
Ecosystems And Energy Flow Pdf Food Web Primary Production This flow is elegantly represented by the energy pyramid, a fundamental concept in ecology that illustrates how energy is transferred and utilized within food chains and food webs. understanding the energy pyramid is crucial for grasping the dynamics of ecosystems, the efficiency of energy transfer, and the limitations that shape ecological. Our findings provide a better understanding of the patterns of energy flows across soil food webs in various ecosystems, as well as the relationships between soil food web structure and energy flux.

Understanding Energy Flow In Forest Ecosystems Course Hero Energetic food web models can help us link biodiversity to ecosystem function and understand how individual taxa contribute and respond to changes in the ecosystem of which they are part [1]. The concepts of food chains and food webs help explain how energy and nutrients move through ecosystems. by understanding these, we can gain insights into how organisms are interdependent and how disruptions to one part of the system can affect the whole. Feedback loops stabilize energy and nutrient flow in ecological food webs and the ecosystems in which they are embedded. in these feedback loops, flow of energy propels nutrients from autotrophs through food chains to decomposers where the nutrients recycle back to autotrophs. In this article, we will delve deep into the mechanism of energy transfer in a food web, exploring key concepts, examples, and the vital roles different organisms play in maintaining ecological harmony. what is a food web? at its core, a food web is a graphical representation of the feeding relationships among various organisms in an ecosystem.
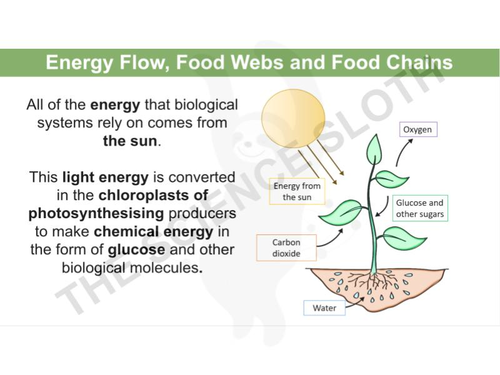
Energy Flow Food Webs And Food Chains Teaching Resources Feedback loops stabilize energy and nutrient flow in ecological food webs and the ecosystems in which they are embedded. in these feedback loops, flow of energy propels nutrients from autotrophs through food chains to decomposers where the nutrients recycle back to autotrophs. In this article, we will delve deep into the mechanism of energy transfer in a food web, exploring key concepts, examples, and the vital roles different organisms play in maintaining ecological harmony. what is a food web? at its core, a food web is a graphical representation of the feeding relationships among various organisms in an ecosystem. Trophic levels: each level in a food chain or web represents a trophic level. these levels denote an organism’s feeding position within the ecosystem. the first trophic level is occupied by the producers, followed by primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores or omnivores), and sometimes tertiary consumers (top predators) food chains: a food chain is a linear sequence. To comprehend how energy enters a food chain, it is essential first to grasp the fundamental principles of energy flow in ecosystems. energy is not created or destroyed; rather, it is transferred and transformed as it moves through different levels of biological organization. Food webs illustrate how energy flows directionally through ecosystems, including how efficiently organisms acquire it, use it, and how much remains for use by other organisms of the food web. In nature, we mostly observe food web as there are many organisms which are omnivores. as a result, they occupy multiple trophic levels. the law of thermodynamics in the ecosystem explains the flow of energy at each trophic level. the first law states that energy is neither created, nor destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another.
