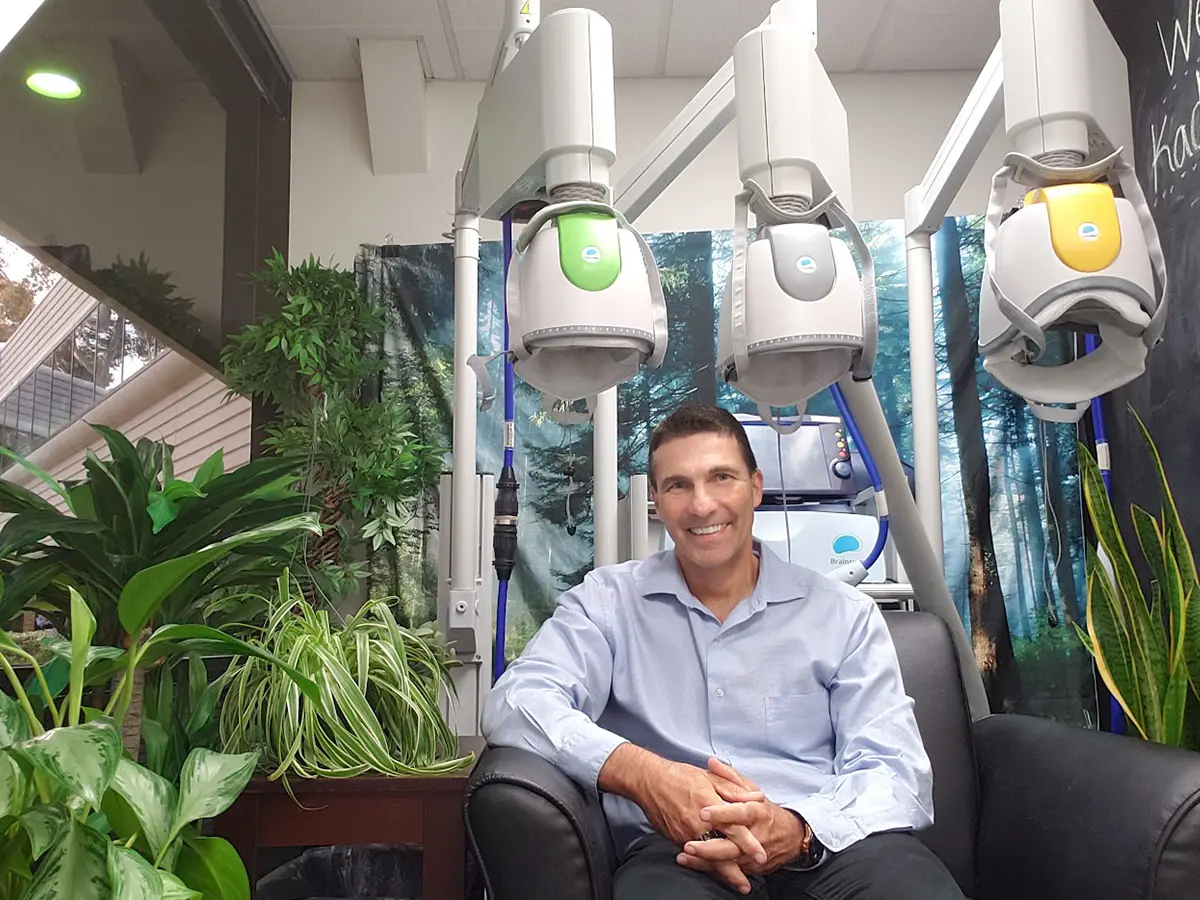

Tms Vs Ect Therapy Choosing A Treatment For Depression How is tms different from ect? tms uses magnetic pulses to cause neuroplasticity – the brain’s ability to mend and build connections between the nerve cells – and targets only the small area of the brain that is understood to cause the symptoms of depression (the prefrontal cortex). this is a non invasive treatment. With new depression treatment options emerging, it’s natural to compare them to tms. let’s see how tms depression treatment in perth compares: while highly effective, ect requires anaesthesia, induces a controlled seizure with electrical stimulation, and can have side effects like memory loss.
