
3d Printing Definition Operation And Applications 3d printing, in manufacturing, any of several processes for fabricating three dimensional objects by layering two dimensional cross sections sequentially, one on top of another. the process is analogous to the fusing of ink or toner onto paper in a printer. Today, we will discuss what is 3d printing? what are different 3d printing process? what kind of 3d printing technologies used? 3d printing resins etc.
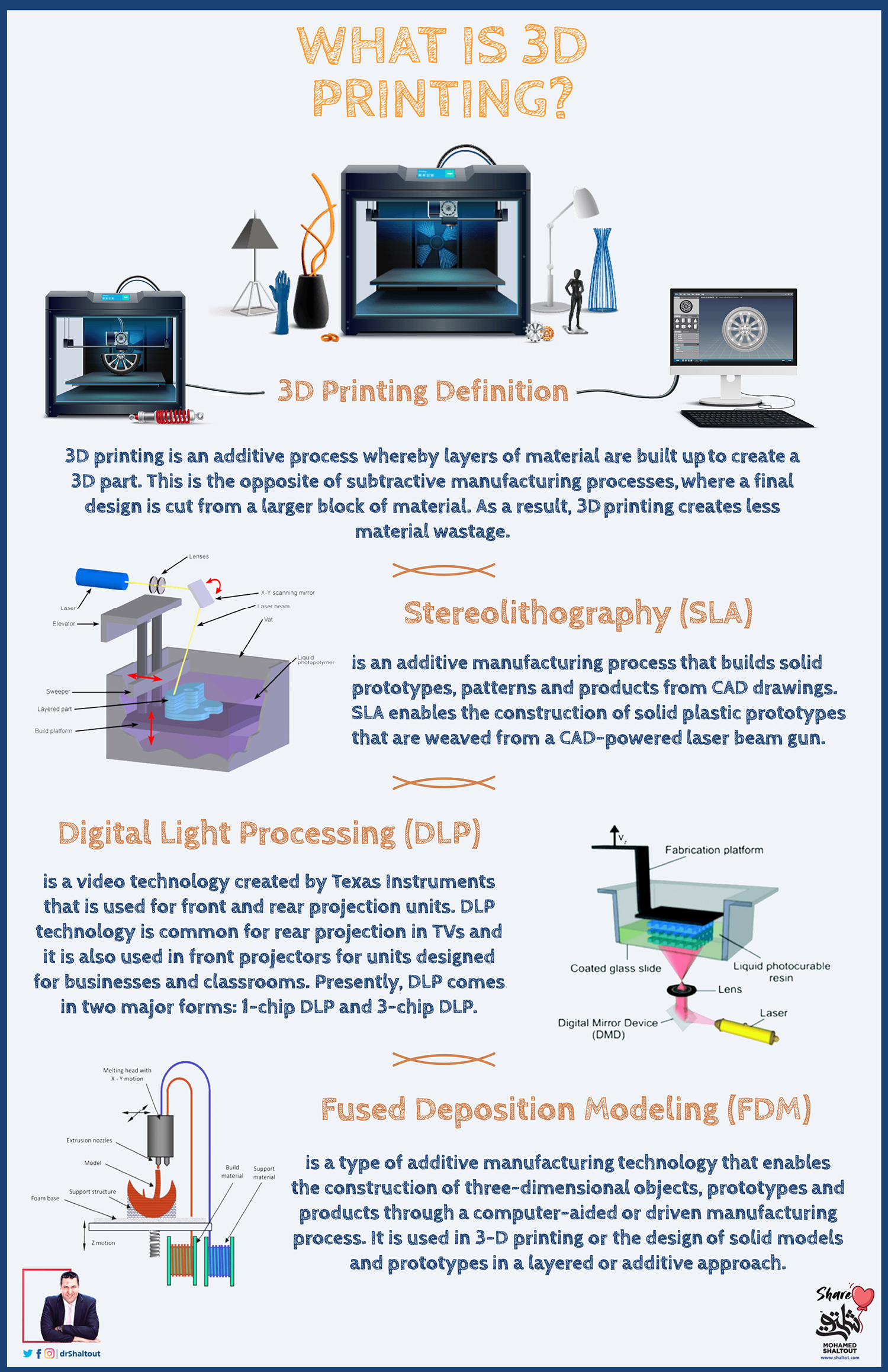
What Is 3d Printing Technology Definition And Types Adobe Education 3d printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three dimensional object from a cad model or a digital 3d model. [1][2][3] it can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, [4] with the material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains be. 3d printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a method of creating a three dimensional object layer by layer using a computer created design. 3d printing is an additive process whereby layers of material are built up to create a 3d part. 3d printing uses computer aided design to create three dimensional objects through a layering method. sometimes referred to as additive manufacturing, 3d printing involves layering materials, like plastics, composites or bio materials to create objects that range in shape, size, rigidity and color. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by successive addition of materials. 3d printing technology is a fast emerging technology.
