Volts And Voltage In Electricity Stock Image Image Of Phase Form
Electricity Clipart Voltage Picture 996126 Electricity Clipart Voltage The volt (symbol: v), named after alessandro volta, is the unit of measurement of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the international system of units (si). [1]. Voltage is a measurement of the electric potential or "pressure" at which electricity flows through a system. voltage is also described as the speed of individual electrons as they move through a circuit and is measured in units called volts.

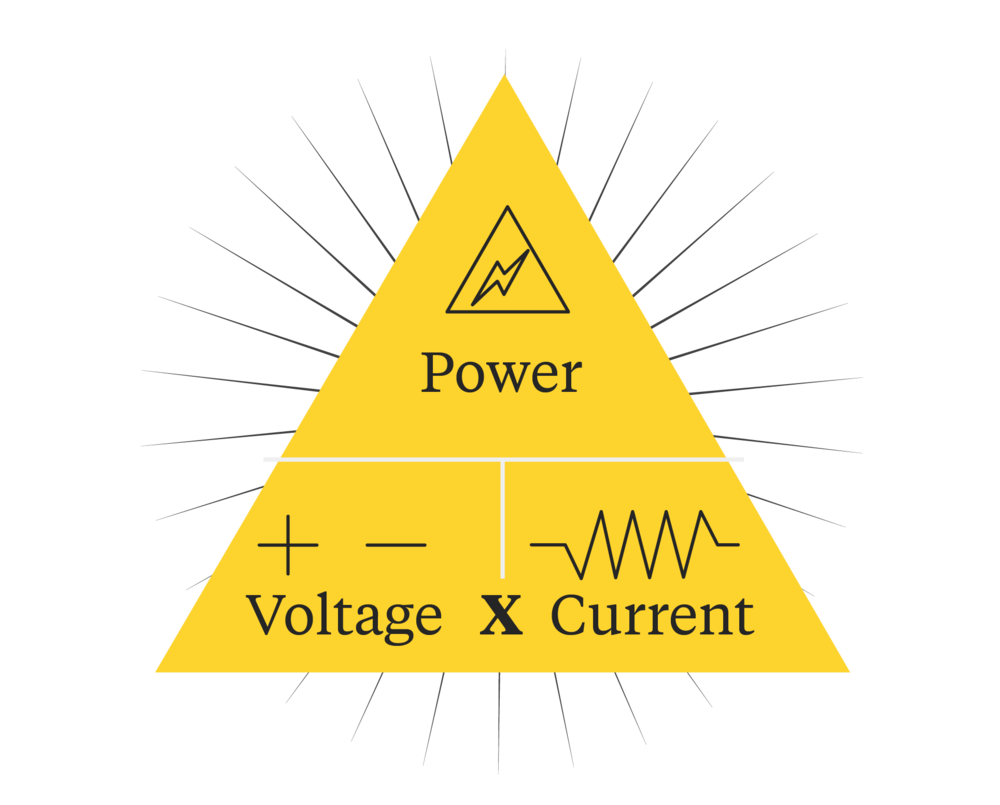
Volts And Voltage In Electricity Stock Image Image Of Phase Form Volt “v”: definition, formula, measurement, conversion and calculation. what is volt? a volt is the derived unit of voltage, electric potential or potential difference and electromotive force (emf). One volt is defined as the “difference in electric potential between two points of a conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power between those points.” the volt is named after the italian physicist alessandro volta. So a volt (v) is simply a unit of measurement of voltage. voltage is created from the buildup of electrons in one area more than another. this happens naturally in clouds before a lightning bolt strikes and even in your body before discharging as a static electric spark. Volt is the electrical unit of voltage. one volt is defined as energy consumption of one joule per electric charge of one coulomb.

Electricity Voltage Performance Free Photo On Pixabay So a volt (v) is simply a unit of measurement of voltage. voltage is created from the buildup of electrons in one area more than another. this happens naturally in clouds before a lightning bolt strikes and even in your body before discharging as a static electric spark. Volt is the electrical unit of voltage. one volt is defined as energy consumption of one joule per electric charge of one coulomb. The difference between volts and watts is that voltage measures electric potential, while wattage measures power. voltage measures the electrical force pushing electrons through a circuit, while watts measure the amount of energy required for an appliance to start and run. Volt, unit of electrical potential, potential difference and electromotive force in the metre–kilogram–second system (si); it is equal to the difference in potential between two points in a conductor carrying one ampere current when the power dissipated between the points is one watt. Learn everything about volts, a voltage unit which you can convert to other units on our website. Volts (v): voltage is the force that drives the flow of electricity, much like water pressure moves water through a pipe. the greater the pressure, the stronger the water flows. similarly, higher voltage means more force pushing electrical current through conductors.

Voltage Electricity Transmission Free Photo On Pixabay Pixabay The difference between volts and watts is that voltage measures electric potential, while wattage measures power. voltage measures the electrical force pushing electrons through a circuit, while watts measure the amount of energy required for an appliance to start and run. Volt, unit of electrical potential, potential difference and electromotive force in the metre–kilogram–second system (si); it is equal to the difference in potential between two points in a conductor carrying one ampere current when the power dissipated between the points is one watt. Learn everything about volts, a voltage unit which you can convert to other units on our website. Volts (v): voltage is the force that drives the flow of electricity, much like water pressure moves water through a pipe. the greater the pressure, the stronger the water flows. similarly, higher voltage means more force pushing electrical current through conductors.

Electricity Voltage Perfomance Free Photo On Pixabay Pixabay Learn everything about volts, a voltage unit which you can convert to other units on our website. Volts (v): voltage is the force that drives the flow of electricity, much like water pressure moves water through a pipe. the greater the pressure, the stronger the water flows. similarly, higher voltage means more force pushing electrical current through conductors.
Comments are closed.