
The Iot Esim Specification Sgp 32 Simplifying Iot Device Integration What is sgp.32 and why it matters for iot esim deployments. the gsma sgp.32 specification is the latest and most important evolution in esim for iot. it’s designed to simplify how iot devices connect to cellular networks globally—especially for constrained devices like gps trackers, sensors, and wearables that lack user interfaces. Don’t let these challenges hold you back! monogoto now offers an sgp.32 evaluation kit, enabling developers to gain hands on experience and get a grasp of the true potential of remote sim provisioning for iot. learn more about the sgp.32 ready kit.
What Does Sgp 32 Iot Remote Sim Provisioning Really Mean For How Gsma sgp .32 outlines technical specifications for remote esim management of internet of things (iot) and mobile device deployments. it facilitates seamless provider switching via simplified esim architecture. thus, reducing deployment costs and accelerating go to market. In summary, the gsma sgp.32 specification brings significant advancements to the iot industry by providing a standardized, efficient, and flexible framework for esim management, addressing. The gsma proposed the new esim iot sgp.31 32 specification to meet the needs of massive iot connectivity and enable the remote management of iot device fleets. numerous stakeholders collaborated to address new esim iot use cases and verticals with this new specification. Sgp.32 will help enterprise operators, and manufacturers transition to a fully esim driven ecosystem. adoption may have appeared to have reached a tipping point, but the industry must address technical integration, regulatory considerations, and business model shifts.

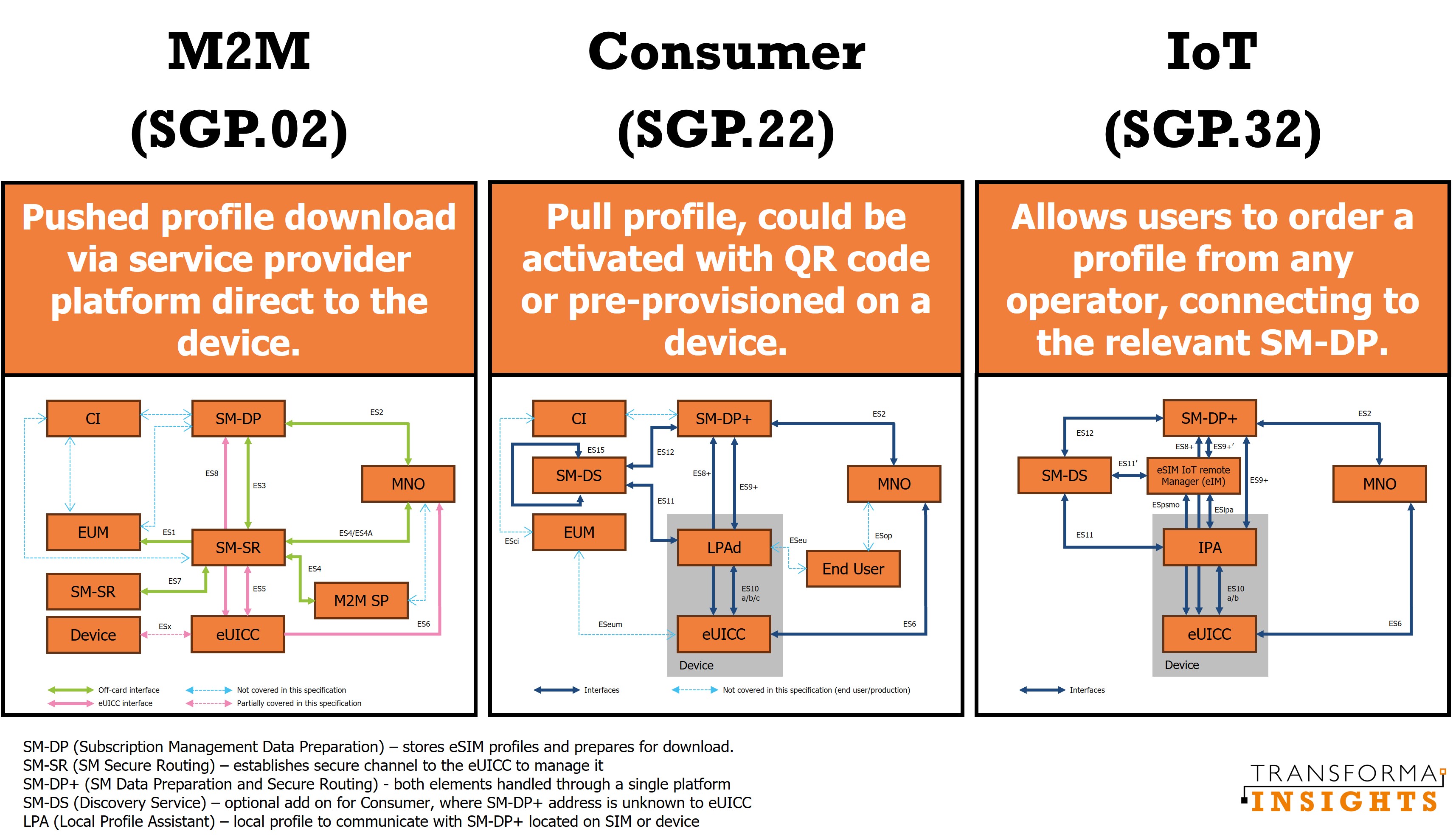
Optimizing Iot With Gsma Sgp 32 Esim Iot Vs M2m Vs Consumer Onomondo The gsma proposed the new esim iot sgp.31 32 specification to meet the needs of massive iot connectivity and enable the remote management of iot device fleets. numerous stakeholders collaborated to address new esim iot use cases and verticals with this new specification. Sgp.32 will help enterprise operators, and manufacturers transition to a fully esim driven ecosystem. adoption may have appeared to have reached a tipping point, but the industry must address technical integration, regulatory considerations, and business model shifts. The gsma, the industry body responsible for mobile communication standards, has played a pivotal role in shaping esim technology. early m2m esim standards (sgp.02) relied on server driven provisioning, often using sms for communication. later, consumer esim standards (sgp.22) were introduced to support devices with a user interface, allowing users to manage sim profiles directly. The commercialization of sgp.32 is fast approaching and is set to mark a significant milestone for the esim iot ecosystem. sgp.32 is the latest gsma backed standard and is expected to accelerate esim adoption in cellular iot, offering greater flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. In a monumental move for the internet of things (iot) industry, the gsma has unveiled the sgp.32 esim iot technical specification, setting the stage for transformative changes in iot device provisioning and connectivity.

Understanding Sgp 32 The New Esim Iot Standard The gsma, the industry body responsible for mobile communication standards, has played a pivotal role in shaping esim technology. early m2m esim standards (sgp.02) relied on server driven provisioning, often using sms for communication. later, consumer esim standards (sgp.22) were introduced to support devices with a user interface, allowing users to manage sim profiles directly. The commercialization of sgp.32 is fast approaching and is set to mark a significant milestone for the esim iot ecosystem. sgp.32 is the latest gsma backed standard and is expected to accelerate esim adoption in cellular iot, offering greater flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. In a monumental move for the internet of things (iot) industry, the gsma has unveiled the sgp.32 esim iot technical specification, setting the stage for transformative changes in iot device provisioning and connectivity.