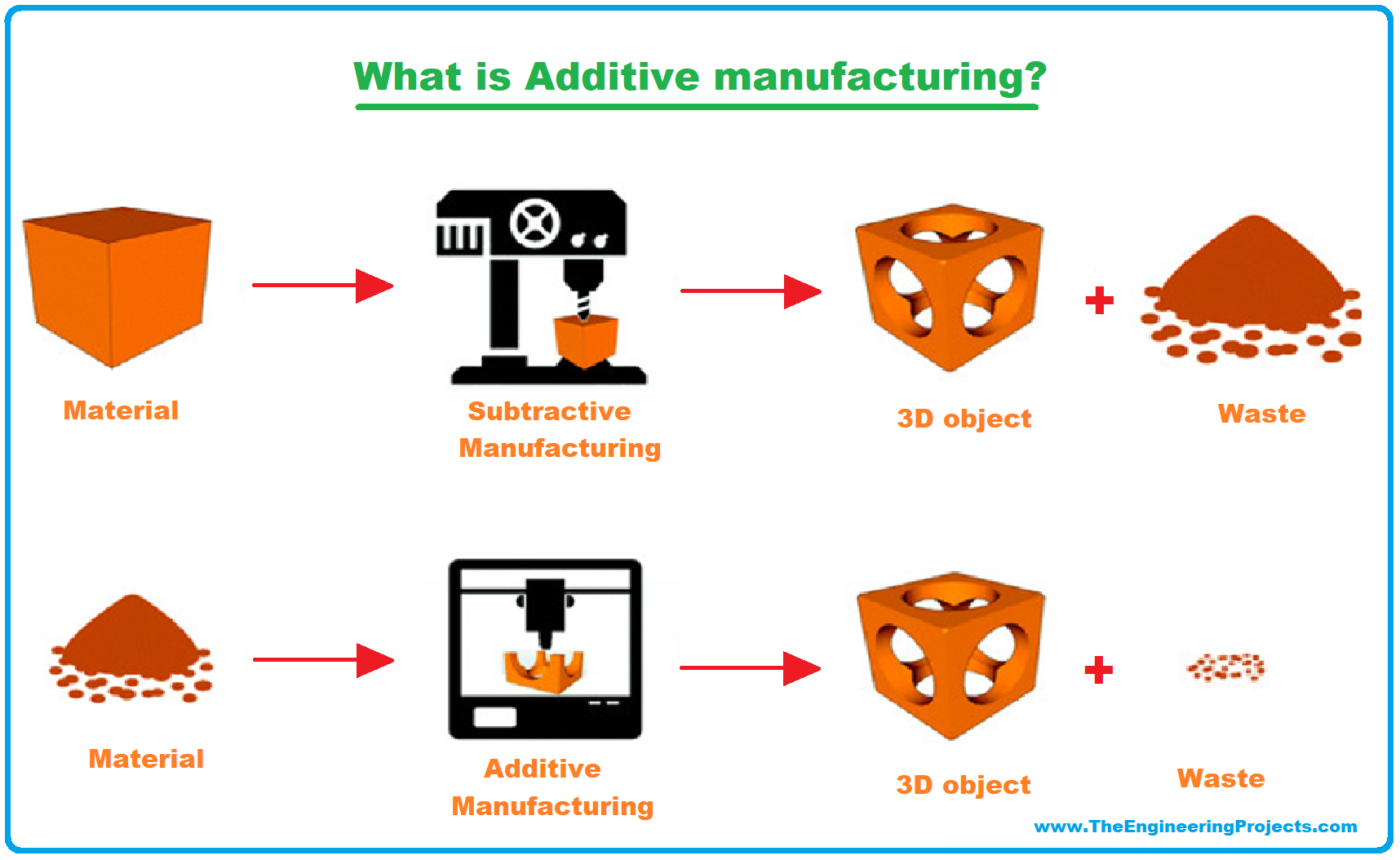
What Is 3d Printing Definition Technology And Applications The 3d printing uses computer aided design to create three dimensional objects through a layering method. sometimes referred to as additive manufacturing, 3d printing involves layering materials, like plastics, composites or bio materials to create objects that range in shape, size, rigidity and color. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by successive addition of materials. 3d printing technology is a fast emerging technology. Let's start with a simple definition: 3d printing is an additive manufacturing method that creates a physical object from a digital model file. the technology works by adding layer upon layer of material to build up a complete object. the 3d printing process was invented in the 1980s and was originally known as ‘rapid prototyping’. 3d printing, or additive manufacturing, is a process of making three dimensional objects from a digital file. the layers of the object can be seen in a thinly sliced cross section of the object. it is called volumetric 3d printing. the volumetric printing of complete structures is made a single time without the use of layer by layer manufacturing. 3 d printing is a manufacturing process that builds layers to create a three dimensional solid object from a digital model. to print a 3 d object, the manufacturer uses a computer aided design (cad) program to create a digital model that gets sliced into very thin cross sections called layers. 3d printing is a transformative technology that can enable personalised fabrication, distributed manufacturing, supply chain resilience and sustainability. with strategic adoption, supportive policies, and addressing evolving concerns, 3d printing holds immense disruptive potential to reshape manufacturing and empower creativity.
