
Summary Killer Whale Communication As humpback whales migrate along populated coastlines, they are likely to encounter noise from vessel traffic which will mask their social signals. since no empirical data exist on baleen whale hearing, the consequences of this are usually assumed, being the modelled reduction in their communication space. In summary, changes in the communication repertoire (in terms of the use of vocal and nonvocal sounds) of humpback whales are specific to wind noise regardless of the level of vessel noise. vocal source levels, on the other hand, increased in response to increased wind noise but not in response to increased noise from vessels.
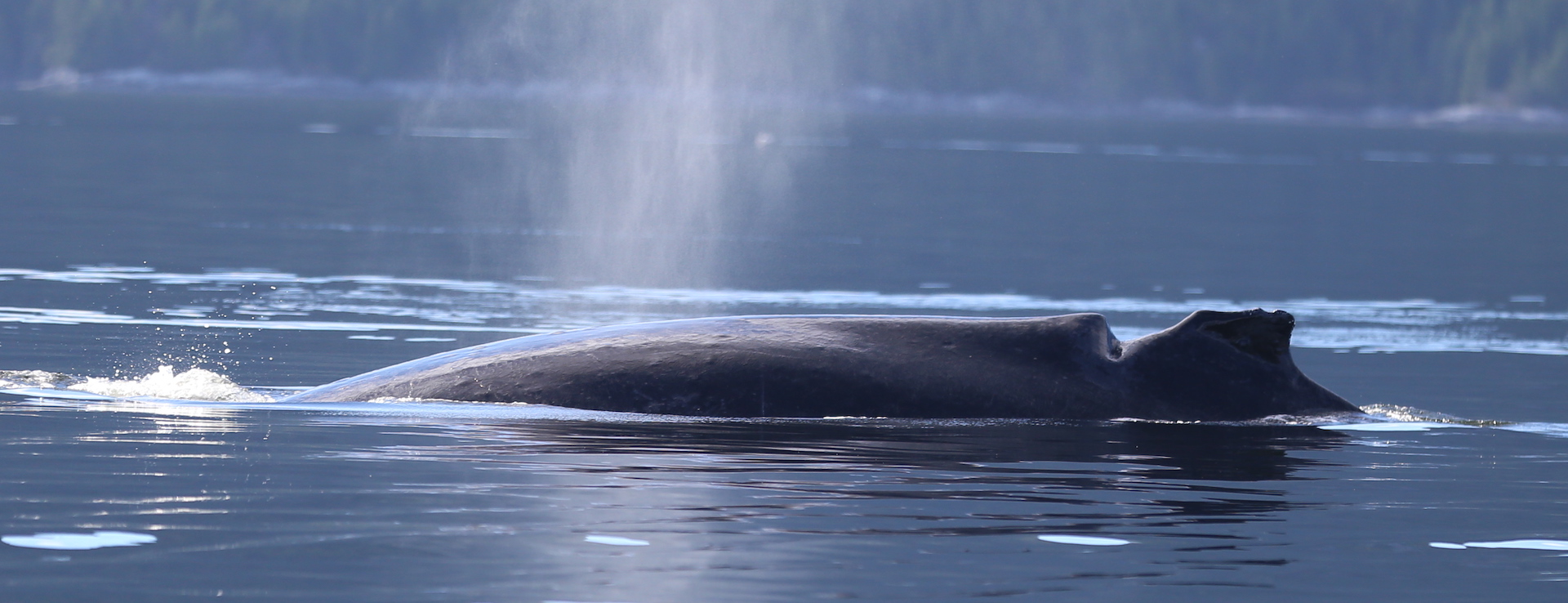

Ocean Noise Whale Sound To test for effects of anthropogenic noise on this defined space, first, the likely extent of a signalling whale’s communication space will be modelled and compared in natural (wind) and anthropogenic (vessel) noise. second, the study will assess the behavioural consequences of increased vessel noise within the communication network, in terms of. As humpback whales migrate along populated coastlines, they are likely to encounter noise from vessel traffic which will mask their social signals. since no empirical data exist on baleen whale hearing, the consequences of this are usually assumed, being the modelled reduction in their communication space. In this study, the response of humpback whales to increasing noise varied according to whether the predominant noise source was from wind or from vessels in the area. four adjustment strategies were tested: changes in the communication repertoire, vocal source levels and changes in the frequency and duration of two common vocal sound types. As humpback whales migrate along populated coastlines, they are likely to encounter noise from vessel traffic which will mask their social signals. since no empirical data exist on baleen whale hearing, the consequences of this are usually assumed, being the modelled reduction in their communication space.

Increase In Ship Strikes And Noise Has Some Whale Lovers Worried In this study, the response of humpback whales to increasing noise varied according to whether the predominant noise source was from wind or from vessels in the area. four adjustment strategies were tested: changes in the communication repertoire, vocal source levels and changes in the frequency and duration of two common vocal sound types. As humpback whales migrate along populated coastlines, they are likely to encounter noise from vessel traffic which will mask their social signals. since no empirical data exist on baleen whale hearing, the consequences of this are usually assumed, being the modelled reduction in their communication space. Vessel noise was emitted with a 60 s ramp up down to avoid an acoustic startle response from the whales. vessel noise was set to different lf weighted broadband source levels (sls) of control (124 db re 1 μpa), low (148 db re 1 μpa), medium (160 db re 1 μpa) and high noise (172 db re 1 μpa rms). figure 1. Effects of elevated noise levels is the reduction in area over which animals are able to acoustically communicate, often termed communication masking. this study utilizes modeling approaches to. Vessel noise overlaps in frequency with fin whale pulses which risks masking fin whale communication signals, an acoustic impact that has been observed in other baleen whale species (e.g.,. The specific goals for this paper were to (a) model and map a representative noise field from whale watching boats in the gulf of tribugá, (b) quantify communication space reduction of a typical humpback whale song caused by whale watching boats and (c) analyze changes in acoustic features of humpback whale song in the presence of boat noise.
Whale Of A Time Research Information About Whales Dolphins And Porpoises Vessel noise was emitted with a 60 s ramp up down to avoid an acoustic startle response from the whales. vessel noise was set to different lf weighted broadband source levels (sls) of control (124 db re 1 μpa), low (148 db re 1 μpa), medium (160 db re 1 μpa) and high noise (172 db re 1 μpa rms). figure 1. Effects of elevated noise levels is the reduction in area over which animals are able to acoustically communicate, often termed communication masking. this study utilizes modeling approaches to. Vessel noise overlaps in frequency with fin whale pulses which risks masking fin whale communication signals, an acoustic impact that has been observed in other baleen whale species (e.g.,. The specific goals for this paper were to (a) model and map a representative noise field from whale watching boats in the gulf of tribugá, (b) quantify communication space reduction of a typical humpback whale song caused by whale watching boats and (c) analyze changes in acoustic features of humpback whale song in the presence of boat noise.
