Understanding Unicode Utf 8 And Utf 16
Unicode Character Set And Utf 8 Utf 16 Utf 32 Encoding 59 Off Unicode transformation format is a method of encoding unicode characters for storage and communication purposes. this format specifies how unicode characters will be converted into a sequence of bytes. the most common utf forms are utf 8, utf 16, utf 32. Utf stands for “unicode transformation format,” and the number (8, 16, or 32) indicates the bit size of the encoding units. utf 8 uses variable length encoding, where characters are.
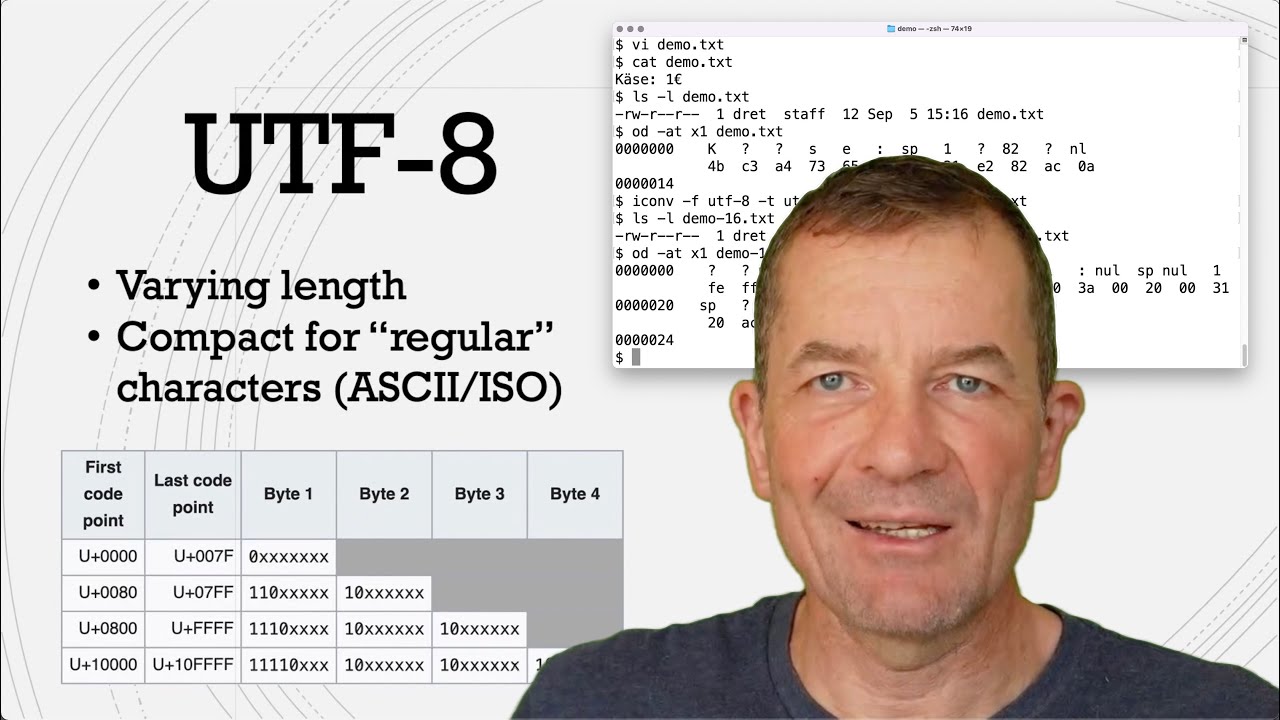
What Are Utf 8 And Utf 16 Working With Unicode Encodings 47 Off Summary: explore the differences between unicode, utf 8, and utf 16, their significance in text encoding, and their applications in the digital world. in t. However, in utf 8 a character may occupy a minimum of 8 bits, while in utf 16 character length starts with 16 bits. main utf 8 pros: basic ascii characters like digits, latin characters with no accents, etc. occupy one byte which is identical to us ascii representation. Dive into a comprehensive guide on utf 8, utf 16, and utf 32 character encodings. understand their differences, benefits, and ideal applications. Explore the key differences between utf 8 and utf 16 character encodings, including their use cases and advantages.
Understanding The Differences Between Utf 8 And Utf 16 Learn It Dive into a comprehensive guide on utf 8, utf 16, and utf 32 character encodings. understand their differences, benefits, and ideal applications. Explore the key differences between utf 8 and utf 16 character encodings, including their use cases and advantages. Learn what character sets are, the difference between ascii, utf 8, and unicode, how encoding works, common pitfalls, and how to fix character encoding errors. includes ascii tables, technical insights, and actionable advice for developers. Utf 16 (16 bit unicode transformation format) is a character encoding that supports all 1,112,064 valid code points of unicode. [1][a] the encoding is variable length as code points are encoded with one or two 16 bit code units. Next, the chapter discusses the issue of writing direction and introduces several special types of characters important for understanding the unicode standard. in particular, the use of combining characters, the byte order mark, and other special characters is explored in some detail.
Comments are closed.