic acid fermentation. Regardless of the type of fermentation (with the possible exception of some transformation processes) an established process may be divided into six basic component parts:. During the fermentation process, these beneficial microbes break down sugars and starches into alcohols and acids, making food more nutritious and preserving it so people can store it for longer periods of time without it spoiling. fermentation products provide enzymes necessary for digestion.
Introduction To Fermentation And Range Of Fermentation Processes Pdf Regardless of the type of fermentation (with the possible exception of some transformation processes) an established process may be divided into six basic component parts:. During the fermentation process, these beneficial microbes break down sugars and starches into alcohols and acids, making food more nutritious and preserving it so people can store it for longer periods of time without it spoiling. fermentation products provide enzymes necessary for digestion. For fermentation’s carried out with single celled organisms such as bacteria and yeast’s, the resistance in the phase boundary between the gas bubble and the liquid is the most important factor controlling the rate of transfer. Strictly speaking, fermentation is the process of anaerobic breakdown or fragmentation of organic compounds by the metabolic processes of micro organisms. Fermentation allows organisms to produce atp under anaerobic conditions, but it is not efficient in terms of capturing the energy potentially available in glucose molecules (only about 2% of the energy available is captured).
Comments are closed.