
Misconduct And Professional Boundaries Georgia Composite Medical Board Memory loss is a common but often overlooked consequence of post traumatic stress disorder (ptsd) and childhood trauma. trauma can significantly impact cognitive functions, particularly short term and long term memory, making it difficult for individuals to recall past experiences or retain new information. On rare occasions, memory loss could be an effect of trauma. how does trauma affect memory? memory loss describes a broad range of symptoms that may present with an inability to recall.

Trauma And Memory In "resilience after trauma: the role of memory suppression" (february 14, p. 756), mary et al. (1) demonstrated in a fmri study that deficits in memory control facilitate the development of ptsd with a group of 102 individuals exposed to the 2015 paris terrorist attacks and a group of 73 unexposed individuals who were not present in paris. We hypothesize that traumatic memory is inherently dissociable from typical autobiographical memory in how it is formed and represented, as recently put forth by perl and colleagues 20, and add. In contrast to the extensive memory of sensory perceptual information, storage of traumatic events in the autobiographic memory is dramatically impeded in patients who suffer from ptsd. memories of traumatic events are characterized by a disconnectedness of sensory perceptual representations from temporal and spatial information about the. Memory and trauma is the deleterious effects that physical or psychological trauma has on memory. memory is defined by psychology as the ability of an organism to store, retain, and subsequently retrieve information. when an individual experiences a traumatic event, whether physical or psychological trauma, their memory can be affected in many.

Can Trauma Cause Memory Loss In contrast to the extensive memory of sensory perceptual information, storage of traumatic events in the autobiographic memory is dramatically impeded in patients who suffer from ptsd. memories of traumatic events are characterized by a disconnectedness of sensory perceptual representations from temporal and spatial information about the. Memory and trauma is the deleterious effects that physical or psychological trauma has on memory. memory is defined by psychology as the ability of an organism to store, retain, and subsequently retrieve information. when an individual experiences a traumatic event, whether physical or psychological trauma, their memory can be affected in many. In the present study, we explored the association between trauma exposure, age at first exposure, and cognitive functioning, defined herein as executive functioning (ef) and episodic memory (em), to clarify the lasting effects of trauma exposure and age at first exposure on the level of and change in adulthood cognitive functioning. In the community, traumatic brain injury (tbi) is common and individuals with tbi frequently have memory problems. it is crucial to study how tbi affects memory to better understand the underlying mechanism and to tailor rehabilitation for patients with a range of pathologies and severity levels. This chapter reviews how memory develops through the lifetime, and how understanding these normal processes illuminates the effects of trauma on memory. it addresses controversies in memory research as well as how memory interacts with other neurological and interpersonal systems. Research suggests that exposure to trauma can lead to alterations in memory processes, including disturbances in autobiographical memory, fragmented or intrusive memories of the traumatic event (flashbacks), and difficulties in differentiating between past and present experiences.

How Does Trauma Affect Memory Headspace In the present study, we explored the association between trauma exposure, age at first exposure, and cognitive functioning, defined herein as executive functioning (ef) and episodic memory (em), to clarify the lasting effects of trauma exposure and age at first exposure on the level of and change in adulthood cognitive functioning. In the community, traumatic brain injury (tbi) is common and individuals with tbi frequently have memory problems. it is crucial to study how tbi affects memory to better understand the underlying mechanism and to tailor rehabilitation for patients with a range of pathologies and severity levels. This chapter reviews how memory develops through the lifetime, and how understanding these normal processes illuminates the effects of trauma on memory. it addresses controversies in memory research as well as how memory interacts with other neurological and interpersonal systems. Research suggests that exposure to trauma can lead to alterations in memory processes, including disturbances in autobiographical memory, fragmented or intrusive memories of the traumatic event (flashbacks), and difficulties in differentiating between past and present experiences.
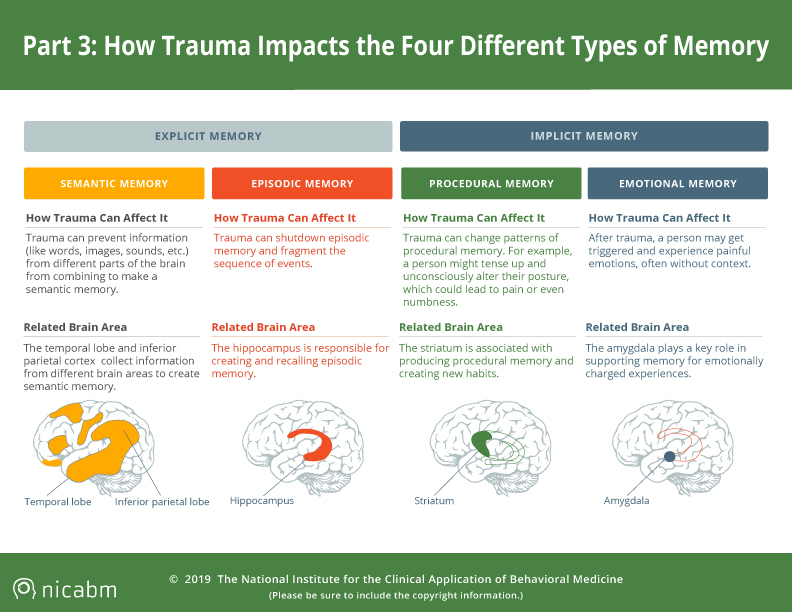
Understanding Trauma S Impact On Four Types Of Memory Infographic This chapter reviews how memory develops through the lifetime, and how understanding these normal processes illuminates the effects of trauma on memory. it addresses controversies in memory research as well as how memory interacts with other neurological and interpersonal systems. Research suggests that exposure to trauma can lead to alterations in memory processes, including disturbances in autobiographical memory, fragmented or intrusive memories of the traumatic event (flashbacks), and difficulties in differentiating between past and present experiences.
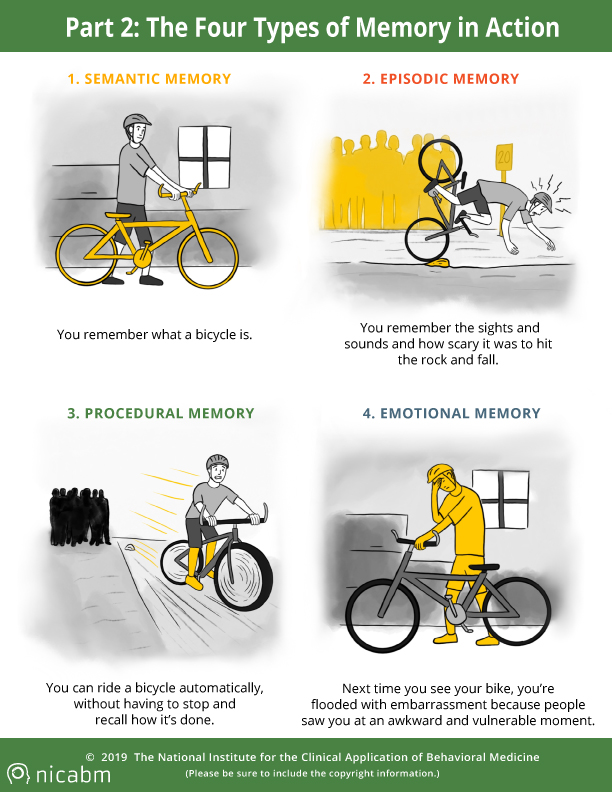
Understanding Trauma S Impact On Four Types Of Memory Infographic