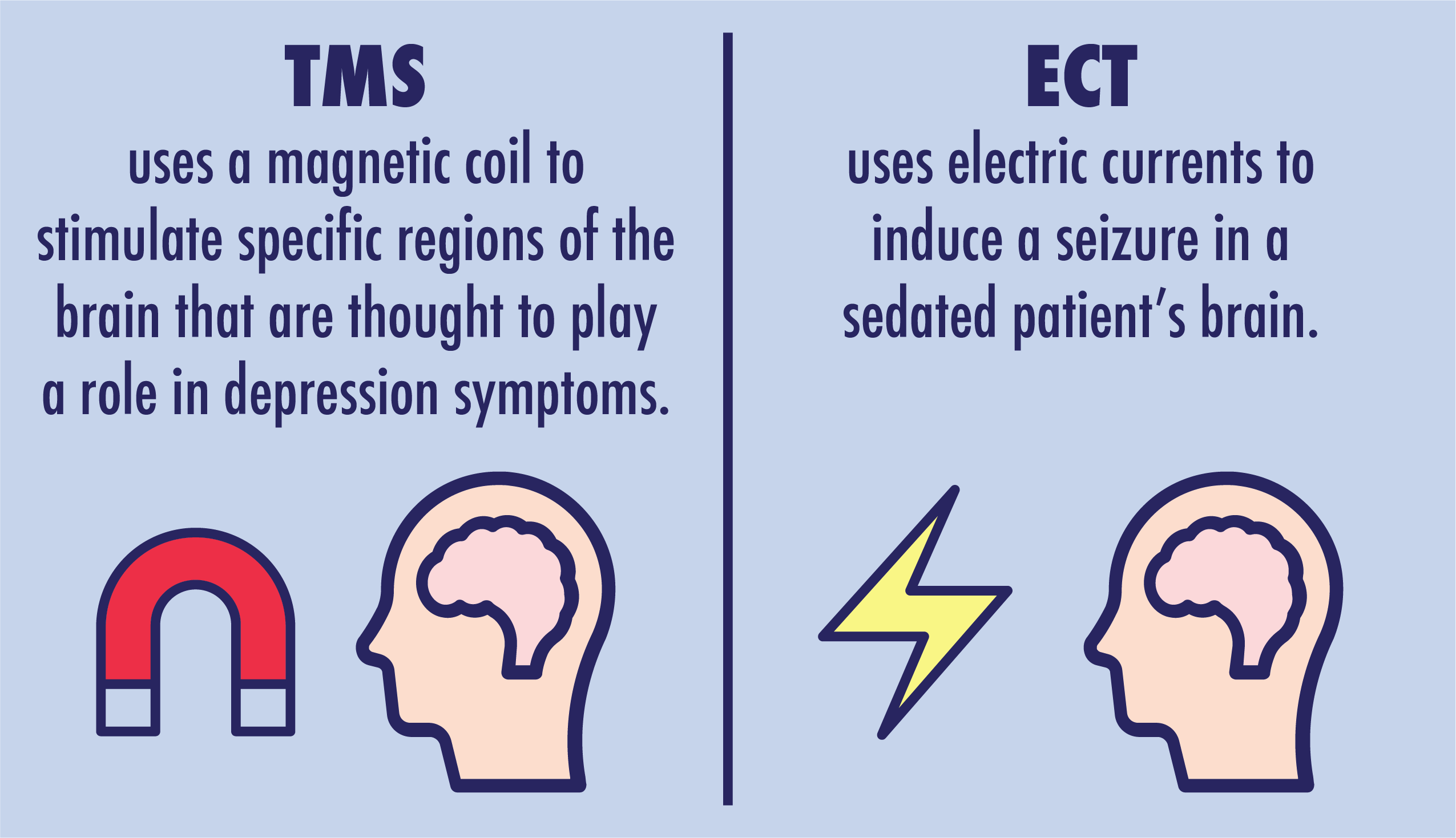
Tms Therapy Vs Ect What S The Difference And When Should 54 Off Tms therapy vs electric shock (ect): tms sessions last about 20 40 minutes and are done while you’re awake and alert. ect sessions are shorter but require preparation for anesthesia. frequency: tms typically requires daily sessions over 4 6 weeks. ect might need fewer sessions but involves recovery time. Tms therapy uses magnetic pulses to stimulate the brain, whereas ect uses electrical currents. tms is non invasive and requires no recovery time, while ect requires general anaesthesia and hospitalisation. ect can be beneficial for severe cases of depression, but tms has fewer and much milder side effects. Comparing tms vs medications transcranial magnetic stimulation (tms), since its introduction in 1985, has been studied for its efficacy in different psychiatric disorders. it has been touted to be an effective treatment modality for major depression, obsessive compulsive disorder, tourette syndrome, and in reducing auditory hallucinations in. Tms is better suited for patients with moderate to severe depression who have not responded to medication but want a non invasive treatment with minimal side effects. ect is preferable for patients with severe, life threatening depression, particularly those experiencing psychotic symptoms, catatonia, or high suicide risk, as it has a higher.

Los Angeles Tms Therapy And Depression Treatment Tms Vs Ect What S Comparing tms vs medications transcranial magnetic stimulation (tms), since its introduction in 1985, has been studied for its efficacy in different psychiatric disorders. it has been touted to be an effective treatment modality for major depression, obsessive compulsive disorder, tourette syndrome, and in reducing auditory hallucinations in. Tms is better suited for patients with moderate to severe depression who have not responded to medication but want a non invasive treatment with minimal side effects. ect is preferable for patients with severe, life threatening depression, particularly those experiencing psychotic symptoms, catatonia, or high suicide risk, as it has a higher. At first mention of transcranial magnetic stimulation (tms) therapy, individuals might confuse it with electroconvulsive therapy (ect). it’s a common association since both therapies entail stimulating the brain and are frequently employed to address treatment resistant depression, and various mood disorders. Electroconvulsive therapy (ect) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (tms) are the leading choices for treatment resistant cases like depression. differences include how they work, the experience, and side effects. knowing these helps guide treatment decisions. informed choices come from knowing these details. what is ect therapy?. Deciding whether tms or ect is the better treatment depends on a person’s unique needs and circumstances. both are effective for major depression, but each one differs in how they work, intensity, and side effects. tms is a less invasive option for moderate cases or when other treatments haven’t worked. While ect can offer rapid relief for severe, treatment resistant conditions, tms provides a more targeted approach with minimal disruption to daily life. it’s an excellent alternative for patients who prefer a less invasive treatment or have concerns about memory loss and other risks associated with ect.