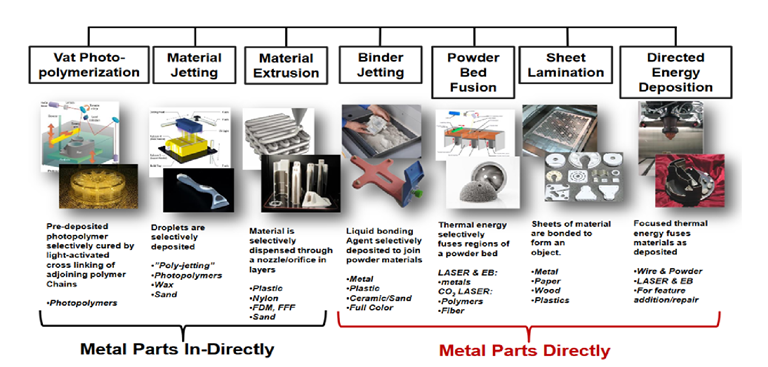
What Is 3d Printing Definition Technology And Applications The Let's start with a simple definition: 3d printing is an additive manufacturing method that creates a physical object from a digital model file. the technology works by adding layer upon layer of material to build up a complete object. the 3d printing process was invented in the 1980s and was originally known as ‘rapid prototyping’. 3d printing, or additive manufacturing, is a process of making three dimensional objects from a digital file. the layers of the object can be seen in a thinly sliced cross section of the object. it is called volumetric 3d printing. the volumetric printing of complete structures is made a single time without the use of layer by layer manufacturing. 3 d printing is a manufacturing process that builds layers to create a three dimensional solid object from a digital model. to print a 3 d object, the manufacturer uses a computer aided design (cad) program to create a digital model that gets sliced into very thin cross sections called layers. 3d printing is a transformative technology that can enable personalised fabrication, distributed manufacturing, supply chain resilience and sustainability. with strategic adoption, supportive policies, and addressing evolving concerns, 3d printing holds immense disruptive potential to reshape manufacturing and empower creativity.
